IPv6 Unicast Forwarding Control
This section describes the different roles of NetEngine 8000 Fs as broadband remote access servers (BRASs), Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 6 (DHCPv6) servers, and DHCPv6 relay agents respectively in Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) unicast forwarding control.
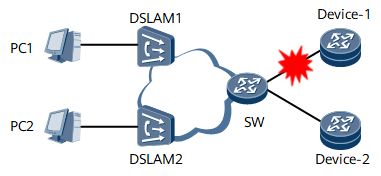
On the network shown in Figure 1, Device-1 and Device-2 function as BRASs and run redundancy user information (RUI). A Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) backup group is configured for the two Devices, with Device-1 as the master and Device-2 as the backup. When the link between the switch (SW) and Device-1 goes faulty, the fault triggers a master/backup VRRP switchover. Then, Device-2 becomes the master and starts neighbor discovery (ND) detection, and Device-1 becomes the backup and stops the ND detection. If the link-local address or MAC address on an interface of Device-2 is different from that of an interface on Device-1, some users will go offline, or some user packets will be discarded.
To prevent a user from detecting the active link fault, Device-2 must use the same link-local address and MAC address as those of Device-1.
Link-local address generation
When an Device sends ND packets, its source IP address must be filled with a link-local address.
After RUI is enabled on the Devices, the master and backup BRASs generate the same link-local address using the virtual MAC address of the VRRP backup group. The link-local address is generated automatically, which is convenient for users.
Protection tunnel forwarding
An address pool backup allows the master and backup BRASs to have the same MAC address. Address pool backup in IPv6 unicast forwarding control is similar to that in IPv4 unicast forwarding control. For details, see chapter IPv4 Unicast Service Forwarding Control
IPv6 unicast forwarding allows the Devices to control traffic through multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) label switched paths (LSPs) and supports simplified protection tunnel configuration, requiring only MPLS LSPs for virtual private networks (VPNs). Each VPN swaps its forwarding labels using a Huawei-proprietary protocol, avoiding the need to configure the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) on the Devices.