LBDT
Context
When a loop occurs on a network, broadcast, multicast, and unknown unicast packets are repeatedly transmitted on the network. This wastes network resources or even causes service interruption on the entire network. To allow the device to detect loops on a Layer 2 network in a timely manner and prevent the network from being severely affected by loops, configure loopback detection. Loopback detection enables the device to periodically send loopback detection packets to detect loops. When a loop is detected on an interface, the device shuts down or blocks the interface to eliminate the loop. The interface can be restored when the device detects that the loop on the interface is eliminated.
Procedure
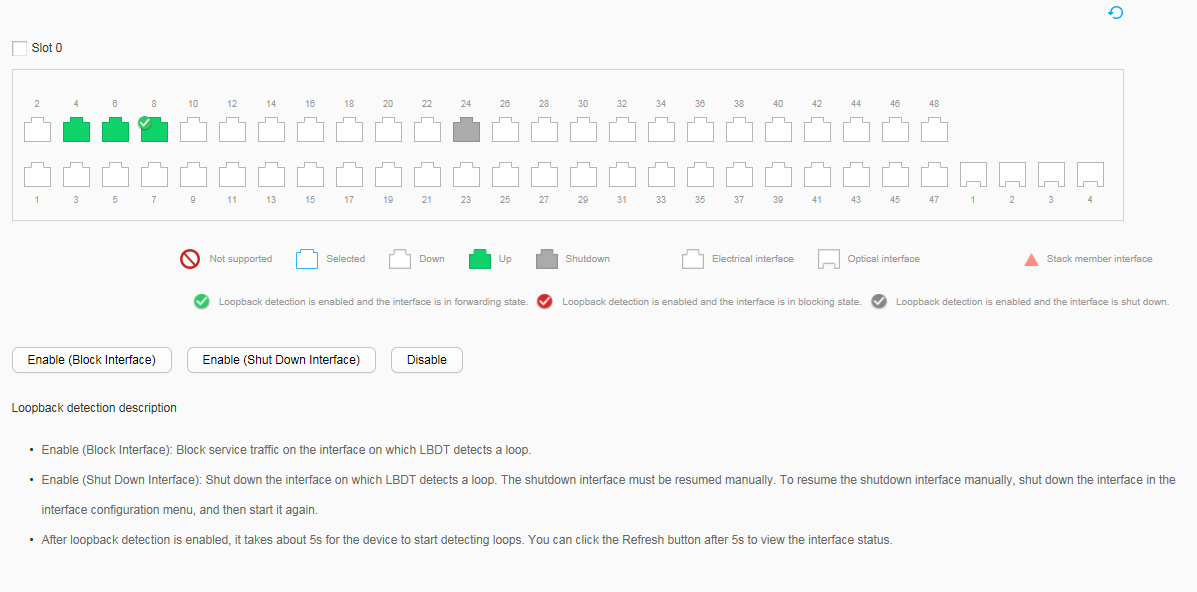
- Choose to access the LBDT page, as shown in Figure 1.
Table 1 describes parameters on the loopback detection configuration page.
Table 1 Parameters on the loopback detection configuration page Parameter
Description
Enable (Block Interface)
Enable loopback detection on an interface and set the action to block.
When a loop is detected, the device blocks the interface and forwards only BPDUs.
Enable (Shut Down Interface)
Enable loopback detection on an interface and set the action to shutdown.
When a loop is detected, the device shuts down the interface.
Disable
Disable loopback detection on the interface.
- Select an interface that you want to configure.
Perform either of the following operations:
- Click the interface icon to select one or more interfaces.
- Drag the mouse to select consecutive interfaces in a batch.
- Select a device panel and all interfaces.
- Click Enable (Block Interface) or Enable (Shut Down Interface) to enable loopback detection on an interface and set the action taken when a loop is detected.
By default, loopback detection is disabled on an interface.

If Enable (Shut Down Interface) is selected, the interface is shut down when a loop is detected. The shutdown interface can be restarted in . For details, see Enable/Disable Interface.
- Check the configuration.
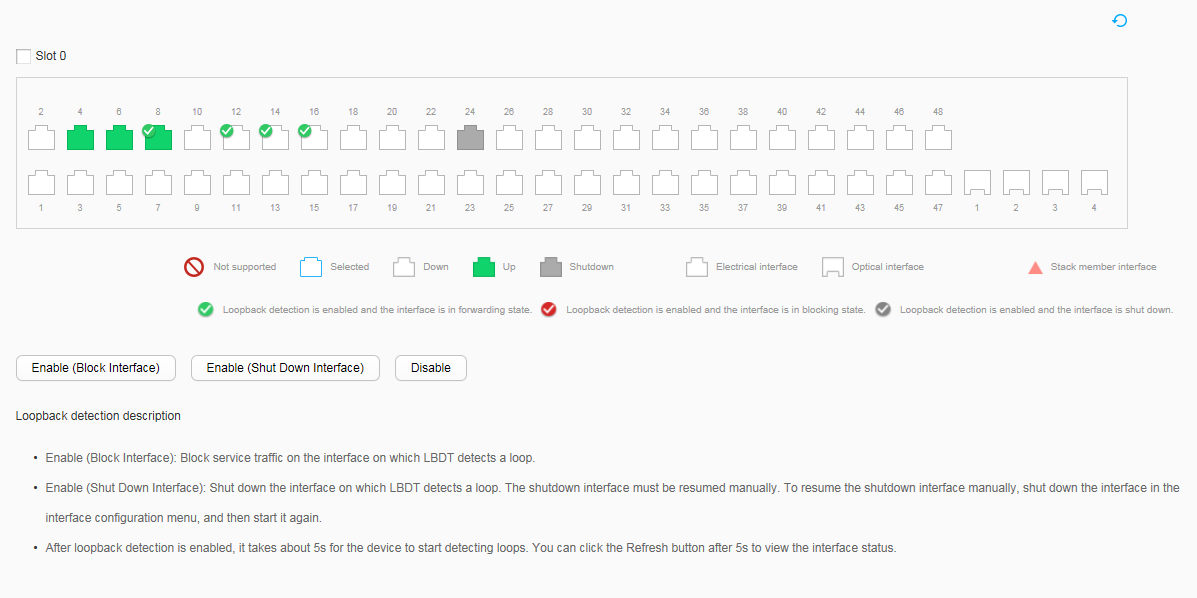
The loopback detection status is displayed on all interfaces that need to be enabled with loopback detection, as shown in Figure 2, the configuration is successful. Otherwise, the configuration fails.

After line loopback detection is enabled, the system detects loops after about 5s. After 5s, click
 to view the interface status.
to view the interface status.