OSPF Mechanism
The OSPF mechanism includes the following steps:
Exchanging Hello packets to establish OSPF neighbor relationships
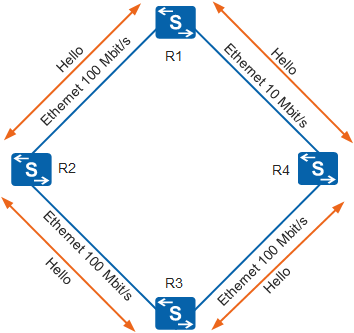
In Figure 1, after OSPF is run on the four routers, these routers send Hello packets on all OSPF-enabled interfaces. If two routers share a data link and successfully negotiate certain parameters specified in their Hello packets, they establish an OSPF neighbor relationship.
Flooding LSAs to advertise link state information
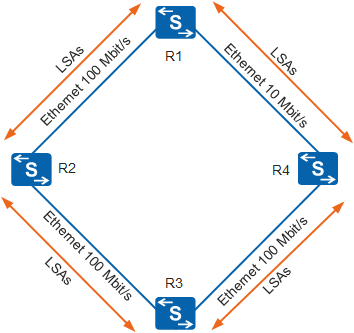
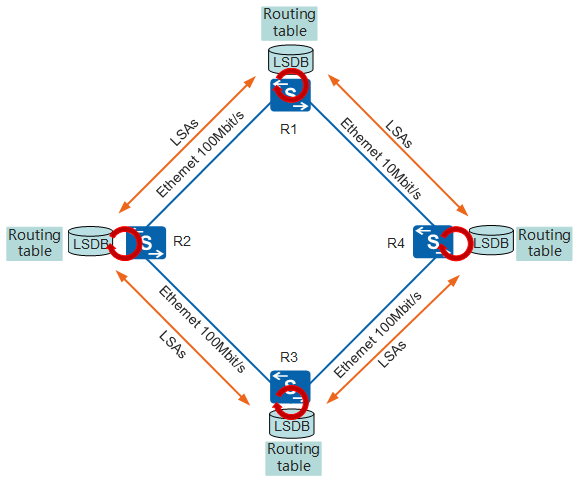
Routers that have established an OSPF neighbor relationship can exchange LSAs to form an OSPF adjacency, as shown in Figure 2. Each router generates LSAs based on its surrounding network topology. LSAs describe information about a router, including all links, interfaces, neighbors, and link state of the router. Routers exchange the link information to learn about the entire network topology. Because of the link diversity, OSPF defines multiple LSA types. For details, see OSPF LSA Types.
Forming an LSDB to create a weighted and directed graph
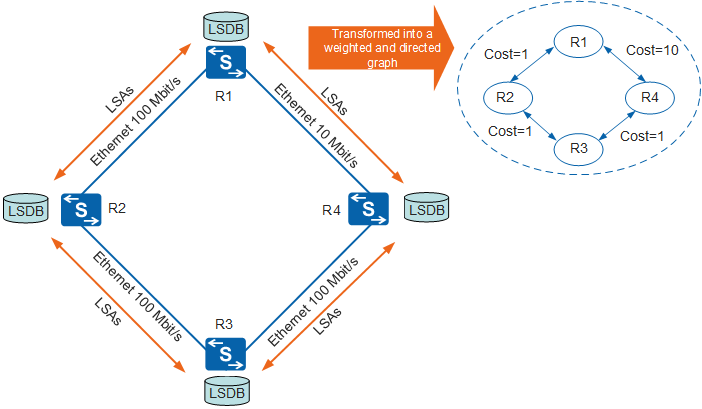
A router floods LSAs and records received LSAs in its LSDB. Subsequently, all routers have the same LSDB, as shown in Figure 3. An LSA describes the surrounding network topology of a router, whereas an LSDB describes the network topology of the entire AS and is the summary of LSAs.
Using an SPF algorithm to calculate and generate routes
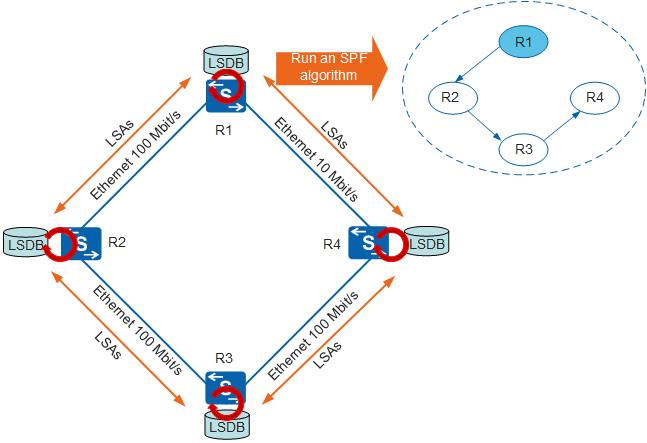
In Figure 4, after LSDB synchronization is complete, each router uses an SPF algorithm to calculate a loop-free topology with itself as the root and describe the shortest path (with the minimum path cost) to each destination. The topology is the SPT, which shows the optimal paths to nodes in an AS.
Maintaining and updating routing tables
After each router uses an SPF algorithm to calculate the SPT, it installs the shortest paths in its routing table. These paths are installed as routing entries to guide data forwarding. The routers then update their routing tables in real time, as shown in Figure 5. Meanwhile, neighbors exchange Hello packets to maintain their neighbor relationships or adjacencies and periodically retransmit LSAs.