Configuring EDSG
Before configuring EDSG, familiarize yourself with the usage scenario, complete the pre-configuration tasks, and obtain the data required for the configuration.
Usage Scenarios
In some regions, small local carriers need to rent backbone carriers' lines to provide Internet access services to users. The local carriers also need to pay the backbone carriers for traffic over the backbone networks. Low fees are charged for traffic over a local network, whereas high fees are charged for traffic over a backbone network. To increase revenues, local carriers need a solution that can distinguish the two types of traffic and perform accounting based on network types. EDSG meets this requirement. Two EDSG services can be configured for the local and backbone networks based on destination addresses to implement differentiated accounting on traffic over both the local and backbone networks.
When campus users access a campus network, the carrier does not charge any fees or charges low fees, and the access rate is unlimited. However, when campus users access an external network, the carrier charges high fees and limits their access rates. To increase the carrier's revenues, configure two EDSG services for the campus and external networks based on destination addresses to implement differentiated accounting and rate limit on traffic over both the campus and external networks.
Many Internet services, such as gaming, File Transfer Protocol (FTP), video on demand (VOD), and news services, have different costs and bandwidth requirements. To implement differentiated accounting and rate limit on various services, configure these services as different EDSG services.
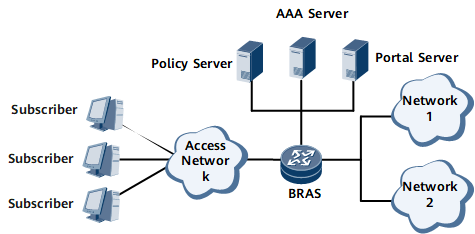
As shown in Figure 1, Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) users access networks 1 and 2. Different fees need to be charged for traffic over networks 1 and 2. The users have different bandwidth requirements for networks 1 and 2. To meet these requirements, configure two EDSG services on the broadband remote access server (BRAS) to perform differentiated accounting and rate limit on traffic over networks 1 and 2. EDSG allows carriers to provide flexible service and accounting policies for different user requirements.

AAA server: provides user authentication, authorization, and accounting. Generally, a RADIUS server is used as a AAA server.
Policy server: delivers EDSG service policies. Only a RADIUS server can be used as a policy server.
Portal server: provides user interfaces. Users can log in to a portal server and select EDSG services as required. A portal server is generally integrated into a AAA or policy server.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring EDSG, complete the following tasks:
Load the BRAS license and the EDSG license.
Configure an authentication scheme, an accounting scheme, and a RADIUS server group for an EDSG service policy (for details, see AAA and User Management Configuration (Access Users)).
Configure an address pool (for details, see Configuring an IPv4 Address Pool and an Address Pool Group).
Configure a domain and bind the authentication scheme, accounting scheme, address pool, and RADIUS server group to the domain (for details, see Configuring a Domain).
Configure a BAS interface (for details, see IPoE Access Configuration and PPPoE Access Configuration).
- Enabling the Value-added Service Function
- A value-added service can be configured only after the value-added service function is enabled.
- Configuring a Policy Server
- EDSG requires a dedicated policy server to deliver an EDSG service policy. This section describes how to configure a policy server.
- Configuring an EDSG Traffic Policy
- To distinguish user traffic over networks 1 and 2, create two service groups and configure an EDSG traffic policy for each service group. This section describes how to configure an EDSG traffic policy.
- Configuring an EDSG Service Policy
- You can configure different EDSG service policies to implement differentiated accounting and rate limiting for user access to different networks.
- (Optional) Applying an EDSG Service Policy to a Domain
- If no EDSG service policy is delivered from the policy server, use the service policy group configured in the AAA domain.
- (Optional) Configuring a Mapping Between a Time Range Template and Service Bandwidth
- This section describes how to configure a mapping between a time range template and EDSG service bandwidth. After the configuration is complete, the EDSG service bandwidth is adjusted when the time range changes.
- (Optional) Configuring the Prepaid Function
- The prepaid function allows the RADIUS server to deliver an EDSG service with a specified time or traffic volume quota in advance. After the quota is exhausted, the BRAS reapplies for an EDSG service quota from the RADIUS server. When the RADIUS server returns a zero quota, the BRAS executes a deactivation or redirection policy. This section describes how to configure the prepaid function.
- (Optional) Configuring a Mode in Which an EDSG Service Policy Is Obtained
- An EDSG service policy can be downloaded from local configurations or a RADIUS server.
- (Optional) Configuring a Rate Limit Mode for EDSG Services
- You can configure different rate limit modes for upstream and downstream EDSG service traffic of users who go online from a AAA domain.
- (Optional) Enabling EDSG Services to Support HQoS Scheduling for Home Users
- This section describes how to enable EDSG services to support HQoS scheduling for home users in a AAA domain.
- (Optional) Configuring EDSG Service Traffic to Match a User Group
- This section describes how to configure EDSG service traffic to match a user group in load-balancing scenarios.
- (Optional) Configuring Accounting Copy for EDSG Services
- This section describes how to enable the copy function for EDSG service accounting packets in a user access domain.
- (Optional) Configuring Accounting Packet Merging for Value-added Services
- This section describes how to configure accounting packet merging for value-added services to reduce the number of packets sent to a RADIUS accounting server.
- (Optional) Enabling the Captive Portal Function Based on EDSG Services
- After an HTTP redirection profile is bound to a service policy, the captive portal function based on EDSG services is enabled. When users visit HTTP web pages matching service traffic, the service traffic is redirected to a specified page.
- (Optional) Configuring the Device to Use the Inner IPv4 Address of Each IPv4-in-IPv6 Packet to Match IPv4 UCLs of EDSG Services
- You can configure this function to allow IPv4-in-IPv6 packets to use inner IPv4 addresses to match IPv4 UCLs of EDSG services.
- (Optional) Configuring RADIUS Attributes
- To enable attributes delivered by a RADIUS server through CoA packets or RADIUS to take effect, you must configure these attributes on the NetEngine 8000 F.
- Verifying the EDSG Configuration
- After configuring different rate limit modes for upstream and downstream EDSG service traffic of users who go online from a AAA domain, verify the configuration.