MST BPDUs
MSTP calculates spanning trees based on Multiple Spanning Tree Bridge Protocol Data Units (MST BPDUs). Switches on an MSTP network transmit MST BPDUs to calculate spanning tree topologies, maintain network topologies, and communicate topology changes.
Table 1 describes differences between TCN BPDUs, configuration BPDUs defined by STP, RST BPDUs defined by RSTP, and MST BPDUs defined by MSTP.
Version |
Type |
Name |
|---|---|---|
0 |
0x00 |
Configuration BPDU |
0 |
0x80 |
TCN BPDU |
2 |
0x02 |
RST BPDU |
3 |
0x02 |
MST BPDU |
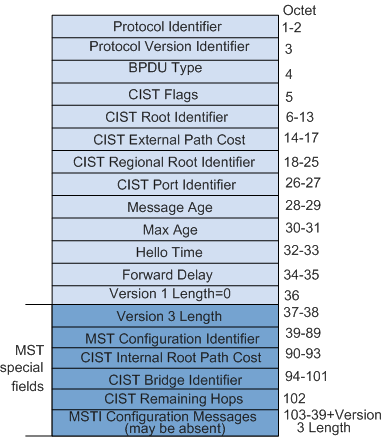
Format of an MST BPDU
Figure 1 shows the format of an MST BPDU.

The first 36 bytes of an MST BPDU are the same as those of an RST BPDU.
Fields from the 37th byte of an MST BPDU are MSTP-specific. The MSTI Configuration Messages field consists of configuration messages of multiple MSTIs.
Table 2 describes the fields in an MST BPDU.
Field |
Length (Bytes) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Protocol Identifier |
2 |
Identifies a protocol. |
Protocol Version Identifier |
1 |
Indicates the protocol version identifier:
|
BPDU Type |
1 |
Indicates the BPDU type:
|
CIST Flags |
1 |
Identifies the CIST. |
CIST Root Identifier |
8 |
Indicates the ID of the CIST root switch. |
CIST External Path Cost |
4 |
Indicates the total path cost from the MST region where the switch resides to the MST region where the CIST root switch resides. This value is calculated based on link bandwidth. |
CIST Regional Root Identifier |
8 |
Indicates the ID of the regional root switch on the CIST. If the root is in this region, the CIST Regional Root Identifier is the same as the CIST Root Identifier. |
CIST Port Identifier |
2 |
Indicates the ID of the designated port in the IST. |
Message Age |
2 |
Indicates the lifecycle of the BPDU. |
Max Age |
2 |
Indicates the maximum lifecycle of the BPDU. If the Max Age timer expires, the link to the root is considered faulty. |
Hello Time |
2 |
Indicates the Hello timer value. The default value is 2 seconds. |
Forward Delay |
2 |
Indicates the forwarding delay timer. The default value is 15 seconds. |
Version 1 Length |
1 |
Indicates the BPDUv1 length, which has a fixed value of 0. |
Version 3 Length |
2 |
Indicates the BPDUv3 length. |
MST Configuration Identifier |
51 |
Indicates the MST configuration identifier, which has four fields. |
CIST Internal Root Path Cost |
4 |
Indicates the total path costs from the local port to the IST master. This value is calculated based on link bandwidth. |
CIST Bridge Identifier |
8 |
Indicates the ID of the designated switch on the CIST. |
CIST Remaining Hops |
1 |
Indicates the number of remaining hops of the BPDU in the CIST. |
MSTI Configuration Messages (may be absent) |
16 |
Indicates an MSTI configuration message. Each MSTI configuration message occupies 16 bytes. If there are n MSTIs, MSTI configuration messages are n*16 bytes long. |
Configurable Format of MST BPDUs
There are two formats of MST BPDUs:
dot1s: BPDU format defined in IEEE 802.1s
legacy: private BPDU format
Remote devices must transmit and receive the same MST BPDU format. If MST BPDU formats are different, loops may occur.
To configure ports on a Huawei switch to automatically adopt the BPDU format of the remote device, use the stp compliance command. The following modes can be set on Huawei switches:
auto
dot1s
legacy
In auto mode, a port uses the dot1s BPDU format by default, but switches format if legacy BPDUs are received from the remote end.
Maximum Number of BPDUs Sent by a Port at a Hello Interval
The maximum number of BPDUs sent by a port during a Hello interval can be configured on Huawei switches.
The number of BPDUs sent during a Hello interval increases as the Hello Time value is increased. Setting the Hello Time to a smaller value limits the number of BPDUs sent by a port during a Hello interval, which helps prevent network topology flapping and excessive use of bandwidth resources by BPDUs.