VLL in CCC Mode
Introduction
A VLL connection in Circuit Cross Connect (CCC) mode is configured manually.
A CCC connection does not require signaling negotiation or exchange of control packets; therefore, it requires few resources and is easy to configure. This mode is best applied to small MPLS networks with simple topologies.
Topology
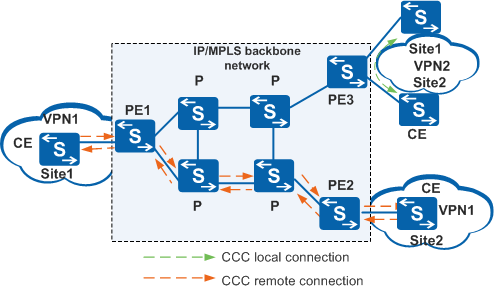
The CCC mode supports both local and remote connections. Figure 1 shows the topology of a network using CCC.
Local connection: Site1 and Site2 of VPN2 connect through a CCC local connection. PE3 acts as a Layer 2 switch for Site1 and Site2, and no LSP is required between the CE devices connected to PE3.
Remote connection: Site1 and Site2 of VPN1 connect through a CCC remote connection. Site1 and Site2 require two static LSPs, one from PE1 to PE2 and one from PE2 to PE1. The two orange dashed lines represent a bidirectional PW, or CCC remote connection. This CCC remote connection is similar to a traditional L2VPN connection.
A CCC remote connection uses static VCs and maps L2PDUs received on one end of a VC to a static LSP. The L2PDUs are forwarded along the static LSP hop by hop based on the MPLS configuration and finally reach the other end of the VC. Unlike other VLL modes, the CCC mode uses a single label to transmit data. This label is swapped on each label switching router (LSR). Therefore, each LSP is used exclusively, and two LSPs in forward and reverse directions must be configured for each CCC connection. The LSPs associated with a CCC connection can only transmit the data of this connection and cannot be used for other MPLS L2VPN connections. In addition, the LSPs cannot be used to set up a BGP/MPLS IP VPN connection or transmit common IP packets.