Example for Configuring Global UCMP for IP Packet Forwarding
This section provides an example for configuring global UCMP for IP packet forwarding.
Networking Requirements
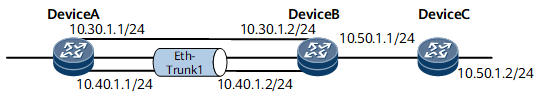
On the network shown in Figure 1, two paths connect DeviceA and DeviceC.
A physical link connects DeviceA's GE 0/1/8 and DeviceB's GE 0/1/8.
DeviceA's GE 0/1/16 and GE 0/1/24 and DeviceB's GE 0/1/16 and GE 0/1/24 are added to Eth-Trunk1.
Eth-Trunk1 contains two GE interfaces, and therefore the bandwidth of Eth-Trunk1 is the sum of the bandwidth of the two member GE links. To load balance IP traffic, configure global UCMP between the two links from DeviceA to DeviceC.

The configurations in this example are performed on DeviceA, DeviceB, and DeviceC. HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F Series can function as DeviceA, DeviceB, and DeviceC.
Device Name |
Interface Name |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|
DeviceA |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.30.1.1/24 |
Eth-Trunk1 |
10.40.1.1/24 |
|
DeviceB |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.30.1.2/24 |
Eth-Trunk1 |
10.40.1.2/24 |
|
DeviceC |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.50.1.1/24 |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.50.1.2/24 |

In this example, the bandwidth of GE 0/1/8 on DeviceA and DeviceB is 1 Gbit/s, that of GE 0/1/16 is 2 Gbit/s, and that of GE 0/1/24 is 3 Gbit/s.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure static routes on every router.
Enable global UCMP on DeviceA, allowing the two paths between DeviceA and DeviceC to perform UCMP based on bandwidth ratios.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Type and number of each interface
IP address of each interface
Eth-Trunk interface number
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each physical interface and Eth-Trunk interface. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure static routes.
# Configure DeviceA.
[~routerA] ip route-static 10.20.1.0 255.255.255.0 gigabitethernet0/1/8 10.30.1.2 [*routerA] ip route-static 10.20.1.0 255.255.255.0 eth-trunk1 10.40.1.2 [*routerA] ip route-static 10.50.1.0 255.255.255.0 gigabitethernet0/1/8 10.30.1.2 [*routerA] ip route-static 10.50.1.0 255.255.255.0 eth-trunk1 10.40.1.2 [*routerA] commit
# Configure DeviceB.
[~routerB] ip route-static 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 gigabitethernet0/1/8 10.30.1.1 [*routerB] ip route-static 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 eth-trunk1 10.40.1.1 [*routerB] ip route-static 10.20.1.0 255.255.255.0 gigabitethernet0/1/10 10.50.1.2 [*routerB] commit
# Configure DeviceC.
[~routerC] ip route-static 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 gigabitethernet0/1/8 10.50.1.1 [*routerC] ip route-static 10.30.1.0 255.255.255.0 gigabitethernet0/1/8 10.50.1.1 [*routerC] ip route-static 10.40.1.0 255.255.255.0 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.50.1.1 [*routerC] commit
- Enable global UCMP on DeviceA.
[~routerA] load-balance unequal-cost enable [*routerA] commit
- Verify the configuration.
# Ping DeviceA at 10.1.1.1 from DeviceC. The ping operation is successful. Run the display interface brief command to view the bandwidth usage of outbound interfaces. The command output shows that Eth-Trunk1's bandwidth usage is similar to GE 0/1/8's bandwidth usage, meaning that UCMP has been enabled and traffic is load-balanced among outbound interfaces based on the bandwidth ratio.
[~routerC] ping -c 100 -t 10 -m 10 10.1.1.1 PING 10.1.1.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=254 time=3 ms Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=254 time=1 ms Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=254 time=1 ms ... --- 10.1.1.1 ping statistics --- 100 packet(s) transmitted 99 packet(s) received 1.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/6 ms [~routerB] display interface brief PHY: Physical *down: administratively down ^down: standby (l): loopback (s): spoofing (b): BFD down (e): EFM down (d): Dampening Suppressed InUti/OutUti: input utility/output utility Interface PHY Protocol InUti OutUti inErrors outErrors Eth-Trunk1 up up 20% 30% 35 210 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 up up 15% 20% 22 120 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 up up 20% 30% 23 125 GigabitEthernet0/1/9 *down down 0% 0% 0 0 GigabitEthernet0/1/11 *down down 0% 0% 0 0 GigabitEthernet0/1/12 *down down 0% 0% 0 0 GigabitEthernet0/1/13 *down down 0% 0% 0 0 GigabitEthernet0/1/14 *down down 0% 0% 0 0 GigabitEthernet0/1/15 *down down 0% 0% 0 0 Ip-Trunk1 down down 0% 0% 0 0 LoopBack0 down up(s) 0% 0% 0 0 NULL0 up up 0% 0% 0 0
Configuration Files
DeviceA configuration file
# sysname routerA # load-balance unequal-cost enable # interface Eth-Trunk1 ip address 10.40.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.30.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown eth-trunk 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/24 undo shutdown eth-trunk 1 # ip route-static 10.20.1.0 255.255.255.0 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.30.1.2 ip route-static 10.20.1.0 255.255.255.0 Eth-Trunk1 10.40.1.2 ip route-static 10.50.1.0 255.255.255.0 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.30.1.2 ip route-static 10.50.1.0 255.255.255.0 Eth-Trunk1 10.40.1.2 #
DeviceB configuration file
# sysname routerB # interface Eth-Trunk1 ip address 10.40.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.30.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/10 undo shutdown ip address 10.50.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown eth-trunk 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/24 undo shutdown eth-trunk 1 # ip route-static 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.30.1.1 ip route-static 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 Eth-Trunk1 10.40.1.1 ip route-static 10.20.1.0 255.255.255.0 GigabitEthernet0/1/10 10.50.1.2 # return
DeviceC configuration file
# sysname routerC # ip route-static 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 GigabitEthernet0/1/10 10.50.1.1 ip route-static 10.30.1.0 255.255.255.0 GigabitEthernet0/1/10 10.50.1.1 ip route-static 10.40.1.0 255.255.255.0 GigabitEthernet0/1/10 10.50.1.1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.20.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/10 undo shutdown ip address 10.50.1.2 255.255.255.0 # return