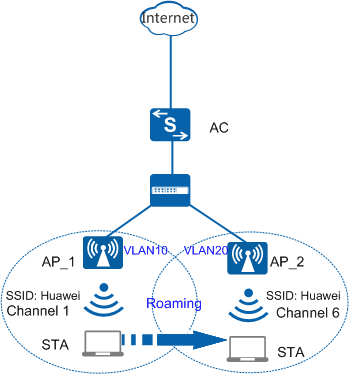
Roaming Between APs in Different Service VLANs
To prevent broadcast storms, users on enterprise WLANs, like wired LANs, are assigned different VLANs according to their floors and departments. If APs deployed on different floors belong to different VLANs, a user's services are interrupted when they roam between those APs. Inter-VLAN Layer 3 roaming prevents service interruption in this case, improving WLAN services.
In roaming between APs in different service VLANs, APs belong to different service VLANs before and after roaming. To prevent a user's services from being interrupted during WLAN roaming, ensure that their service VLAN remains unchanged after they roam between two APs.
Roaming between APs in different service VLANs includes fast and non-fast roaming, depending on STA support fast roaming. For details on the implementation of fast and non-fast roaming, see Roaming Between APs in the Same Service VLAN. In Figure 1, when the STA roams from AP_1 to AP_2 in different VLANs, the process of keeping the service VLAN of the STA unchanged is as follows:
- When the STA accesses the Internet through AP_1 in VLAN 10, the AC determines that the STA has done so for the first time. The AC then creates and saves STA service data, including the service VLAN of the AP, AP name, radio, and VAP information.
- The STA moves from AP_1 to AP_2 in VLAN 20 and re-associates with the AC through AP_2. The AC determines that the STA is roaming based on user information, so it updates the service database. It also updates the AP name, radio, and VAP information to be consistent with AP_2 information, without changing the VLAN ID. The VLAN is still the service VLAN to which AP_1 belongs.
- The STA disassociates from AP_1. Although the STA resides on different subnets after roaming between two APs, the AC still considers that the STA accesses the Internet from the first VLAN (VLAN 10). This allows the STA to retain its IP address to ensure nonstop service interruption.