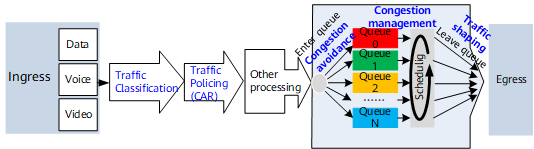
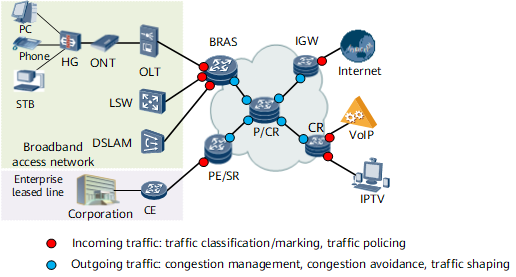
Components in the DiffServ Model
Classification and Marking: classification classifies packets while keeping the packets unchanged. Traffic marking sets different priorities for packets and therefore changes the packets.

Traffic marking refers to external re-marking, which is implemented on outgoing packets. Re-marking modifies the priority field of packets to relay QoS information to the next-hop device.
Internal marking is used for internal processing and does not modify packets. Internal marking is implemented on incoming packets for the device to process the packets based on the marks before forwarding them. The concept of internal marking is discussed later in this document.
Policing and Shaping: restricts the traffic rate to a specific value. When traffic exceeds the specified rate, traffic policing drops excess traffic, and traffic shaping buffers excess traffic.
Congestion management: places packets in queues for buffering when traffic congestion occurs and determines the forwarding order based on a specific scheduling algorithm.
Congestion avoidance: monitors network resources. When network congestion intensifies, the device proactively drops packets to regulate traffic so that the network is not overloaded.