QoS Priority Fields
DiffServ provides differentiated services for packets that carry different QoS information in specific fields. This section describes these fields.
ToS Field in an IPv4 Packet Header
In an IPv4 packet header, the three left-most bits (IP precedence) in the ToS field or the six left-most bits (DSCP field) in the ToS field are used to identify the QoS priority. The IP precedence classifies packets into a maximum of eight classes, and the DSCP field classifies packets into a maximum of 64 classes.
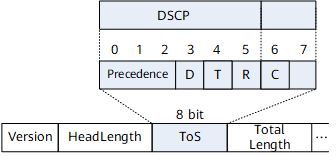
Bits in the ToS field as follows:
- Bits 0 to 2 refer to the precedence. The value ranges from 0 to 7. The larger the value, the higher the precedence. The largest values (7 and 6) are reserved for routing and updating network control communications. User-level applications can use only the precedence levels from 0 to 5.
- The D bit refers to the delay. The value 0 indicates no specific requirements for delay and the value 1 indicates that the network is required to minimize delay.
- The T bit refers to the throughput. The value 0 indicates no specific requirements for throughput and the value 1 indicates that the network is required to maximize throughput.
- The R bit refers to the reliability. The value 0 indicates no specific requirements for reliability and the value 1 indicates that the network is required to maximize reliability.
- The C bit refers to the monetary cost. The value 0 indicates no specific requirements for monetary cost and the value 1 indicates that the network is required to minimize monetary cost.
- Bit 7 is reserved.
Relevant standards define bits 0 to 5 as the DSCP field, and the three left-most bits indicate the class selector code point (CSCP) value, which identifies a class of DSCP. Devices that support DiffServ apply PHBs to packets based on the DSCP value in the packets. For details about DSCP and PHB, see DSCP and PHB.
TC Field in an IPv6 Header
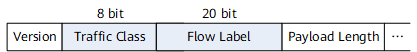
Two fields in an IPv6 header are related to QoS, Traffic Class (TC), and Flow Label (FL). The TC field has eight bits and functions the same as the ToS field in an IPv4 packet header to identify the service type. The FL field has 20 bits and is used to identify packets in the same data flow. The FL, together with the source and destination addresses, identifies a data flow. All packets in one data flow share the same FL so that a device can process the packets that have the same QoS requirement as a whole.
EXP Field in an MPLS Header
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets are classified based on the EXP field value. The EXP field in MPLS packets is similar in function to the ToS field or DSCP field in IP packets.

The EXP field is 3 bits long and indicates precedence. The value ranges from 0 to 7 with a larger value reflecting a higher precedence.
The precedence field in an IP header also has three bits. Therefore, one precedence value in an IP header exactly corresponds to one precedence value in an MPLS header. However, the DSCP field in an IP header has 6 bits, unlike the EXP length. Therefore, multiple DSCP values correspond to only one EXP value. As the IEEE standard defines, the three left-most bits in the DSCP field (the CSCP value) correspond to the EXP value, regardless of what the three right-most bits are.
802.1p Value in a VLAN Packet
VLAN packets are classified based on the 802.1p value in the packets. The PRI field (802.1p value) in a VLAN packet header identifies the QoS requirement. Figure 1-4 illustrates a VLAN packet header.

The PRI field is 3 bits long and indicates precedence. The value ranges from 0 to 7 with a larger value reflecting a higher precedence.
802.1p/IP Precedence |
Typical Applications |
|---|---|
7 |
Reserved for network control packets (such as routing protocol packets) |
6 |
|
5 |
Voice streams |
4 |
Videoconferencing |
3 |
Call signaling |
2 |
High-priority data streams |
1 |
Medium-priority data streams |
0 |
Best effort (BE) data streams |