Example for Configuring Static Routes for Load Balancing
Static Route Overview
Static routes use less bandwidth than dynamic routes and do not use CPU resources for route calculation and update analysis. They are manually configured by administrators. If a network fault occurs or the topology changes, static routes must be manually reconfigured as they cannot be automatically updated. Static routes have five parameters: destination IP address, mask, outbound interface, next hop, and priority.
Static routes are generally suitable for simple networks. However, they can be used on complex networks to improve network performance and ensure bandwidth for important applications.
Configuration Notes
- Communication between two devices is bidirectional, so reachable routes must be available in both directions. To enable two devices to communicate through static routes, configure a static route on the local device and then configure a return route on the peer device.
- If an enterprise network has two egresses, two equal-cost static routes can be configured for load balancing. In this case, two non-equal-cost static routes can be configured for active/standby backup. When the active link is faulty, traffic is switched from the active link to the standby link.
- For the fixed switch models and versions that support this example, see Applicable Products and Versions.
Networking Requirements
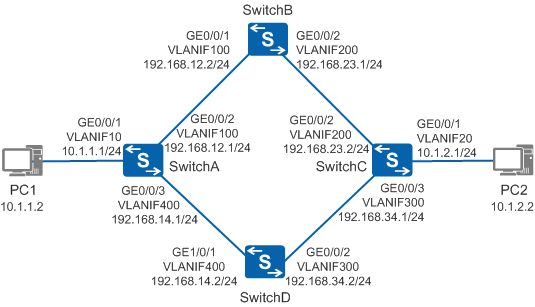
On the network shown in Figure 1, PC1 and PC2 are connected through four switches. Data traffic can be transmitted from PC1 to PC2 through two links: PC1->SwitchA->SwitchB->SwitchC->PC2 and PC1->SwitchA->SwitchD->SwitchC->PC2. To improve link efficiency, users want to implement load balancing between the two links. That is, traffic from PC1 to PC2 is evenly balanced between the two links. When faults occur on one of the two links, traffic is automatically switched to the other link.

In this scenario, ensure that all connected interfaces have STP disabled. If STP is enabled and VLANIF interfaces of switches are used to construct a Layer 3 ring network, an interface on the network will be blocked. As a result, Layer 3 services on the network cannot run normally.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Create VLANs, add interfaces to the VLANs, and assign IP addresses to VLANIF interfaces.
- Configure static routes in two directions of data traffic.
- Configure IP address and default gateways for hosts.
Procedure
- Specify the VLANs to which interfaces belong.
# Configure SwitchA. The configurations of SwitchB, SwitchC, and SwitchD are similar.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname SwitchA [SwitchA] vlan batch 10 100 400 [SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type access [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port default vlan 10 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type trunk [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit [SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/3 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port link-type trunk [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port trunk allow-pass vlan 400 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] quit
- Configure an IP address for each VLANIF interface.
# Configure SwitchA. The configurations of SwitchB, SwitchC, and SwitchD are similar.
[SwitchA] interface vlanif 10 [SwitchA-Vlanif10] ip address 10.1.1.1 24 [SwitchA-Vlanif10] quit [SwitchA] interface vlanif 100 [SwitchA-Vlanif100] ip address 192.168.12.1 24 [SwitchA-Vlanif100] quit [SwitchA] interface vlanif 400 [SwitchA-Vlanif400] ip address 192.168.14.1 24 [SwitchA-Vlanif400] quit
- Configure static routes from PC1 to PC2.
# On SwitchA, configure two equal-cost static routes. The next hop of one route points to SwitchB, and that of the other route points to SwitchD. This configuration can implement load balancing for traffic from PC1 to PC2.
[SwitchA] ip route-static 10.1.2.0 24 192.168.12.2 [SwitchA] ip route-static 10.1.2.0 24 192.168.14.2
# Configure SwitchB.
[SwitchB] ip route-static 10.1.2.0 24 192.168.23.2# Configure SwitchD.
[SwitchD] ip route-static 10.1.2.0 24 192.168.34.1 - Configure static routes from PC2 to PC1.
# On SwitchC, configure two equal-cost static routes. The next hop of one route points to SwitchB, and that of the other route points to SwitchD. This configuration can implement load balancing for traffic from PC2 to PC1.
[SwitchC] ip route-static 10.1.1.0 24 192.168.23.1 [SwitchC] ip route-static 10.1.1.0 24 192.168.34.2
# Configure SwitchB.
[SwitchB] ip route-static 10.1.1.0 24 192.168.12.1# Configure SwitchD.
[SwitchD] ip route-static 10.1.1.0 24 192.168.14.1 - Configure hosts.
Assign IP address 10.1.1.2/24 and default gateway IP address 10.1.1.1 to PC1; assign IP address 10.1.2.2/24 and default gateway IP address 10.1.2.1 to PC2.
- Verify the configuration.
# Check the IP routing table on SwitchA.
[SwitchA] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Tables: Public Destinations : 9 Routes : 10 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.1 Vlanif10 10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif10 10.1.2.0/24 Static 60 0 RD 192.168.12.2 Vlanif100 Static 60 0 RD 192.168.14.2 Vlanif400 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 192.168.12.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 192.168.12.1 Vlanif100 192.168.12.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif100 192.168.14.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 192.168.14.1 Vlanif400 192.168.14.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif400
The IP routing table on SwitchA contains two equal-cost routes to network segment 10.1.2.0/24. In this situation, data traffic is evenly balanced between two different links, achieving load balancing.
Configuration Files
SwitchA configuration file
# sysname SwitchA # vlan batch 10 100 400 # interface Vlanif10 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface Vlanif100 ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0 # interface Vlanif400 ip address 192.168.14.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type access port default vlan 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 400 # ip route-static 10.1.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.12.2 ip route-static 10.1.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.2 # return
SwitchB configuration file
# sysname SwitchB # vlan batch 100 200 # interface Vlanif100 ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0 # interface Vlanif200 ip address 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 200 # ip route-static 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.12.1 ip route-static 10.1.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.23.2 # return
SwitchC configuration file
# sysname SwitchC # vlan batch 20 200 300 # interface Vlanif20 ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 # interface Vlanif200 ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0 # interface Vlanif300 ip address 192.168.34.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type access port default vlan 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 200 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 300 # ip route-static 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.23.1 ip route-static 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.34.2 # return
SwitchD configuration file
# sysname SwitchD # vlan batch 300 400 # interface Vlanif300 ip address 192.168.34.2 255.255.255.0 # interface Vlanif400 ip address 192.168.14.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 400 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 300 # ip route-static 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.1 ip route-static 10.1.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.34.1 # return
Applicable Products and Versions
Product |
Product Model |
Software Version |
|---|---|---|
S3700 |
S3700-SI/S3700-EI |
V100R006C05 |
S3700-HI |
V200R001C00 |
|
S5700 |
S5700-SI |
V200R001C00, V200R002C00, V200R003C00, V200R005C00 |
S5700-EI |
V200R001(C00&C01), V200R002C00, V200R003C00, V200R005(C00&C01&C02&C03) |
|
S5710-EI |
V200R001C00, V200R002C00, V200R003C00, V200R005(C00&C02) |
|
S5720-EI |
V200R007C00, V200R008C00, V200R009C00, V200R010C00, V200R011C00, V200R011C10, V200R012C00, V200R013C00, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S5720-SI, S5720S-SI |
V200R008C00, V200R009C00, V200R010C00, V200R011C00, V200R011C10, V200R012C00, V200R013C00, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S5720I-SI |
V200R012C00, V200R013C00, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S5730-SI |
V200R011C10, V200R012C00, V200R013C00, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S5730S-EI |
V200R011C10, V200R012C00, V200R013C00, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S5700-HI |
V200R001(C00&C01), V200R002C00, V200R003C00, V200R005(C00SPC500&C01&C02) |
|
S5710-HI |
V200R003C00, V200R005(C00&C02&C03) |
|
S5720-HI |
V200R006C00, V200R007(C00&C10), V200R008C00, V200R009C00, V200R010C00, V200R011C00, V200R011C10, V200R012C00, V200R013C00, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S5730-HI |
V200R012C00, V200R013C00, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S5731-H |
V200R013C02, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S5731-S, S5731S-S |
V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S5731S-H |
V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S5732-H |
V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S5735-S, S5735S-S |
V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S5700 |
S5735-S-I |
V200R019C10 |
S6700 |
S6700-EI |
V200R001(C00&C01), V200R002C00, V200R003C00, V200R005(C00&C01&C02) |
S6720-EI |
V200R008C00, V200R009C00, V200R010C00, V200R011C00, V200R011C10, V200R012C00, V200R013C00, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S6720S-EI |
V200R009C00, V200R010C00, V200R011C00, V200R011C10, V200R012C00, V200R013C00, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S6720-SI, S6720S-SI |
V200R011C00, V200R011C10, V200R012C00, V200R013C00, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S6720-HI |
V200R012C00, V200R013C00, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S6730-H |
V200R013C02, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S6730S-H |
V200R019C10 |
|
S6730-S, S6730S-S |
V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S7700 |
S7703, S7706, S7712 |
V200R001(C00&C01), V200R002C00, V200R003C00, V200R005C00, V200R006C00, V200R007C00, V200R008C00, V200R009C00, V200R010C00, V200R011C10, V200R012C00, V200R013C00, V200R013C02, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
S7703 PoE |
V200R013C00, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S7706 PoE |
V200R013C00, V200R019C00, V200R019C10 |
|
S9700 |
S9703, S9706, S9712 |
V200R001(C00&C01), V200R002C00, V200R003C00, V200R005C00, V200R006C00, V200R007(C00&C10), V200R008C00, V200R009C00, V200R010C00, V200R011C10, V200R012C00, V200R013C00 |

For details about software mappings, visit Hardware Query Tool and search for the desired product model.