Inter-AC Roaming
Network Architecture
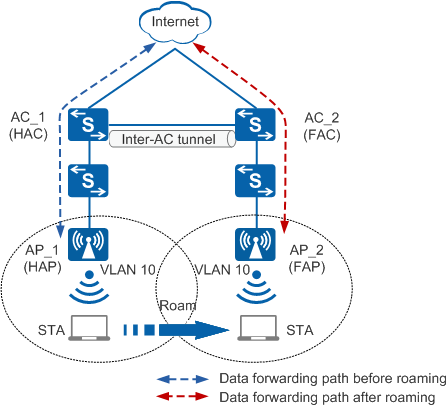
Figure 1 shows the inter-AC roaming network architecture. AC_1 and AC_2 manage APs on the WLAN. AP_1 associates with AC_1, and AP_2 associates with AC_2. A STA roams on the WLAN. During roaming, the STA associates with different APs. The roaming process is as follows:
The STA moves from the coverage area of AP_1 to AP_2. Since AP_1 and AP_2 associate with AC_1 and AC_2, respectively, the STA implements inter-AC roaming. AP_1 and AC_1 are the STA's home AP (HAP) and home AC (HAC), and AP_2 and AC_2 are the STA's foreign AP (FAP) and foreign AC (FAC). AC_1 and AC_2 must belong to the same mobility group. The STA can only roam between ACs in the same mobility group. ACs in a mobility group synchronize data of each other and forward packets over the inter-AC tunnel.
- HAC: AC in a mobility group with which a STA associates for the first time, for example, AC_1 in Figure 1
- HAP: AP in a mobility group with which a STA associates for the first time, for example, AP_1 in Figure 1
- FAC: AC to which a STA roams, for example, AC_2 in Figure 1
- FAP: AP to which a STA roams, for example, AP_2 in Figure 1
Inter-AC roaming: A STA roams between different ACs. As shown in Figure 1, the STA roams between different ACs when roaming from AP_1 to AP_2.
- Mobility group: You can add ACs on a WLAN to different groups. STAs can roam between ACs in the same group. This group is called mobility group.
- Inter-AC tunnel: Inter-AC roaming requires that ACs in a mobility group synchronize STA and AP information with each other. To enable inter-AC roaming, the ACs set up a tunnel to synchronize data and forward packets. An inter-AC tunnel is also a CAPWAP tunnel. For example, AC_1 and AC_2 in Figure 1 set up a tunnel for data synchronization and packet forwarding.
Layer 2 Roaming
As shown in Figure 1, after Layer 2 roaming, the STA remains in the same subnet. The FAP/FAC processes packets of the Layer 2 roaming STA in the same way as it processes packets of a common online STA. The FAP/FAP forwards the packets on the local network but does not send the packets back to the HAP/HAC over the inter-AC tunnel.
Before Roaming |
After Roaming |
|---|---|
|
|