OSPF Characteristics
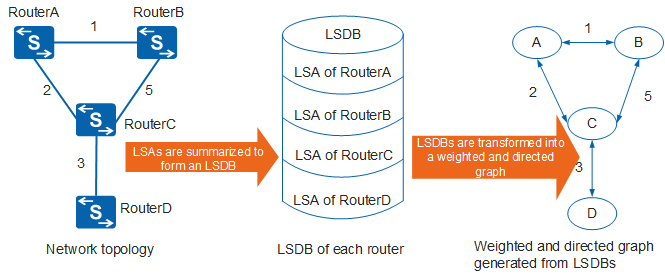
In an OSPF network, each router generates a link-state advertisement (LSA) based on its surrounding network topology and transmits this LSA in an update packet to other routers in the network.
RIP devices exchange routes, whereas OSPF devices exchange link state information. That is, in RIP, routers select routes based on routing information of neighbors, without checking whether the information transmitted by neighbors is correct. In OSPF, routers calculate routes by themselves and select routes based on LSAs.
Each router learns about the whole network topology based on its link state database (LSDB). In Figure 1, each router collects LSAs sent from other routers, and all LSAs form the LSDB of this router. An LSA describes the surrounding network topology of a router, whereas an LSDB describes the network topology of the entire AS. A router transforms its LSDB into a weighted and directed graph, which reflects the topology of the entire AS. When the network topology is stable, all routers in the same area have the same graph.
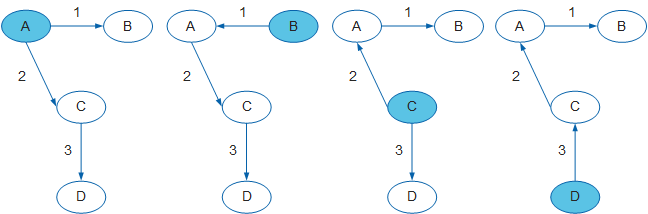
A router calculates shortest paths to destinations using a shortest path first (SPF) algorithm instead of obtaining routing information through route advertisements. In Figure 2, based on the weighted and directed graph, each router uses an SPF algorithm to calculate a shortest path tree (SPT) with itself as the root. The SPT shows routes to nodes in the AS. This mechanism greatly improves routers' capabilities in independent route selection and frees routers from selecting routes based on route advertisements.
An LSDB ensures that a router can learn about the whole network topology, and an SPF algorithm ensures that a router can quickly calculate shortest paths to destinations.