Multicast VPN Basics
BGP/MPLS IP VPN Concepts
BGP/MPLS IP VPN, a L3VPN technology, uses the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to advertise VPN routes and uses Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) to forward VPN packets on backbone networks (IP networks) of service providers (SPs). IP packets are transmitted on VPNs.
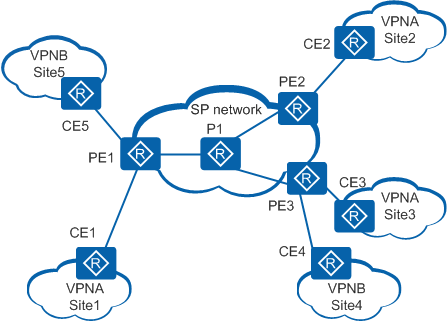
Figure 1 shows a typical BGP/MPLS IP VPN network containing with PE, P, and customer edge (CE) routers. The SP network is a public network, and the VPN sites are private networks. Each of these device types is described as follows:
- PE: an edge device on the SP network. A PE router is directly connected to CE devices and completes all VPN packet processing.
- P: a backbone device on the SP network. A P router is not directly connected to CE devices. It provides only basic MPLS forwarding capability and does not maintain VPN information.
- CE: an edge device on a customer network. A CE device provides interfaces that are directly connected to the SP network. A CE can be a router, switch, or host. Generally, CE devices do not need to support MPLS and are generally unaware of VPNs.
For details about BGP/MPLS IP VPN features, see BGP/MPLS IP VPN Configuration in the S2720, S5700, and S6700 V200R019C10 Configuration Guide - VPN.
Multicast VPN Implementation
When multicast services are deployed on the network shown in Figure 1, users in VPN sites can receive multicast data from the VPNs to which they belong.
For example, when multicast source S1 on VPNA sends multicast data to multicast group G, only group members belonging to VPNA can receive the multicast data. Multicast data is transmitted in multicast mode within the VPN sites and on the public network. The VPN devices must support the following multicast capabilities:
Devices at each site support multicast functions.
The P router can implement multicast functions in the public network instance.
PE routers can implement multicast functions in the public network instance and VPN instances by:
- Connecting to sites through VPN instances.
- Connecting the P router through the public network instance.
- Converting and transmitting data between the public network instance and VPN instances.