Synchronization Between LDP and IGP
Synchronization between LDP and IGP ensures consistent IGP and LDP traffic by suppressing IGP route advertisement. This minimizes packet loss and improves network reliability.
Background
- When a primary link fails, both the IGP route and LSP are switched to backup link. After the primary link recovers, the IGP route is switched to the original primary link before LDP convergence completes. As a result, traffic is dropped during attempts to use the unreachable LSP.
- When an IGP route of the primary link is reachable and an LDP session between nodes on the primary link fails, traffic is directed using the IGP route of the primary link, while the LSP over the primary link is torn down. Since a preferred IGP route of the backup link is unavailable, an LSP over the backup link cannot be established, causing traffic loss.
- When the primary/backup switchover occurs on a node, the LDP session is established after IGP GR completion. IGP advertises the maximum cost of the link, causing route flapping.
Synchronization between LDP and IGP helps prevent traffic loss caused by these problems.
Related Concepts
Hold-down timer: controls the period of time before establishing IGP neighbor relationships.
Hold-max-cost timer: controls the interval for advertising the maximum link cost on an interface.
Delay timer: controls the period of time before LSP establishment.
Implementation
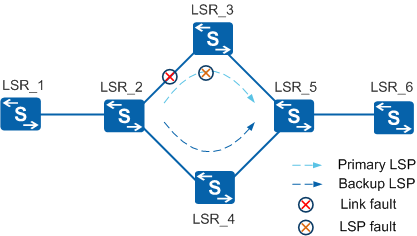
Figure 1 shows the implementation of switching between primary/backup links.
Synchronization between LDP and IGP is implemented as follows:
- The primary link recovers from a physical fault.
The faulty link between LSR_2 and LSR_3 recovers.
An LDP session is set up between LSR_2 and LSR_3. IGP starts the Hold-down timer to suppress establishment of the neighbor relationship.
Traffic keeps traveling through the backup LSP.
After the link fault is rectified, LSR2 and LSR3 discover each other as LDP peers and reestablish an LDP session (along the path LSR2 -> LSR4 -> LSR5 -> LSR3). LSR2 and LSR3 send a Label Mapping message to each other to establish an LSP and instruct IGP to start synchronization.
IGP establishes a neighbor relationship and switches traffic back to the primary link. The LSP is reestablished and its route converges on the primary link.
- IGP on the primary link is normal and the LDP session is Down.
An LDP session between nodes along the primary link becomes Down.
LDP notifies the primary link of the session fault. IGP starts the Hold-max-cost timer and advertises the maximum cost on the primary link.
The IGP route of the backup link becomes reachable.
An LSP is established over the backup link and the LDP module on LSR_2 delivers forwarding entries.
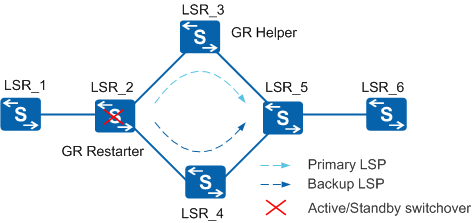
- Figure 2 shows
synchronization between LDP and IGP upon a primary/backup switchover
on a node.
Synchronization between LDP and IGP is implemented as follows:
An IGP on the GR Restarter advertises the actual cost of the primary link and starts the GR Delay timer. The GR Restarter does not end the GR process before the GR Delay timer expires. An LDP session is established during this period.
Before the GR Delay timer expires, the GR Helper retains the original IGP route and the LSP. If the LDP session goes Down, LDP does not notify the IGP link that the session is Down. In this case, IGP still advertises the actual link cost, ensuring the IGP route is not switched to the backup link. If the GR Delay timer expires, GR is complete. If the LDP session is not established, IGP starts the Hold-max-cost timer and advertises the maximum cost of the primary link, so the IGP route is switched to the backup link.
If the LDP session is established or the Hold-max-cost timer expires, IGP resumes the actual link cost of the interface and then switches the IGP route back to the primary link.