Example for Setting Up a Stack Using Service Ports (V200R003 and Later Versions)
Overview
Service port connection allows member switches to be connected using service ports, without requiring dedicated stack cards.
Ordinary cable connection: Switches use optical cables, network cables, and high-speed cables to set up a stack.
Dedicated cable connection: Switches use dedicated stack cables to set up a stack. The two ends of a dedicated stack cable are the master end with the Master tag and the slave end without any tag.
Networking Requirements
A new enterprise network needs to provide sufficient ports for access devices, and the network structure should be simple to facilitate configuration and management.
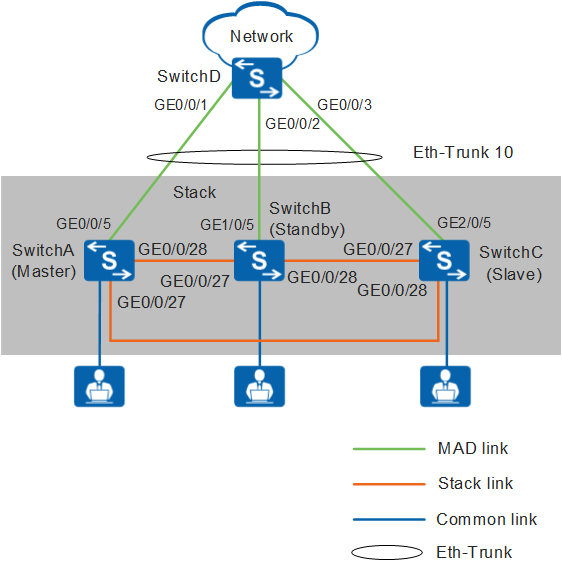
As shown in Figure 1, SwitchA, SwitchB, and SwitchC need to set up a stack in a ring topology and connect to SwitchD through an inter-device Eth-Trunk. SwitchA, SwitchB, and SwitchC are the master, standby, and slave switches respectively, with stack IDs of 0, 1, and 2 and stack priorities of 200, 100, and 100. As the three switches function as one logical device on the network, the number of ports is increased and network management and maintenance are simplified.
In this example, S5700-28X-LI-AC set up a stack.
Configuration Roadmap
Configure logical stack ports and add physical member ports to the corresponding logical stack ports to enable packet forwarding between member switches.
Configure stack IDs and stack priorities for member switches to facilitate device management and identification.
Turn off power supplies of SwitchA, SwitchB, and SwitchC, connect physical member ports using SFP+ stack cables, and then power on the three switches.
Configure an inter-device Eth-Trunk to increase reliability and uplink bandwidth.
Configure multi-active detection (MAD) in relay mode to ensure network availability when the stack splits.
Procedure
- Configure logical stack ports and add physical member ports to them.

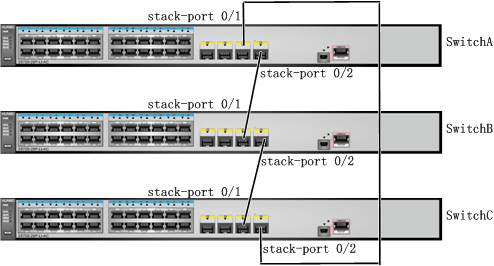
Interface stack-port 0/1 of one switch must be connected to interface stack-port 0/2 of another switch. Otherwise, the stack cannot be set up.
# Configure service ports GigabitEthernet0/0/27 and GigabitEthernet0/0/28 on SwitchA as physical member ports and add them to corresponding logical stack ports.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname SwitchA [SwitchA] interface stack-port 0/1 [SwitchA-stack-port0/1] port interface gigabitethernet 0/0/27 enable [SwitchA-stack-port0/1] quit [SwitchA] interface stack-port 0/2 [SwitchA-stack-port0/2] port interface gigabitethernet 0/0/28 enable [SwitchA-stack-port0/2] quit
# Configure service ports GigabitEthernet0/0/27 and GigabitEthernet0/0/28 on SwitchB as physical member ports and add them to corresponding logical stack ports.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname SwitchB [SwitchB] interface stack-port 0/1 [SwitchB-stack-port0/1] port interface gigabitethernet 0/0/27 enable [SwitchB-stack-port0/1] quit [SwitchB] interface stack-port 0/2 [SwitchB-stack-port0/2] port interface gigabitethernet 0/0/28 enable [SwitchB-stack-port0/2] quit
# Configure service ports GigabitEthernet0/0/27 and GigabitEthernet0/0/28 on SwitchC as physical member ports and add them to corresponding logical stack ports.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname SwitchC [SwitchC] interface stack-port 0/1 [SwitchC-stack-port0/1] port interface gigabitethernet 0/0/27 enable [SwitchC-stack-port0/1] quit [SwitchC] interface stack-port 0/2 [SwitchC-stack-port0/2] port interface gigabitethernet 0/0/28 enable [SwitchC-stack-port0/2] quit
- Configure stack IDs and stack priorities. The default stack ID is 0, and the default stack priority is 100.
[SwitchA] stack slot 0 priority 200 //Set the stack priority of the master switch to 200, which is larger than those of other member switches, and use the default stack ID 0.
[SwitchB] stack slot 0 renumber 1 //Use the default stack priority 100 and set the stack ID to 1.
[SwitchC] stack slot 0 renumber 2 //Use the default stack priority 100 and set the stack ID to 2.
- Turn off power supplies of SwitchA, SwitchB, and SwitchC, connect physical member ports using SFP+ stack cables as shown in Figure 2, and then power on the three switches.

- Run the save command to save the configurations before you power off the switches.
- To ensure that a stack can be set up successfully, you are advised to perform operations in the following sequence. To specify a member switch as the master switch, power on that switch first. In this example, SwitchA becomes the master switch after you complete the following operations.
- Power off SwitchA, SwitchB, and SwitchC.
- Connect SwitchA and SwitchB with a stack cable.
- Power on and start SwitchA and then power on SwitchB.
- Check whether SwitchA and SwitchB set up a stack successfully. For details, see step 4.
- Connect SwitchC to SwitchB and SwitchA using stack cables and then power on SwitchC.
- Check whether SwitchA, SwitchB, and SwitchC set up a stack successfully. For details, see step 4.
- Check whether a stack is set up successfully.
# Check the stack indicator status.
Press the MODE button on any member switch to change the mode status indicator to the stack mode.
- If the mode status indicators on all the member switches change to the stack mode, the stack is set up successfully.
- If the mode status indicator on any member switch does not change to the stack mode, the stack is not set up.

- The S5700-SI, S5700-EI, S5700-HI, S6700-EI, S5710-C-LI use the same mode status indicator to show the stack and speed modes. After you press the MODE button, the indicator is steady red and off after 45 seconds, indicating that the switch enters the stack mode.
- The S5732-H, S6730-S, S6730S-S, S6720-HI, S6730-H, and S6730S-H have an independent stack master/slave indicator to show the MST. If the indicator is off, the switch is not a stack master. If the indicator is steady green, the switch is a stack master or standalone switch.
- Other models have an independent stack mode indicator (STCK indicator). After you press the MODE button, the indicator is steady green or blinking and off after 45 seconds, indicating that the switch enters the stack mode.
# Check basic stack information.
Log in to the stack through the console port of any member switch to check whether the number of member switches in the stack is the same as the actual value and whether the stack topology is the same as the actual hardware connection.
<SwitchA> system-view [SwitchA] sysname Stack [Stack] display stack Stack mode: Service-port Stack topology type : Ring Stack system MAC: 0018-82d2-2e85 MAC switch delay time: 10 min Stack reserved vlan : 4093 Slot of the active management port: 0 Slot Role Mac address Priority Device type ------------------------------------------------------------- 0 Master 0018-82d2-2e85 200 S5700-28P-LI-AC 1 Standby 0018-82c6-1f44 100 S5700-28P-LI-AC 2 Slave 0018-82c6-1f4c 100 S5700-28P-LI-AC
- Configure an inter-device Eth-Trunk.
# Create an Eth-Trunk in the stack and configure uplink physical ports as Eth-Trunk member ports.
[Stack] interface eth-trunk 10 [Stack-Eth-Trunk10] trunkport gigabitethernet 0/0/5 [Stack-Eth-Trunk10] trunkport gigabitethernet 1/0/5 [Stack-Eth-Trunk10] trunkport gigabitethernet 2/0/5 [Stack-Eth-Trunk10] quit
# Create an Eth-Trunk on SwitchD and configure the ports connected to the stack as Eth-Trunk member ports.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname SwitchD [SwitchD] interface eth-trunk 10 [SwitchD-Eth-Trunk10] trunkport gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchD-Eth-Trunk10] trunkport gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [SwitchD-Eth-Trunk10] trunkport gigabitethernet 0/0/3 [SwitchD-Eth-Trunk10] quit
- Verify the Eth-Trunk configuration.# Check Eth-Trunk member port information. The following displays information about Eth-Trunk member ports in the stack.
[Stack] display trunkmembership eth-trunk 10 Trunk ID: 10 Used status: VALID TYPE: ethernet Working Mode : Normal Number Of Ports in Trunk = 3 Number Of Up Ports in Trunk = 3 Operate status: up Interface GigabitEthernet0/0/5, valid, operate up, weight=1 Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5, valid, operate up, weight=1 Interface GigabitEthernet2/0/5, valid, operate up, weight=1
- Configure MAD in relay mode on SwitchD and configure SwitchD as the relay agent.
# In the stack, configure MAD in relay mode on the inter-device Eth-Trunk.
[Stack] interface eth-trunk 10 [Stack-Eth-Trunk10] mad detect mode relay [Stack-Eth-Trunk10] return
# On SwitchD, configure MAD in relay mode on the Eth-Trunk.
[SwitchD] interface eth-trunk 10 [SwitchD-Eth-Trunk10] mad relay [SwitchD-Eth-Trunk10] return
- Verify the MAD configuration.
# Check the MAD configuration of the stack.
<Stack> display mad verbose Current MAD domain: 0 Current MAD status: Detect Mad direct detect interfaces configured: Mad relay detect interfaces configured: Eth-Trunk10 Excluded ports(configurable): Excluded ports(can not be configured): GigabitEthernet0/0/27 GigabitEthernet0/0/28 GigabitEthernet1/0/27 GigabitEthernet1/0/28 GigabitEthernet2/0/27 GigabitEthernet2/0/28
# Check the MAD proxy configuration on SwitchD.
<SwitchD> display mad proxy Mad relay interfaces configured: Eth-Trunk10
Configuration Files
Stack configuration file (the stack configuration is written to the flash memory instead of the configuration file)
# sysname Stack # interface Eth-Trunk10 mad detect mode relay # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/5 eth-trunk 10 # interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5 eth-trunk 10 # interface GigabitEthernet2/0/5 eth-trunk 10 # return
-
# sysname SwitchD # interface Eth-Trunk10 mad relay # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 eth-trunk 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 eth-trunk 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 eth-trunk 10 # return