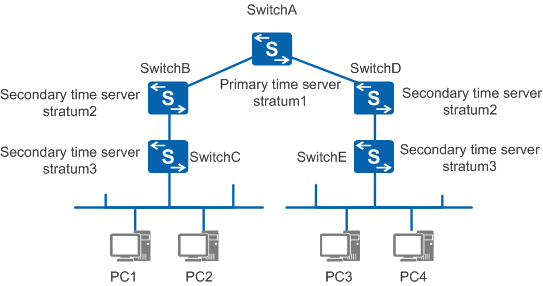
Network Architecture
Primary time server
Directly synchronizes its clock with a standard reference clock through a cable or radio. Typically, the standard reference clock is either a radio clock or the Global Positioning System (GPS).
Secondary time server
Synchronizes its clock with either the primary time server or other secondary time servers within the network. A secondary time server transmits the time information to other hosts within the local area network (LAN) through NTP.
Stratum
A hierarchical standard for clock synchronization. It represents the precision of a clock. The value of a stratum ranges from 1 to 16. A smaller value indicates higher precision. The value 1 indicates the highest precision, and 16 indicates that the clock is not synchronized.
Synchronization subnet
Consists of the primary time server, secondary time servers, PC clients, and interconnecting transmission paths displayed in Figure 1.
Under typical circumstances within a synchronization subnet, the primary time server and the secondary time servers are arranged in a hierarchical-master-slave structure. In this structure, the primary time server is located at the root, and the secondary time servers are located near leaf nodes. As their stratum increases, their precision decreases accordingly. The decreased precision of the secondary time servers varies based upon both network path and local clock stability.

When the synchronization subnet has multiple primary time servers, the optimal server is selected.
- The synchronization subnet will automatically be reconstructed into another hierarchical-master-slave structure when faults occur. These can occur on one or more primary or secondary time servers, or any of the network paths connecting them. This reconstruction ensures the most precise and reliable time possible.
- When all primary time servers in the synchronization subnet are invalid, a standby primary time server will temporarily replace it. Other secondary time servers are synchronized among themselves. These secondary time servers become independent of the synchronization subnet and automatically run at the last synchronized time and frequency.
- When a switch with a stable oscillator becomes independent of the synchronization subnet for a defined period of time, its timing error will remain below several milliseconds per day. This is due to highly precise calculations.