Bluetooth Tag Location
Basic Concepts
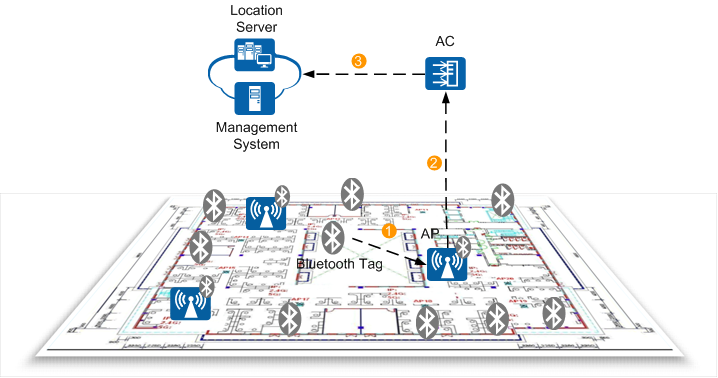
As shown in Figure 1, a Blue tag location
system is composed of multiple Blue tags, at least three APs with
built-in Blue modules, one or more ACs, one location server, and one
management system.
Functions of each component in a Blue tag location system
are as follows:
Bluetooth tag: is manufactured by Bluetooth tag vendors and generates Bluetooth signals based on the BLE protocol. Bluetooth tags periodically send BLE broadcast frames.
- AP: scans BLE broadcast frames sent by Blue tags to obtain Blue tag information and reports the information to an AC or a location server. The information includes RSSI calibration values, battery power, and Blue tag disconnection alarms.
- AC: delivers the Blue location function configuration, and reports Blue tag information and Blue tag offline alarms to the location server.
- Location server: You can make a location map model on a location server. After APs with built-in Blue modules are added to a location server, the location server can determine AP installation locations, compute Blue tag locations, and monitor Blue tag status.
- Management system: obtains Blue tag information from a location server, analyzes the information, and manages assets and guests that bring Blue tags.
Implementation
As shown in Figure 1, Blue tag location technology
is used to locate Blue tags by the following procedure:
The built-in Blue module of an AP scans surrounding Blue tags and collects BLE broadcast frames sent by Blue tags. A BLE broadcast frame contains Blue tag information including the RSSI calibration value, battery power, and Blue tag disconnection alarms.
Blue tags periodically send BLE broadcast frames and do not need to access a WLAN. Figure 2 shows the format of a BLE broadcast frame.Fields of a BLE broadcast frame are described from the left to the right as follows:- Data Length: total length of the BLE Flags and Flag Data fields
- BLE Flags: field defined by the BLE protocol. For details, see Chapter 18.1 of Part C in Volume 3 of Blue 4.0 Core Specification.
- Flag Data: field defined by the BLE protocol. For details, see Chapter 18.1 of Part C in Volume 3 of Blue 4.0 Core Specification.
- Data Length: total length of the Company Manufacture Data, Company ID, BLE Type, Battery volume, Current, Reference RSSI, and Reserved fields.
- Company Manufacture Data: vendor information.
- Company ID: company ID applied by Huawei from the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (Bluetooth SIG).
- BLE Type: tag type. Currently, only 0x00 is supported, which indicates the universal tag.
- Battery volume: battery power level ranging from 0 to 100 in decimal notation that corresponds to battery power from 0% to 100%.
- Current: Bluetooth tag disconnection alarm. The value 0 indicates that a Bluetooth tag is connected, while 1 indicates that a Bluetooth tag is disconnected. For devices that do not support Blue tag disconnection alarms, the field value is fixed at 0.
- Reference RSSI: RSSI calibration value, which is measured 1 meter away from a Blue tag. The distance between a Blue tag and an AP is calculated based on this field.
- Reserved: field defined by tag vendors. The field length is less than or equal to 20 bytes.
The AP reports the obtained information about Blue tags to an AC.
- The AC reports information about all Blue tags and Blue tag offline alarms to a location server.
- Make a floor plan and location map model on the location server. After APs with built-in Blue modules are added to the location server, the location server can determine AP installation locations, compute Blue tag locations, and monitor Blue tag status.