DiffServ Model
The DiffServ model is the most commonly used QoS model on IP networks. Technologies described in this document are based on the DiffServ model.
DiffServ Model
DiffServ classifies incoming packets on the network edge and manages packets of the same class as a whole to ensure the same transmission rate, delay, and jitter.
Network edge nodes mark packets with a specific service class in packet headers, and then apply traffic management policies to the packets based on the service class. Interior nodes perform specific behaviors for packets based on packet information.
Figure 1 DiffServ model
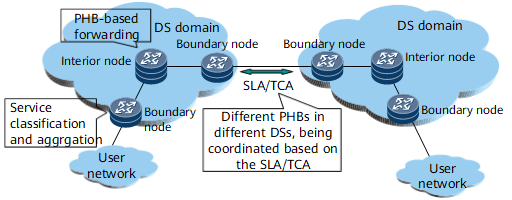

- DiffServ (DS) node: a network node that implements the DiffServ function.
- DS boundary node: connects to another DS domain or a non-DS-aware domain. The DS boundary node classifies and manages incoming traffic.
- DS interior node: connects to DS boundary nodes and other interior nodes in one DS domain. DS interior nodes implement simple traffic classification based on DSCP values, and manage traffic.
- DS domain: a contiguous set of DS nodes that adopt the same service policy and per-hop behavior (PHB). One DS domain covers one or more networks under the same administration. For example, a DS domain can be an ISP's networks or an organization's intranet. For an introduction to PHB, see the next section.
- DS region: consists of one or more adjacent DS domains. Different DS domains in one DS region may use different PHBs to provide differentiated services. The service level agreement (SLA) and traffic conditioning agreement (TCA) are used to allow for differences between PHBs in different DS domains. The SLA or TCA specifies how to maintain consistent processing of the data flow from one DS domain to another.
- SLA: The SLA refers to the services that the ISP promises to provide for individual users, enterprise users, or adjacent ISPs that need intercommunication. The SLA covers multiple dimensions, including the accounting protocol. The service level specification (SLS) provides technique description for the SLA. The SLS focuses on the traffic control specification (TCS) and provides detailed performance parameters, such as the committed information rate (CIR), peak information rate (PIR), committed burst size (CBS), and peak burst size (PBS).