IPv4 Multicast Forwarding Control
This section describes how to control IPv4 multicast service forwarded to a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) set top box (STB).
Dual-device hot backup must be configured before multicast hot backup is configured.
Dual-Device Hot Backup for Multicast Traffic Sent to a DHCP STB
Procedure for getting online and ordering multicast programs
If a user device is connected to a DHCP STB, the user device sends DHCP packets to attempt to get online. The procedure for getting online from a broadband remote access server (BRAS) enabled with dual-device hot backup is as follows:
- A user device sends DHCP packets to request for an IP address.
- After receiving DHCP packets, the master BRAS attempts to authenticate user information. If authentication is successful, the master BRAS allocates an IP address to the user. The slave BRAS does not provide access services for the user.
- The user gets online successfully.
- The master BRAS sends user information to the slave BRAS along a backup channel. The slave BRAS uses the information to locally generate control and forwarding information for the user.
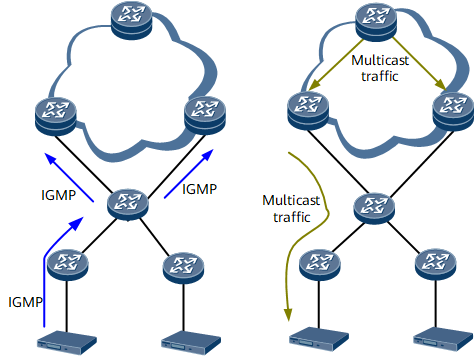
On the network shown in Figure 1, the procedure for ordering multicast programs is as follows:
- A DHCP STB sends an Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Report message to an aggregation switch, and the switch forwards the message to both the master and slave BRASs.
- Both the master and slave BRASs receive the IGMP Report message, and pull multicast traffic from multicast sources.
- The master BRAS replicates multicast traffic to the STB, but the slave BRAS does not.
Dual-Device Hot Backup for Multicast Traffic Sent to a PPPoE STB
When users attached to a PPPoE STB order multicast programs, the multicast replication point can only be a single BRAS. PPPoE data flows are transmitted between the STB and the BRAS in end-to-end mode. An STB MAC address and a BRAS MAC address identify a PPPoE connection, and a session ID identifies a PPPoE session.
After a PPPoE STB sends an IGMP Report message, the master BRAS, not the slave BRAS, can receive this message. To protect multicast services on the master BRAS, hot backup is implemented to allow the slave BRAS to synchronize IGMP messages with the master BRAS.
After dual-device hot backup is implemented, the procedure for forwarding multicast traffic from the master BRAS to the PPPoE STB is as follows:
- The STB establishes a Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) connection to the master BRAS. The BRAS backs up the STB information to the slave BRAS. After receiving the information, the slave BRAS locally generates control and forwarding information for the PPP user.
- The STB sends an IGMP Report message. After receiving the message, the master BRAS backs the message up to the slave BRAS, sends a Join message to the RP to pull multicast traffic, and establishes a rendezvous point tree (RPT).
- After receiving the IGMP Report message from the backup channel, the slave BRAS sends a Join message to the RP to pull multicast traffic and establishes an RPT.
- The master BRAS replicates multicast traffic to the STB, but the slave BRAS does not.
Master/Slave Switchover in the Case of a Fault in Multicast Dual-Device Hot Backup
If an access- or network-side fault occurs on the NetEngine 8000 F or the NetEngine 8000 F fails, a master/backup VRRP switchover is performed. After the backup NetEngine 8000 F switches to the Master state, it forwards traffic. The original master NetEngine 8000 F switches to the Backup state and prunes traffic.