Proactive Loop Detection
Triggering Condition
Interface going Up
If an Ethernet interface, Ethernet trunk interface, or a specified Ethernet trunk member interface physically goes Up, the proactive loop detection function is triggered to detect whether the Ethernet interface, all members of the Ethernet trunk interface, or the specified Ethernet trunk member has a loop. If they have a loop, this function sets them to Down. Note that if an Ethernet interface goes Down, its associated sub-interfaces also go Down.
Interface bound to a VSI
If an Ethernet interface, Ethernet sub-interface, Ethernet trunk interface, or Ethernet trunk sub-interface is bound to a VSI, proactive loop detection is triggered on the Ethernet interface, Ethernet sub-interface, or trunk member interfaces. If they have a loop, this function sets them to Down. An Ethernet trunk sub-interface can be a dot1q sub-interface, dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface, or QinQ VLAN tag termination sub-interface.
Detection Principles
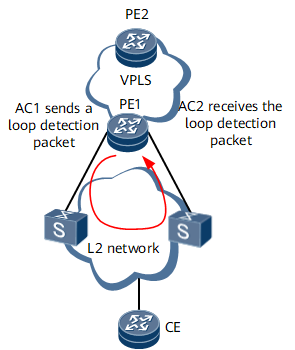
When a device's Ethernet or Eth-Trunk interface goes Up or an interface is bound to a VSI, the interface proactively sends a loop detection packet. If the device receives the loop detection packet sent through a VPLS domain within the configured period, a loop occurs on the network. In this case, the device blocks the interface sending the loop detection packet and reports an alarm.
On the network shown in Figure 1, AC1 sends a loop detection packet. If AC2 receives this packet within a loop detection period, a loop occurs on the network.

Proactive loop detection applies only to VPLS scenarios, not VLAN scenarios.

Loop Detection Period
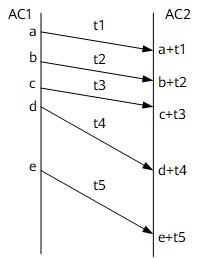
An interface can send a loop detection packet for a maximum of five times: the sending interval is 3s for the first three times and 10s for the latter two times. The maximum loop detection period is therefore 29s.
In Figure 2, t1 = t2 = t3 = 3s, and t4 = t5 = 10s. AC2 processes only the most recently sent loop detection packet. For example, if AC1 sends a loop detection packet at the a second, AC2 determines whether the packet was sent at the a second by AC1 upon receiving the packet.
- If so, a loop occurs. The device then sets the link layer protocol of AC1 to Down and reports an alarm to the NMS.
- If not, the device simply waits for the packet to be sent.