Example for Configuring Static ARP
Overview
Static ARP allows a network administrator to create fixed mappings between IP and MAC addresses.
Dynamic ARP can leave networks vulnerable to ARP spoofs or attacks (when malicious devices send falsified ARP messages to link an attacker's MAC address with the IP address of a legitimate device). As a result, ARP entries may be incorrectly learned. However, if a static ARP entry is configured on a device, the device can communicate with the peer device using only the specified MAC address. Network attackers cannot modify the mapping between the IP and MAC addresses using ARP packets, ensuring communication between the two devices.
- Networks contain critical devices such as servers. Network attackers cannot update the ARP entries containing IP addresses of the critical devices on the switch using ARP attack packets, ensuring communication between users and the critical devices.
- Networks contain user devices with multicast MAC addresses. By default, a device does not learn ARP entries when the source MAC addresses of received ARP packets are multicast MAC addresses.
- A network administrator wants to prevent an IP address from accessing devices. The network administrator binds the IP address to an unavailable MAC address.
Configuration Notes
- The number of static ARP entries configured on the device cannot exceed the maximum number of static ARP entries on the device. You can run the display arp statistics all command to check the number of existing ARP entries on the device.
This example applies to all versions of all S series switches.

For details about software mappings, visit Hardware Query Tool and search for the desired product model.
Networking Requirements
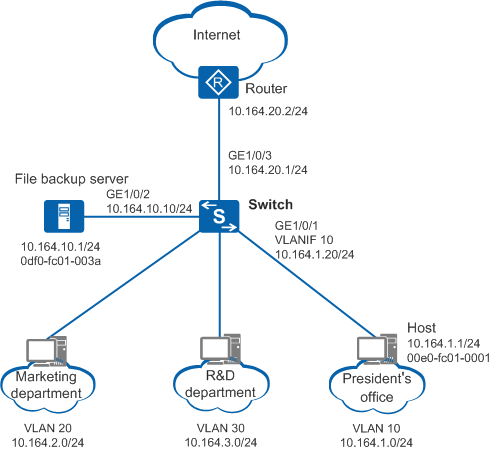
As shown in Figure 1, the Switch connects different departments of an enterprise. The departments are added to different VLANs. Fixed IP addresses have been manually assigned to the file backup server and hosts in the president's office, and dynamic IP addresses have been assigned to hosts in other departments using DHCP. Hosts in the marketing department can access the Internet and are often attacked by ARP packets. Attackers attack the Switch and modify dynamic ARP entries on the Switch. As a result, communication between hosts in the president's office and external devices is interrupted and hosts in departments fail to access the file backup server. The company requires that static ARP entries be configured on the Switch so that hosts in the president's office can communicate with external devices and hosts in departments can access the file backup server.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Configure static ARP entries for hosts in the president's office on the Switch to prevent ARP entries of the hosts in the president's office from being modified by ARP attack packets.
- Configure a static ARP entry for the file backup server on the Switch to prevent the ARP entry of the file backup server from being modified by ARP attack packets.
Procedure
- Create VLANs on the Switch and configure an IP address
for each interface.
# Create VLAN 10, add the interfaces to VLAN 10, and configure an IP address for VLANIF 10.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname Switch [Switch] vlan batch 10 [Switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-type access [Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port default vlan 10 [Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit [Switch] interface vlanif 10 [Switch-Vlanif10] ip address 10.164.1.20 24 [Switch-Vlanif10] quit
# Configure GE1/0/2 as the primary interface and configure an IP address for it.
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] undo portswitch [Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] ip address 10.164.10.10 24 [Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Configure GE1/0/3 as the primary interface and configure an IP address for it.
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] undo portswitch [Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ip address 10.164.20.1 24 [Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit

If the Switch does not support the configuration that uses the undo portswitch command to configure an interface as the primary interface and then configures an IP address for it, configure the interface as a VLANIF interface and then configure an IP address for it.
- Configure static ARP entries on the Switch.
[Switch] arp static 10.164.1.1 00e0-fc01-0001 vid 10 interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 //Configure a static ARP entry for hosts in the president's office [Switch] arp static 10.164.10.1 0df0-fc01-003a interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 //Configure a static ARP entry for the file backup server
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the display arp static command to check the configured static ARP entries.
[Switch] display arp static IP ADDRESS MAC ADDRESS EXPIRE(M) TYPE INTERFACE VPN-INSTANCE VLAN/CEVLAN ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 10.164.1.1 00e0-fc01-0001 S-- GE1/0/1 10/- 10.164.10.1 0df0-fc01-003a S-- GE1/0/2 40/- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Total:2 Dynamic:0 Static:2 Interface:0# Ping the IP address 10.164.20.2/24 of the interface on the Router connecting to the Switch from a host (the IP address is 10.164.1.1/24, using Windows 7 operating system as an example) in the president's office. The ping succeeds.
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator> ping 10.164.20.2 Pinging 10.164.20.2 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 10.164.20.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=128 Reply from 10.164.20.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=128 Reply from 10.164.20.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=128 Reply from 10.164.20.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=128 Ping statistics for 10.164.20.2: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 1ms# Ping the IP address 10.164.10.10/24 of the file backup server from a host (for example, using the IP address 10.164.2.100/24 and Windows 7 operating system) in the marketing department. The ping succeeds.
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator> ping 10.164.10.10 Pinging 10.164.10.10 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 10.164.10.10: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=125 Reply from 10.164.10.10: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=125 Reply from 10.164.10.10: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=125 Reply from 10.164.10.10: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=125 Ping statistics for 10.164.10.10: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 1ms# Ping the IP address 10.164.10.10/24 of the file backup server from a host (for example, using the IP address 10.164.3.100/24 and Windows 7 operating system) in the R&D department. The ping succeeds.
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator> ping 10.164.10.10 Pinging 10.164.10.10 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 10.164.10.10: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=125 Reply from 10.164.10.10: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=125 Reply from 10.164.10.10: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=125 Reply from 10.164.10.10: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=125 Ping statistics for 10.164.10.10: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 1ms
Configuration Files
Switch configuration file
#
sysname Switch
#
vlan batch 10
#
interface Vlanif10
ip address 10.164.1.20 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-type access
port default vlan 10
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
undo portswitch
ip address 10.164.10.10 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
undo portswitch
ip address 10.164.20.1 255.255.255.0
#
arp static 10.164.1.1 00e0-fc01-0001 vid 10 interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
arp static 10.164.10.1 0df0-fc01-003a interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
#
return