SRLG
Shared risk link group (SRLG) is a constraint to calculating a backup or a bypass CR-LSP on a network with CR-LSP hot standby or TE FRR configured. SRLG prevents bypass and primary CR-LSPs from being set up on links with the same risk level, which enhances TE tunnel reliability.
Background
A network administrator often uses CR-LSP hot standby or TE FRR technology to ensure MPLS TE tunnel reliability. However, CR-LSP hot standby or TE FRR may fail in real-world application.
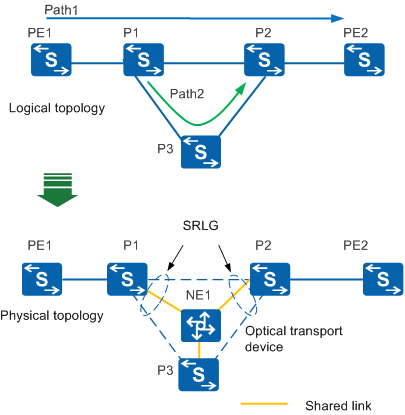
In Figure 1, Path 1 is the primary CR-LSP and Path 2 is the bypass CR-LSP. The link between P1 and P2 requires TE FRR protection.
Core nodes P1, P2, and P3 on the backbone network are connected by a transport network device. In Figure 1, the top diagram is an abstract version of the actual topology below. NE1 is a transport network device. During network construction and deployment, two core nodes may share links on the transport network. For example, the yellow links in Figure 1 are shared by P1, P2, and P3. A shared link failure affects primary and bypass CR-LSPs and makes FRR protection invalid. To enable TE FRR to protect the CR-LSP, bypass and primary CR-LSPs must be set up over links of different risk levels. SRLG technology can be deployed to meet this requirement.
However, an SRLG is a set of links that share the same risks. If one of the links fails, other links in the group may fail as well. Therefore, protection fails even if other links in the group function as the hot standby or bypass CR-LSP for the failed link.
Implementation
SRLG is a link attribute, expressed by a numeric value. Links with the same SRLG value belong to a single SRLG.
The SRLG value is advertised to the entire MPLS TE domain using IGP TE. Nodes in a domain can then obtain SRLG values of all the links in the domain. The SRLG value is used in CSPF calculations together with other constraints such as bandwidth.
MPLS TE SRLG works in either of the following modes:
Strict mode: The SRLG value is a mandatory constraint when CSPF calculates paths for hot standby and bypass CR-LSPs.
Preferred mode: The SRLG value is an optional constraint when CSPF calculates paths for hot standby and bypass CR-LSPs. If CSPF fails to calculate a path based on the SRLG value, CSPF excludes the SRLG value when recalculating the path.
Usage Scenario
SRLG applies to networks with CR-LSP hot standby or TE FRR configured.
Benefits
SRLG constraints the path calculation for hot standby and bypass CR-LSPs, which avoids primary and bypass CR-LSPs with the same risk level.