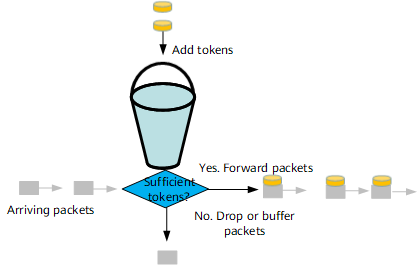
Token Bucket
What Is a Token Bucket
A token bucket is a commonly used mechanism that measures traffic passing through a device.
A token bucket can be considered a container of tokens, which has a pre-defined capacity. Tokens are put into the token bucket at a preset rate. When the token bucket is full of tokens, no more tokens can be added. Figure 1 shows a token bucket.
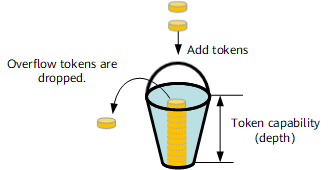

A token bucket measures traffic but does not filter packets or perform any action, such as dropping packets.
As shown in Figure 2, when a packet arrives, the device obtains enough tokens from the token bucket for packet transmission. If the token bucket does not have enough tokens to send the packet, the packet either waits for enough tokens or is discarded. This feature limits packets to be sent at a rate less than or equal to the rate at which tokens are generated.
The token bucket mechanism widely applies to QoS technologies, such as the committed access rate (CAR), traffic shaping, and Line Rate (LR).

This section only describes how to meter and mark packets using token buckets.
Two Token Bucket Markers
Relevant standards define two token bucket markers respectively: single rate three color marker (srTCM), and two rate three color marker (trTCM). Both token bucket mark the packets either green, yellow, or red. The srTCM focuses on the burst packet size, whereas the trTCM focuses on the burst traffic rate. The srTCM, which is simpler than the trTCM, is widely used for traffic metering.
Both token bucket markers operate in Color-Blind or Color-Aware mode. The widely used Color-Blind mode is the default one.
Parameters for srTCM
The following parameters are involved in srTCM:
- Committed Information Rate (CIR): the rate at which tokens are put into a token bucket. The CIR is expressed in kbit/s.
- Committed Burst Size (CBS): the committed volume of traffic that an interface allows to pass through, also the depth of a token bucket. The CBS is expressed in bytes. The CBS must be greater than or equal to the size of the largest possible packet in the stream. Note that sometimes a single packet can consume all the tokens in the token bucket. The larger the CBS is, the greater the traffic burst can be.
- Extended burst size (EBS): the maximum size of burst traffic before all traffic exceeds the CIR. The EBS is expressed in bytes.
A packet is marked green if it does not exceed the CBS, yellow if it exceeds the CBS but does not exceed the EBS, and red if it exceeds the EBS.
Mechanism for srTCM
The NetEngine 8000 F uses two token buckets for srTCM.
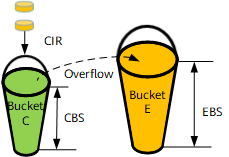
The srTCM uses two token buckets, C and E, which both share the common rate CIR. The maximum size of bucket C is the CBS, and the maximum size of bucket E is the EBS.
When the EBS is 0, no token is added in bucket E. Therefore, only bucket C is used for srTCM. When only bucket C is used, packets are marked either green or red. When the EBS is not 0, two token buckets are used and packets are marked either green, yellow or red.
Method of Adding Tokens for srTCM
In srTCM, both buckets C and E are initially full. Tokens are put into bucket C and then bucket E after bucket C is full of tokens. After both buckets C and P are filled with tokens, subsequent tokens are dropped.
Both buckets C and E are initially full.
Rules for srTCM
Tc and Te refer to the number of tokens in buckets C and P, respectively. The initial values of Tc and Te are respectively the CBS and EBS.
In Color-Blind mode, the following rules apply when a packet of size B arrives at time t:
- When one token bucket is used:
- If Tc(t) – B ≥ 0, the packet is marked green, and Tc is decremented by B.
- If Tc(t) – B < 0, the packet is marked red, and Tc remains unchanged.
- When two token buckets are used:
- If Tc(t) – B ≥ 0, the packet is marked green, and Tc is decremented by B.
- If Tc(t) – B < 0 but Te(t) - B ≥ 0, the packet is marked yellow, and Te is decremented by B.
- If Te(t) – B < 0, the packet is marked red, and neither Tc nor Te is decremented.
In Color-Aware mode, the following rules apply when a packet of size B arrives at time t:
- When one token bucket is used:
- If the packet has been pre-colored as green and Tc(t) - B ≥ 0, the packet is re-marked green, and Tc is decremented by B.
- If the packet has been pre-colored as green and Tc(t) – B < 0, the packet is re-marked red, and Tc remains unchanged.
- If the packet has been pre-colored as yellow or red, the packet is re-marked red regardless of the packet length. The Tc value remains unchanged.
- When two token buckets are used:
- If the packet has been pre-colored as green and Tc(t) - B ≥ 0, the packet is re-marked green, and Tc is decremented by B.
- If the packet has been pre-colored as green and Tc(t) – B < 0 but Te(t) - B ≥ 0, the packet is marked yellow, and Te is decremented by B.
- If the packet has been pre-colored as yellow and Te(t) – B ≥ 0, the packet is re-marked yellow, and Te is decremented by B.
- If the packet has been pre-colored as yellow and Te(t) – B < 0, the packet is re-marked red, and Te remains unchanged.
- If the packet has been pre-colored as red, the packet is re-marked red regardless of the packet length. The Tc and Te values remain unchanged.
Parameters for trTCM
trTCM covers the following parameters:
- CIR: the rate at which tokens are put into a token bucket. The CIR is expressed in bit/s.
- CBS: the committed volume of traffic that an interface allows to pass through, also the depth of a token bucket. The CBS is expressed in bytes. The CBS must be greater than or equal to the size of the largest possible packet entering a device.
- PIR: the maximum rate at which an interface allows packets to pass and is expressed in bit/s. The PIR must be greater than or equal to the CIR.
- PBS: the maximum volume of traffic that an interface allows to pass through in a traffic burst.
Mechanism for trTCM
The trTCM uses two token buckets and focuses on the burst traffic rate. The trTCM uses two token buckets, C and P, with rates CIR and PIR, respectively. The maximum size of bucket C is the CBS, and the maximum size of bucket P is the PBS.
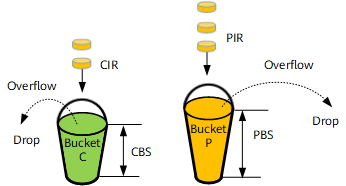
Method of Adding Tokens for trTCM
Tokens are put into buckets C and P at the rate of CIR and PIR, respectively. When one bucket is full of tokens, any subsequent tokens for the bucket are dropped, but tokens continue being put into the other bucket if it is not full.
Buckets C and P are initially full.
Rules for trTCM
The trTCM focuses on the traffic burst rate and checks whether the traffic rate is conforming to the specifications. Therefore, traffic is measured based on bucket P and then bucket C.
Tc and Tp refer to the numbers of tokens in buckets C and P, respectively. The initial values of Tc and Tp are respectively the CBS and PBS.
In Color-Blind mode, the following rules apply when a packet of size B arrives at time t:
- If Tp(t) – B < 0, the packet is marked red, and The Tc and Tp values remain unchanged.
- If Tp(t) – B ≥ 0 but Tc(t) – B < 0, the packet is marked yellow, and Tp is decremented by B.
- If Tc(t) – B ≥ 0, the packet is marked green and both Tp and Tc are decremented by B.
In Color-Aware mode, the following rules apply when a packet of size B arrives at time t:
- If the packet has been pre-colored as green, and Tp(t) – B < 0, the packet is re-marked red, and neither Tp nor Tc is decremented.
- If the packet has been pre-colored as green and Tp(t) – B ≥ 0 but Tc(t) – B < 0, the packet is re-marked yellow, and Tp is decremented by B, and Tc remains unchanged.
- If the packet has been pre-colored as green and Tc(t) – B ≥ 0, the packet is re-marked green, and both Tp and Tc are decremented by B.
- If the packet has been pre-colored as yellow and Tp(t) – B < 0, the packet is re-marked red, and neither Tp nor Tc is decremented.
- If the packet has been pre-colored as yellow and Tp(t) – B ≥ 0, the packet is re-marked yellow, and Tp is decremented by B and Tc remains unchanged.
- If the packet has been pre-colored as red, the packet is re-marked red regardless of what the packet length is. The Tp and Tc values remain unchanged.