Bit-Error-Triggered Static CR-LSP/PW/E-PW APS
Background
In PW/E-PW over static CR-LSP scenarios, if primary and secondary PWs are configured, deploy bit-error-triggered protection switching. If bit errors occur, service traffic is switched from the primary PW to the secondary PW.
Implementation Principles
The MAC-layer SD alarm function (Trigger-LSP type) must be enabled on interfaces, and then MPLS-TP OAM must be deployed to monitor CR-LSPs/PWs. Static PWs/E-PWs are classified as SS-PWs or MS-PWs.
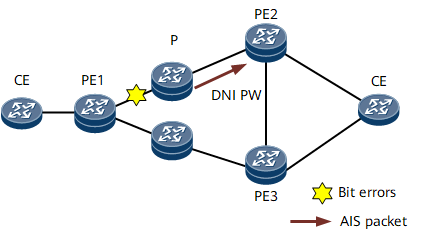
In an SS-PW networking scenario (see Figure 1), the bit error generation and clearing process is as follows:
Bit error generation:
- If the BER on an inbound interface of the P node reaches a specified threshold, the CRC module detects the bit error status of the inbound interface, notifies all static CR-LSP modules, and constructs and sends AIS packets to PE2.
- Upon receipt of the AIS packets, PE2 notifies static PWs established over the CR-LSPs of the bit errors and instructs the TP OAM module to perform APS. APS triggers a primary/backup CR-LSP switchover, and a PW established over the new primary CR-LSP takes over traffic.
Bit error clearing: After bit errors are cleared, the CRC module cannot detect the bit error status on the inbound interface. The CRC module informs the TP OAM module that the bit errors have been cleared. Upon receipt of the notification, the TP OAM module stops sending AIS packets to PE2 functioning as the egress. PE2 does not receive AIS packets after a specified period and determines that the bit errors have been cleared. PE2 then generates an AIS clear alarm and instructs the TP OAM to perform APS. APS triggers a primary/backup CR-LSP switchover, and services are switched back to the PW over the primary CR-LSP.
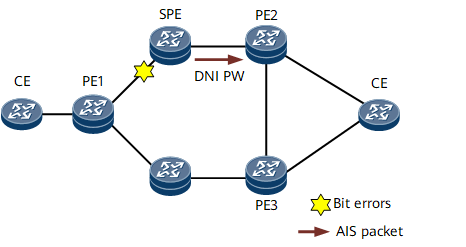
In an MS-PW networking scenario (see Figure 2), the bit error generation and clearing process is as follows:
Bit error generation:
- The CRC module of an inbound interface on the SPE detects bit errors and determines to send either an SF or SD alarm based on a specified BER threshold. The CRC module then notifies the TP OAM module of the bit errors. The TP OAM module notifies the bit error status, sends RDI packets, and performs APS. The APS module instructs the peer node to perform a traffic switchover, which triggers a primary/backup CR-LSP switchover. The PW established over the bit-error-free CR-LSP takes over traffic.
- If the BER on an inbound interface of the SPE reaches a specified threshold, the CRC module detects the bit error status of the inbound interface, sets all static CR-LSP modules to the bit error status, and constructs and sends AIS packets to PE2.
- Upon receipt of the AIS packets, PE2 notifies the TP OAM module. The TP OAM module then performs APS, which triggers a primary/backup CR-LSP switchover. The PW established over the bit-error-free CR-LSP takes over traffic.
Bit error clearing: After bit errors are cleared, the CRC module cannot detect the bit error status on the inbound interface. The CRC module informs the TP OAM module that the bit errors have been cleared. Upon receipt of the notification, the TP OAM module stops sending AIS packets to PE2 functioning as the egress. PE2 does not receive AIS packets after a specified period and determines that the bit errors have been cleared. PE2 then generates an AIS clear alarm and instructs the TP OAM to perform APS. APS triggers a primary/backup CR-LSP switchover, and services are switched back to the PW over the primary CR-LSP.

If a tunnel protection group has been deployed for static CR-LSPs carrying PWs/E-PWs, bit errors preferentially trigger static CR-LSP protection switching. Bit-error-triggered PW protection switching is performed only when bit-error-triggered static CR-LSP protection switching fails to protect services against bit errors (for example, bit errors occur on both the primary and backup CR-LSPs).
Usage Scenario
If static CR-LSPs/PWs/E-PWs are used to carry user services and MPLS-TP OAM is deployed to ensure reliability, deploy bit-error-triggered APS to minimize the impact of bit errors on user services and improve service quality.