Understanding WDS
WDS Concepts
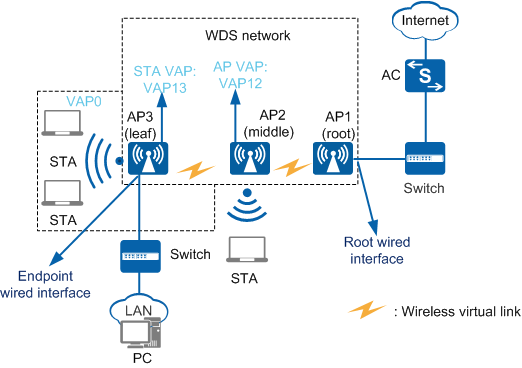
- Service VAP: On a traditional WLAN, an AP is a physical entity that provides WLAN services to STAs. A service virtual access point (VAP) is a logical entity that provides access service for users. Multiple VAPs can be created on an AP to provide access service for multiple user groups. In Figure 1, VAP0 created on AP3 is a service VAP.
- WDS VAP: On a WDS network, an AP is a functional entity that provides WDS service for neighboring devices. WDS VAPs include AP and STA VAPs. The ID of STA VAPs is fixed as 13, and that of AP VAPs is fixed at 12. AP VAPs provide connections for STA VAPs. In Figure 1, VAP13 created on AP3 is a STA VAP, and VAP12 created on AP2 is an AP VAP.
- Wireless virtual link (WVL): a connection set up between a STA VAP and an AP VAP on neighboring APs, as shown in Figure 1.
AP working mode: Depending on its location on a WDS network, an AP can work in root, middle, or leaf mode, as shown in Figure 1.
- Root: The AP directly connects to an AC through a wired link and uses an AP VAP to set up wireless virtual links with a STA VAP.
- Middle: The AP uses a STA VAP to connect to an AP VAP on an upstream AP and uses an AP VAP to connect to a STA VAP on a downstream AP.
- Leaf: The AP uses a STA VAP to connect to an AP VAP on an upstream AP.
- Working mode of an AP's wired interface: On a WDS network, depending on the location of the AP, a wired interface works in root or endpoint mode.
- Root: The wired interface connects to an upstream wired network.
- Endpoint: The wired interface connects to a downstream user host or LAN.

On a WDS network, one wired interface must work in root mode to connect to the wired network.
WDS Implementation
AP online process
After WDS is enabled on an AP, the AP automatically creates WDS VAPs (AP VAP and STA VAP). The AP uses the WDS VAPs to set up WVLs with other APs. The AP connects to the AC through the WVL and obtains configurations from the AC.
Service intercommunication
On a WDS network, service data is transmitted over the WVLs. After an AP goes online, it needs to set up service links through WVLs. Figure 2 shows how a service link is set up between AP2 and AP3 on the WDS network shown in Figure 1.
Probe request
AP3 broadcasts a Probe Request frame carrying a WDS-Name field (similar to SSID in WLAN service).
Probe response
AP2 receives the Probe Request frame and sends AP3 a Probe Response frame.
Authentication request
After AP3 receives the Probe Response frame, it sends AP2 an Authentication Request frame.
Authentication response
After AP2 receives the Authentication Request frame, it determines whether to allow access from AP3, depending on the WDS whitelist configuration:- If the WDS whitelist is not enabled, AP2 allows access from AP3 and sends an Authentication Response frame to notify AP3 that the authentication has succeeded.
- If the WDS whitelist is enabled, AP2 checks whether the MAC address of AP3 is included in the WDS whitelist.
- If the MAC address of AP3 is included in the WDS whitelist, AP2 allows access from AP3 and sends an Authentication Response frame to notify AP3 that the authentication has succeeded.
- If the MAC address of AP3 is not included in the WDS whitelist, AP2 sends an Authentication Response frame with an error code, indicating that the authentication has failed. The process ends and the service wireless virtual link (WVL) cannot be set up.
Association request
After AP3 receives the Authentication Response frame indicating successful authentication, it sends an Association Request frame to AP2.
Association response
After AP2 receives the Association Request frame, it sends an Association Response frame to request AP3 to start the access authentication.
Access authentication
On a WDS network, the access authentication method for a STA VAP must be WPA2-PSK. Therefore, AP3 and AP2 use a pre-configured shared key for negotiation. If they decrypt messages sent from each other using the shared key, they have the same shared key and the access authentication is successful.
Key negotiation
AP3 and AP2 negotiate an encryption key to encrypt service packets.

- After a service link is set up, APs periodically send link status messages to each other. If one AP does not receive any from the other AP, it disconnects the service link and starts to set up a new one.
- If the AC delivers new WDS parameter settings to APs, the APs use them to set up service links.
WDS Network Architecture
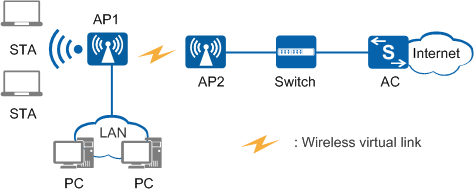
Point-to-point deployment
As shown in Figure 3, AP1 sets up wireless virtual links with AP2 to provide wireless access service for users.
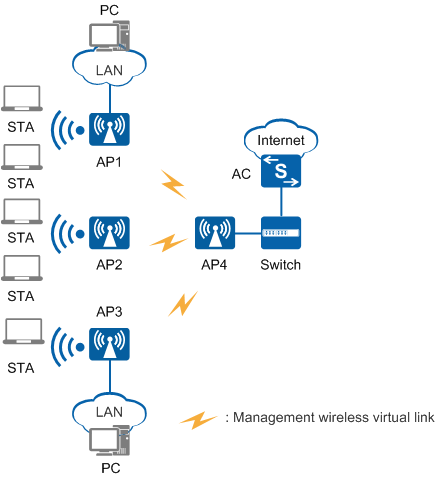
Point-to-multipoint deployment
As shown in Figure 4, AP1, AP2, and AP3 set up wireless virtual links with AP4. Data from all STAs associating with AP1, AP2, and AP3 is forwarded by AP4.