Understanding Hotspot 2.0
Hotspot 2.0 Network Architecture
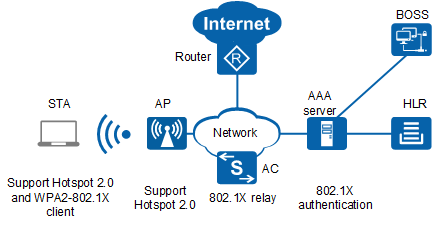
Based on the cellular network infrastructure, the operator deploys a Hotspot 2.0 network to provide Wi-Fi access. Figure 1 shows the network architecture.
NE |
Description |
|---|---|
STA |
Wireless terminals that support Hotspot 2.0 and WPA2-802.1X client. STAs function as the ANQP clients and can obtain Hotspot 2.0 network information through ANQP. |
AP |
Wireless access points that support Hotspot 2.0 and WAP2-802.1X access. The APs function as the ANQP servers and can send Hotspot 2.0 network information to STAs through ANQP. |
AC |
Wireless controller that manages and configures APs in batches, and supports 802.1X authentication. |
AAA server |
Authentication, authorization, and accounting server that supports 802.1X authentication and EAP-SIM/AKA/TLS/TTLS encryption. It can obtain authentication vectors and WLAN registration information from the HLR. |
HLR |
Home location register (HLR), a database that stores user information on mobile communication networks, including the user registration information, mobile station location information, MSISDNs, and IMSIs. |
BOSS |
The operation support platform provides end-to-end business flow support for the carrier to handle routine tasks such as customer service, rating, billing, settlement and dunning. |
Concepts
Hotspot 2.0 is implemented based on IEEE 802.11u standards. IEEE 802.11u defines a mechanism for terminals to obtain WLAN information. On home or roaming networks, terminals can obtain WLAN information through Beacon or Probe frames or the generic advertisement service (GAS). Based on the received WLAN information, the terminals automatically select the optimal WLAN network to access, where the terminals will be automatically authenticated.
- GAS: a mechanism defined by 802.11u through which the STA obtains network information by exchanging Request and Response packets with the network side.
- Access Network Query Protocol (ANQP): a network information query protocol encapsulated in GAS packets.
ANQP defines the network parameters that are used to identify networks, as shown in Table 2.
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
NAI Realm |
Service provider information, including the realm name and authentication type. |
3GPP Cellular PLMN |
Cellular network identifier composed of MNC and MCC. |
Roaming Consortium List |
Operator Identifiers (OIs) of service providers having roaming relationships with each other. STAs can determine the authentication type based on the OI. |
Domain Name |
Domain name of the access network operator, which is the identifier of the operated Hotspot 2.0 network. |
Venue Name |
Venue name that specifies the location of the Hotspot 2.0 network. |
Venue Info |
Venue information that specifies the type of the location where the Hotspot 2.0 network resides. |
Operator Friendly Name |
Friendly operator name displayed on the user terminal. |
IP Address Type Availability Information |
Available IP address types, for example, IPv4, IPv6, and NAT. |
WAN Metrics |
Load on wired interface, including link status, and uplink and downlink rates and loads. |
Connection Capability |
Connection capability, including allowed IP protocols and ports of the network. |
Operating Class Indication |
Operating class indication, indicating the working channel of the APs providing the same SSID and at the same location. |
Network Authentication Type Information |
Information used for HTTP/HTTPS redirection and DNS redirection. |
HESSID |
Homogenous Extended Service Set Identifier which is globally unique and uses the BSSID of one AP to identify APs of the same service provider. HESSID helps STAs to determine whether network parameters need to be renewed and assist the STAs in network selection. |
Access Network Type Field |
Access network type: whether the WLAN is a private network or public network, or whether it is chargeable or free. |
Internet Available Field |
Whether the Hotspot 2.0 network provides Internet access. |
BSS Load Information Element |
AP load information, including STA quantity and channel usage. |
Hotspot 2.0 Indication |
Hotspot 2.0 indication field, which indicates that the AP supports Hotspot 2.0 and whether the AP is allowed to forward downstream broadcast or multicast packets. |
Network Discovery and Selection
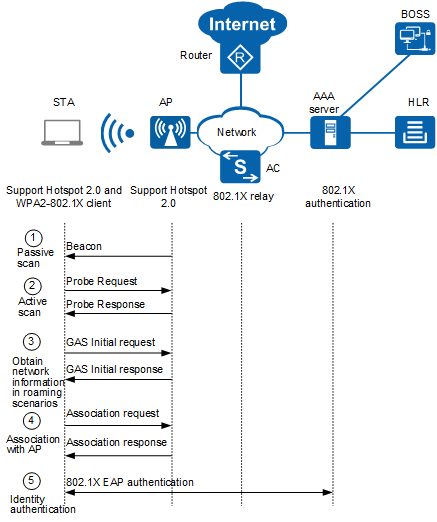
Figure 2 shows the process of Hotspot2.0 network discovery and selection which involves packet exchanges between the STA and AP. Step 1 and Step 2 are parallel. Based on different STA and AP settings, a STA may perform an active or passive scan.
STA passive scan or active scan
STA passive scan
An AP sends a Beacon frame which contains information including the Hotspot 2.0 indication, BSS load, Internet connectivity flag, network type, and information of service providers.
Upon receiving the Beacon frame, the STA checks whether the received Beacon frame carries the Hotspot 2.0 indication. If so, the STA determines that the AP supports Hotspot 2.0. The STA then parses the Roaming Consortium field included in the received frame to obtain the OI of the WLAN service provider. In this way, the STA determines whether it is allowed to access the WLAN. Before network access, the STA can also learn the BSS load information and then select a lightly loaded AP to access the WLAN.
STA active scan
The STA sends to the home AP a Probe Request frame with access network type information. After receiving the Probe Request frame, the AP checks whether the network type contained in the frame matches the allowed network type configured on the AP. If so, the AP responds with a Probe Response frame, which includes Hotspot 2.0 indication, BSS load, Internet connectivity flag, network type, and information of one to three service providers.
When receiving the Probe Response frame, the STA checks whether the received frame carries the Hotspot 2.0 indication. If so, the STA determines that the AP supports Hotspot 2.0. The STA then parses the Roaming Consortium field included in the received frame to obtain the OI of the WLAN service provider. In this way, the STA determines whether it is allowed to access the WLAN. Before network access, the STA can also learn the BSS load information and then select a lightly loaded AP to access the WLAN.
STA obtaining network information in roaming scenarios
The STA sends a GAS Initial Request frame to obtain more WLAN information, including a list of all available service providers, supported authentication types, hotspot operators, IP addresses and ports, and traffic over the wired port. The AP replies a GAS Initial Response frame, which carries ANQP network parameters.
STA association with the AP
The STA selects a WLAN to access based on the obtained WLAN information (such as the realm name and authentication type), preset NAI, and access credential. Upon determining a target WLAN, the STA sends an Association Request frame to the AP. The Association Request frame carries the Hotspot 2.0 indication which indicates that AES encryption and 802.1X authentication are used. The AP replies with an Association Response frame.
STA identity authentication
The STA sends an 802.1X authentication request, and the AC forwards it to the AAA server. The STA also reports NAI information. Based on the route information carried in the NAI field, the home AAA server connects to the authentication server of the home service provider for authentication of the STA. After passing the authentication, the STA can access the WLAN.