DSCP and PHB
Per-hop behavior (PHB) is an important concept in the DiffServ model. The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) redefined the type of service (ToS) for IPv4 packets and Traffic Class (TC) for IPv6 packets as the Differentiated Service (DS) field for the DiffServ model. The value of the DS field is the DiffServ code point (DSCP) value. Different DSCP values correspond to different PHBs, as described in this section.
DSCP
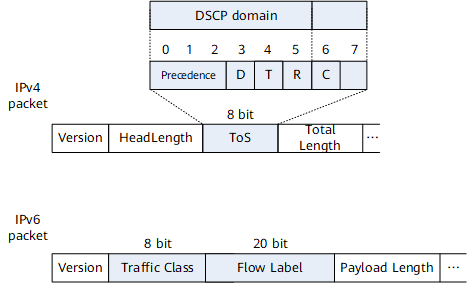
In an IPv4 packet, the six left-most bits (0 to 5) in the DS field are defined as the DSCP value. Bits 0 to 2 are the Class Selector Code Point (CSCP) value, indicating a class of DSCP. Devices that support the DiffServ function perform forwarding behaviors for packets based on the DSCP value.
In IPv6 packet headers, two fields are related to QoS: TC and Flow Label (FL). The TC field contains eight bits and functions the same as the ToS field in IPv4 packets to identify the service type. The FL field contains 20 bits and identifies packets in the same data flow. The FL field, together with the source and destination addresses, uniquely identifies a data flow. All packets in one data flow share the same FL field, and devices can rapidly process packets in the same data flow.
PHB
Per-hop Behavior (PHB) is a description of the externally observable forwarding treatment applied at a differentiated services-compliant node to a behavior aggregate. A DS node performs the same PHB for packets with the same DSCP value. The PHB defines some forwarding behaviors but does not specify the implementation mode.
At present, the IETF defines four types of PHBs: Class Selector (CS), Expedited Forwarding (EF), Assured Forwarding (AF), and best-effort (BE). BE PHB is the default.
PHB |
DSCP Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
CS |
XXX000, where X is 0 or 1. When Xs are all 0s, this PHB is the default PHB. For the CS PHB, the DSCP value is equal to the IP precedence value multiplied by 8. For example, CS6 = 6 x 8 and CS7 = 7 x 8. |
The CS PHB indicates the same service class as the IP precedence value. |
EF |
101110 |
The EF PHB defines that the rate at which packets are sent from any DS node must be higher than or equal to the specified rate. The EF PHB cannot be re-marked in the DS domain but can be re-marked on the edge nodes. The EF PHB functions the same as a virtual leased line to provide services with a low packet loss rate, delay, and jitter and a specific bandwidth. The EF PHB applies to real-time services that require a short delay, low jitter, and low packet loss rate, such as video, voice, and video conferencing. |
AF |
XXXYY0, where X is 0 or 1. XXX indicates the IP precedence. YY indicates the drop precedence. The larger the value, the higher the drop priority. Currently, four AF classes with three levels of drop precedence in each AF class are defined for general use. An IP packet that belongs to an AF class i and has drop precedence j is marked with the AF codepoint AFij, where i ranges from 1 to 4 and j ranges from 1 to 3. |
The AF PHB defines that traffic that exceeds the specified bandwidth (as agreed to by users and an ISP) can be forwarded. Traffic that does not exceed the bandwidth specification is forwarded as required, and the traffic that exceeds the bandwidth specification is forwarded at a lower priority. Carriers provide differentiated bandwidth resources for the AF PHB. After the AF PHB is allocated sufficient bandwidths, other data can consume the remaining bandwidths. The AF PHB applies to services that require a short delay, low packet loss rate, and high reliability, such as e-commerce and VPN services. |
BE |
000000 |
The BE PHB focuses only on whether packets can reach the destination, regardless of the transmission performance. Traditional IP packets can be transmitted in BE mode. Any router must support the BE PHB. |
PHB |
Applications |
|---|---|
CS6 and CS7 |
CS6 and CS7 PHBs are used for protocol packets by default, such as OSPF and BGP packets. If these packets are not forwarded, protocol services are interrupted. |
CS5 |
CS5 PHB is used for VoIP and video service signaling, such as SIP and H.323. |
CS4 |
CS4 PHB is used for video conference (including only voice and video. Data is classified as CS1), HD video, interactive game. |
CS3 |
CS3 PHB is used for broadcast television, real-time video surveillance service. |
CS2 |
CS2 PHB is used for network O&M, maintenance, and management services, such as SNMP, Syslog, and SSH. |
CS1 |
CS1 PHB is used for non-real-time elastic services, such as entertainment video traffic. |
EF |
EF PHB is used for voice services. Voice services require a short delay, low jitter, and low packet loss rate, and are second only to protocol packets in terms of importance. NOTE:
The bandwidth dedicated to EF PHB must be restricted so that other services can use the bandwidth. |
AF4 |
AF4 PHB is used for signaling of voice services. NOTE:
Signaling is used for call control, during which a seconds-long delay is tolerable, but no delay is allowed during a conversation. Therefore, the processing priority of voice services is higher than that of signaling. |
AF3 |
AF3 PHB is used for BTV services of IPTV. Live programs are real-time services, requiring continuous bandwidth and a large throughput guarantee. |
AF2 |
AF2 PHB is used for VoD services of IPTV. VoD services require lower real-time performance than BTV services and allow delays or buffering. |
AF1 |
AF1 PHB is used for leased-line services, which are second to IPTV and voice services in terms of importance. Bank-based premium services, one type of leased-line services, can use the AF4 or even EF PHB. |
BE |
BE PHB applies to best-effort services on the Internet, such as email and telnet services. |