ICMPv6
The Internet Control Message Protocol version 6 (ICMPv6) is one of the basic IPv6 protocols.
In IPv4, ICMP reports IP packet forwarding information and errors to the source node. ICMP defines certain messages such as Destination Unreachable, Packet Too Big, Time Exceeded, Echo Request, and Echo Reply to facilitate fault diagnosis and information management. ICMPv6 provides additional mechanisms alongside the current ICMPv4 functions such as Neighbor Discovery (ID), stateless address configuration (including duplicate address detection), and Path Maximum Transmission Unit (PMTU) discovery.
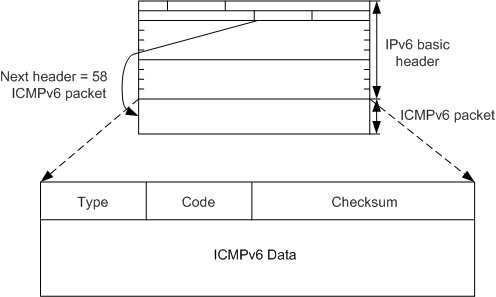
The protocol number of ICMPv6 (that is, the value of the Next Header field in an IPv6 packet) is 58. Figure 1 shows the ICMPv6 packet format.
Some fields in the packet are described as follows:
Type: specifies a message type. Values 0 to 127 indicate the error message type, and values 128 to 255 indicate the informational message type.
Code: indicates a specific message type.
Checksum: indicates the checksum of an ICMPv6 packet.
Classification of ICMPv6 Error Messages
ICMPv6 error messages are generated when errors occur during IPv6 packet forwarding. They are classified into the following four types:
Destination Unreachable message
During IPv6 packet forwarding, if an IPv6 node detects that the destination address of a packet is unreachable, it sends an ICMPv6 Destination Unreachable message to the source node carrying information about the causes for the error message.
In an ICMPv6 Destination Unreachable message, the value of the Type field is 1. Depending on the cause, the value of the Code field can be:
- 0: No route to the destination device.
1: Communication with the destination device is administratively prohibited.
2: Not assigned.
3: Destination IP address is unreachable.
4: Destination port is unreachable.
Packet Too Big message
If an IPv6 node, during IPv6 packet forwarding, detects that the size of a packet exceeds the link MTU of the outbound interface, it sends an ICMPv6 Packet Too Big message to the source node. The link MTU of the outbound interface is carried in the message. PMTU discovery is implemented based on Packet Too Big messages.
In a Packet Too Big message, the Type field value is 2 and the Code field value is 0.
Time Exceeded message
During the transmission of IPv6 packets, when a device receives a packet with a hop limit of 0 or a device reduces the hop limit to 0, it sends an ICMPv6 Time Exceeded message to the source node. During the processing of a packet to be fragmented and reassembled, an ICMPv6 Time Exceeded message is also generated when the reassembly time is longer than the specified period.
In a Time Exceeded message, the Type field value is 3. Depending on the cause, the Code field value can be:
- 0: Hop limit exceeded in packet transmission.
- 1: Fragment reassembly timeout.
Parameter Problem message
When a destination node receives an IPv6 packet, it checks the validity of the packet. If it detects an error, it sends an ICMPv6 Parameter Problem message to the source node.
In a Parameter Problem message, the Type field value is 4. Depending on the cause, the Code field value can be:
0: A field in the IPv6 basic header or extension header is incorrect.
1: The Next Header field in the IPv6 basic header or extension header cannot be identified.
2: Unknown options exist in the extension header.
Classification of ICMPv6 Information Messages
Echo Request messages: Echo Request messages are sent to destination nodes. After receiving an Echo Request message, the destination node responds with an Echo Reply message. In an Echo Request message, the Type field value is 128 and the Code field value is 0.
Echo Reply messages: After receiving an Echo Request message, the destination node responds with an Echo Reply message. In an Echo Reply message, the Type field value is 129 and the Code field value is 0.