Multicast VPN Concepts
In multicast VPN, the public network maintains a multicast distribution tree (MDT) for each VPN instance. MDTs are automatically set up after multicast VPN is configured, regardless of whether multicast services are running on the network. Multicast packets from a VPN site are encapsulated on a PE device and forwarded along the MDT to a remote PE device bound to the same VPN instance. If the site connected to the remote PE device has receivers of the specified group, the PE device forwards the multicast packets to the CE device. If there are no receivers of the specified group, the PE device drops the multicast packets.
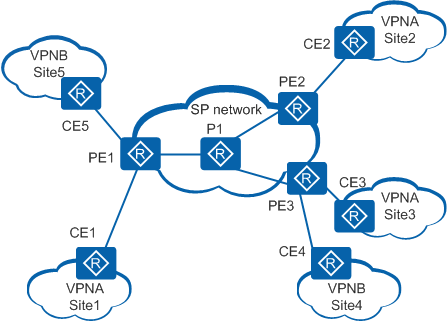
On the network shown in Figure 1, PE1 has the public network instance and VPN instances (VPNA and VPNB) configured. Each instance functions as an independent virtual device. Multicast packets are exchanged between PE and CE devices using the VPN instances, and between PE and P devices using the public network instance.
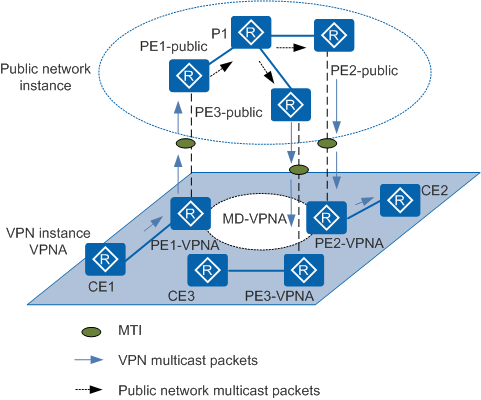
Figure 2 shows multicast packet forwarding on VPNA. Multicast VPN concepts are described based on this figure.
MD
An MD specifies the range within which multicast data from a VPN can be transmitted on the public network. The boundary of an MD is all PE devices bound to the VPN instance. Different VPN instances belong to different MDs. In Figure 2, the circle in the middle of VPNA represents the MD serving VPNA. All multicast data on VPNA is transmitted within this MD.
A VPN instance identifies an MD, and an MD belongs to only one VPN instance. This is known as one-to-one mapping.
PE multi-instance
A public network instance and multiple VPN instances can be created on a PE device, and they run Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) independently. PE devices use VPN instances to exchange multicast data with CE devices on VPNs, and use the public network instance to exchange multicast data with P devices on the public network. PE devices need to encapsulate VPN packets before sending them to the public network and decapsulate packets received from the public network.
VPN instances and the public network instance can use different PIM modes.
Multicast tunnel (MT) and multicast tunnel interface (MTI)
An MT is established on a PE device to transmit VPN data. VPN users only need to know that all PE devices in an MD are connected to an MT.
An MTI is the inbound and outbound interface of an MT and MD. A local PE device sends VPN data through an MTI, and the remote PE receives data from the MTI. An MTI is the tunnel for data exchange between the public network instance and the VPN instance. A PE device connects to an MT through an MTI. VPN instances on PE devices in an MD establish PIM neighbor relationships with each other through MTIs.
A local PE encapsulates VPN multicast packets into public network multicast data packets and forwards them along the MDT on the public network.

All interfaces belonging to a VPN, including the MTIs and PE interfaces bound to the VPN instance, must use the same PIM mode.
MDT
An MDT is used to transmit multicast data on a public network. Packets are forwarded along an MDT and are replicated at dividing points. This reduces resource consumption on the public network. MDTs established between PE devices of the same VPN include Share-MDT and Switch-MDT.
When packets are forwarded along a Share-MDT, all PE devices of the corresponding VPN instance receive the packets. When packets are forwarded along a Switch-MDT, only PE devices with receivers attached in the VPN instance receive the packets.
For details on how a Share-MDT is set up, see Share-MDT Establishment. For details on how a Switch-MDT is set up, see Switch-MDT Switchover.
Share-MDT
A Share-MDT connects all PE devices bound to a VPN instance. All multicast packets from the VPN are forwarded along the Share-MDT, regardless of the PE devices from which the packets enter the public network. A Share-MDT is identified by a Share-Group address.
Share-Group
A Share-Group is a multicast address that identifies an MD on the public network and is used to establish a Share-MDT for the MD. VPN multicast packets are transparent to the public network. PE devices do not distinguish the multicast groups to which these packets belong or the packet type (protocol or data). PE devices encapsulate VPN multicast packets into public network multicast data packets and use the Share-Group address of the MD as the group address of the packets.
A Share-Group corresponds to an MD. That is, an MD has only one Share-Group address, and a Share-Group belongs to only one MD.
Switch-MDT
When a PE device detects that the traffic rate on a Share-Group exceeds the limit, the PE sends a switchover notification to the downstream PE devices to trigger a switchover from Share-MDT to Switch-MDT. The switchover notification carries the Switch-Group address. After receiving the notification, the downstream PE devices with receivers attached join the Switch-Group, and a Switch-MDT is set up. The ingress PE forwards encapsulated VPN multicast data along the Switch-MDT on the public network, and only the PE devices with receivers attached receive the packets. This improves multicast data forwarding efficiency and reduces the load on PE devices. Compared to a Share-MDT, a Switch-MDT cuts off remote PE devices that do not require multicast data, improving multicast data forwarding efficiency.
Switch-Group and Switch-Group-Pool
A Switch-Group is the group address of a Switch-MDT. A Switch-Group-Pool defines the range of available multicast group addresses. When VPN multicast data traffic rate reaches or exceeds the limit, a Switch-MDT switchover is triggered. A PE device selects an idle address from the Switch-Group-Pool as the Switch-Group address. A Switch-MDT is then established from this PE (source) to downstream PE devices connected to sites with receivers. All VPN multicast packets from the source PE are encapsulated using this Switch-Group address.
An MD has only one Switch-Group-Pool, and a Switch-Group-Pool belongs to only one MD.