Overview of L2TP Access
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a VPN tunneling protocol that allows remote users (such as enterprise branches and traveling staff) to securely communicate with private network servers over public networks (such as the Internet).
L2TP tunnels PPP packets, allows Layer 2 link endpoints and PPP session endpoints to reside on different devices, and uses the packet switching technology for information exchange. Functioning as an IETF industry standard, L2TP extends the PPP model and combines the advantages of the Layer Two Forwarding Protocol (L2F) and Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP).
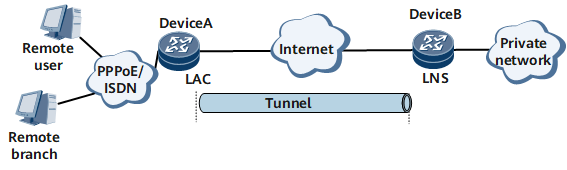
Figure 1 shows a typical L2TP network topology. This network consists of the following components:
Remote system
A remote system is a remote user or a remote branch that connects to the private network of an enterprise. It is usually a host of a dial-up user or a device on a private network.
L2TP access concentrator (LAC)
A LAC is one endpoint of an L2TP tunnel. Located between an L2TP network server (LNS) and a remote system, a LAC encapsulates packets received from the remote system into L2TP packets and sends the packets to the LNS. After receiving packets from the LNS, the LAC decapsulates and sends the packets to the remote system.
LNS
An LNS is the other endpoint of an L2TP tunnel and is the logical endpoint of the PPP sessions established over the L2TP tunnel. An LNS provides PPP and L2TP processing capabilities and is usually located at the edge of an enterprise private network. Through the L2TP tunnel on the public network, PPP connections from the remote system are extended from the original NAS (functioning as a LAC) to the LNS.
A device that functions as both an LNS and LAC is called an L2TP tunnel switch (LTS).
Common L2TP Tunneling Modes
NAS-initiated mode
In NAS-initiated mode, after a dial-up user of a remote system accesses a LAC through PPPoE or ISDN, the LAC initiates an L2TP tunnel setup request to an LNS. L2TP tunnels in NAS-initiated mode have the following features:
- The remote system needs to support only the PPP protocol and does not need to support L2TP.
- The authentication and accounting for remote dial-in users can be performed by the LAC or LNS.
Client-initiated mode
In client-initiated mode, a LAC client, which is a remote system that supports L2TP, directly initiates L2TP tunnel setup requests to an LNS. The LAC client has a public IP address and can communicate with the LNS through the Internet. L2TP tunnels in client-initiated mode have the following features:
- L2TP tunnels are directly established between the remote system and the LNS for higher security.
- L2TP tunnels in client-initiated mode require the remote system to be a LAC client that supports L2TP and can communicate with the LNS. Therefore, this mode has poor scalability.