Configuring Destination-Based QPPB
Destination-based QPPB differentiates routes to different destinations and associates differentiated QoS policies with them.
Usage Scenario
QPPB is applicable to both IBGP and EBGP and can be configured for one or more ASs.
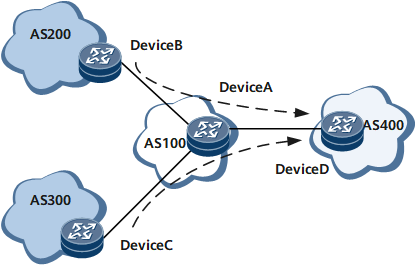
As shown in Figure 1, traffic is transmitted from provider B (AS 200) and provider C (AS 300) to provider D (AS 400) through provider A (AS 100). Providers B and C function as BGP route senders and provider A functions as a BGP route receiver. Based on the traffic control policies that are signed between providers A and D, provider A needs to limit the rate of the traffic sent to provider D.
Providers B and C advertise BGP routes carrying the community attribute to provider A. After receiving the BGP routes, provider A matches the routes with the community list, ACL list, or AS_Path list, and associates QoS policy IDs with QoS behaviors for the routes. Destination-based QPPB is enabled on the provider A interface that allows traffic to pass through. Therefore, QPPB local policies are applied to all traffic that passes through provider A.
Destination-based QPPB is applicable to both incoming and outgoing traffic on a device.
- Configuring Routing Policies on a BGP Route Sender
- This section describes how to configure routing policies on a BGP route sender.
- Configuring Routing Policies on a BGP Route Receiver
- This section describes how to configure routing policies on a BGP route receiver.
- Configuring Traffic Behaviors on a Route Receiver
- You can configure different traffic behaviors for different traffic classifiers on a BGP receiver to implement differentiated services.
- Configuring QPPB Local Policies on a BGP Route Receiver
- QPPB allows QoS policies to be configured for routes that match the BGP community list, ACL, or BGP AS_Path list. After the QPPB local policy is applied to the inbound and outbound interfaces of traffic, relevant QoS policies are implemented on the traffic.
- Applying a QPPB Local Policy to an Interface
- After a QPPB local policy is applied to an interface, the associated traffic behavior is performed for the packets that meet the matching rule.
- Checking the Configuration
- After QPPB is configured, you can view QPPB information.