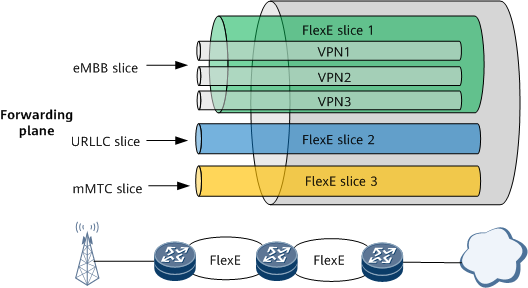
FlexE Channelization for 5G Network Slicing
5G network slicing involves the management, control, and forwarding planes. FlexE is an important technology for implementing forwarding-plane slicing. In standard Ethernet, all services share interfaces, whereas in FlexE, channelization provides physical-layer service hard isolation between different FlexE clients at the interface level and provides different service SLAs. As shown in Figure 1, enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), and Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC) services on a 5G network can be carried on the same IP network through slicing.