Descriptions of Traps in the Trap Buffer
The output format of a trap on a CLI terminal
is as follows:
Aug 7 2015 12:44:01 HUAWEI %%01LDP/1/Session-Down-MIB(t):CID=0x801c043c-OID=1.3.6.1.2.1.10.166.4.0.4;
The LDP session status is Down. (PeerLsrId=19.19.19.19:0, VrfName=_public_, SessionType=Local, IfName=GigabitEthernet0/1/1, SubReason=0,
Reason=The LDP Keepalive timer expired.)
Figure 1 shows the output
format of a trap.
Figure 1 Output format of traps
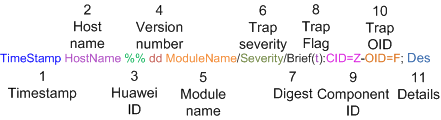
Table 1 Output format description of traps
Field
|
Meaning
|
Description
|
TimeStamp
|
Timestamp, that is, time to output log information
|
Five timestamp formats are available: - boot: indicates that the timestamp is expressed in the format
of relative time, a period of time since the start of the system.
The format is xxxxxx.yyyyyy. xxxxxx is the higher order 32 bits of
the milliseconds elapsed since the start of the system; yyyyyy is
the lower order 32 bits of the milliseconds elapsed since the start
of the system.
- data: indicates that the timestamp employs the current data and
time of the system and is expressed in the format of "mm dd yyyy hh:mm:ss".
- short-date: indicates that the timestamp employs the short date.
The timestamp of this type is almost the same as that of the data
type, with the only difference lying in that the short-date type cancels
the display of the year.
- format-date: indicates that the timestamp is expressed in YYYY-MM-DD
hh:mm:ss format.
- none: indicates that no timestamp is contained in log information.
A timestamp and a host name are separated by a space.
The format of the trap timestamp is configurable.
|
HostName
|
Host name or virtual system name
|
The default name is HUAWEI.
|
%%
|
Huawei identifier
|
Indicates that the trap is output by a Huawei device.
|
dd
|
Version number
|
Indicates the version of the trap format.
|
ModuleName
|
Module name
|
Indicates the name of the module by which traps are output.
|
Severity
|
Trap level
|
Indicates the severity of a trap.
Trap levels are
classified into eight levels. The lower the value of the trap level,
the higher the severity is. 0: emergency
A fatal fault, such as a abnormal program
or a memory error, occurs on the device. The system must restart.
1: alert
A major fault occurs, such as the device memory
threshold reaches the upper limit. The fault needs to be rectified
immediately.
2: critical
A critical fault occurs, such as the device
memory threshold reaches the lower limit, the temperature reaches
the lower limit, the BFD device is unreachable, or an internal fault generated by the device itself. The fault needs
to be analyzed and rectified.
3: error
A fault caused by an incorrect operation or
wrong process occurs, such as an incorrect user password or a wrong
protocol packet is received from another device. The fault needs to
be addressed.
4: warning
An abnormal situation occurs, such as the
user disables the routing process, BFD detects
the packet loss, or a wrong protocol packet is received. The
fault needs to be addressed.
5: notice
Indicates the key operations that are used
to keep the device functioning properly, such as the shutdown command,
neighbor discovery, or the state machine.
6: informational
Indicates the common operations that
are used to keep the device functioning properly, such as the display
command.
7: debugging
Indicates that a routine operation is performed,
and no action is required.
|
Brief
|
Description
|
Indicates the information type.
|
(t)
|
Information type
|
Indicates the trap information.
|
CID=Z
|
System component ID
|
Indicates the system component ID.
|
OID=F
|
Trap OID
|
Indicates the trap OID, which is an object identifier defined
in a MIB file.
|
Des
|
Information about details
|
Indicates the detail information about the system component
output. Each time before the trap is output, the module fills up its
contents.
|
