NTP Fundamentals
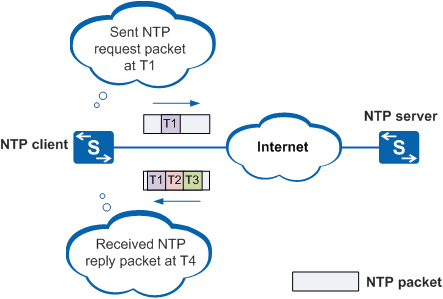
In Figure 1, the NTP client and server connected to each other. The clock systems of each are independent, and system clock synchronization utilizes NTP.
The characteristics of these clocks are as follows:
Prior to the synchronization of system clocks, the clock of the NTP client is set to Ta and the clock of the NTP server is set to Tb.
The NTP server functions as the NTP clock server. The NTP client requires clock synchronization with the NTP clock server, which is in this case the NTP server.
It is assumed that the precision of system clocks on both the NTP client and server is 0. A precision of 0 denotes complete precision.
NTP implementation follows these steps:
The NTP client sends an NTP request to the NTP server at time 1 (T1). This packet carries timestamp T1, which is the departure time of the packet from the client.
The request packet is received and processed by the NTP server. Time 2 (T2) is added to the packet.
The NTP server sends an NTP reply packet at time 3 (T3). T3 is added to the packet.
The NTP client receives the reply packet at time (T4).
Through the preceding interaction, the NTP client obtains four time parameters: T1, T2, T3, and T4. The time difference must be adjusted by the NTP client. As the clocks of the NTP client and server are precise, the time difference can be calculated using the following formulas:
Calculate the time (Delay) taken sending an NTP packet from the client to server using the following formula:
Delay = [(T4 - T1) - (T3 – T2)]/2
Calculate the time difference (Offset) between the clocks of client and server.
At T4, for example, the server clock is T3 + Delay. The Offset is calculated using the following formula:
T4 + Offset = T3 + Delay
To calculate Offset, the above formula can be converted algebraically as follows:
Offset = T3 + Delay - T4
Entering example values, the final formula is as follows:
T3 + [(T4 - T1) - (T3 - T2)]/2 – T4 = [(T2 - T1) + (T3 – T4)]/2
The NTP client clock will be adjusted based on the Offset. This synchronizes the NTP client clock with the server.

Clocks in the preceding description are precise. However, this cannot be assumed of all client and server clocks, as clocks may differ. RFC 1305 defines complex algorithms, allowing NTP to ensure the precision of clock synchronization.
Comparisons between synchronous Ethernet and other clock synchronization protocols
Clock Protocol |
Whether Frequency Synchronization Is Supported |
Whether Time Synchronization Is Supported |
Time Synchronization Accuracy |
Signal Transmission Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
NTP |
No |
Yes |
Millisecond accuracy |
Time signals are transmitted using NTP packets. |
Synchronous Ethernet |
Yes |
No |
- |
Clock signals are transmitted using serial data streams at the physical layer, without affecting upper-layer services and CPU performance. |
PTP |
Yes |
Yes |
Sub-microsecond accuracy |
Clock and time signals are transmitted using PTP packets, and higher time accuracy is achieved with the assistance of hardware. |