802.1X Port-based Authentication Process
EAP Relay
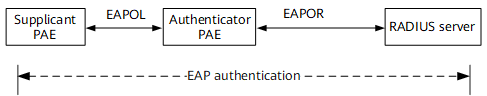
The IEEE 802.1X port-based authentication uses the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to exchange authentication messages among the supplicant, authenticator, and authentication server. EAP supports multiple authentication methods, such as MD5-Challenge, PEAP, and EAP-PEAP. EAP packets are encapsulated in EAPOL format between the supplicant PAE and authenticator PAE. EAP packets are exchanged between the authenticator PAE and authentication server in EAP relay mode or EAP termination mode. Therefore, 802.1X port-based authentication can be performed in either of the following modes: EAP relay and EAP termination.
On the network as shown in Figure 1, the authenticator PAE relays EAP packets between the supplicant PAE and RADIUS server:
- Re-encapsulates EAPOR packets into EAPOL packets and sends them to the supplicant PAE.
- Re-encapsulates EAPOL packets into EAROR packets and sends them to the RADIUS server.
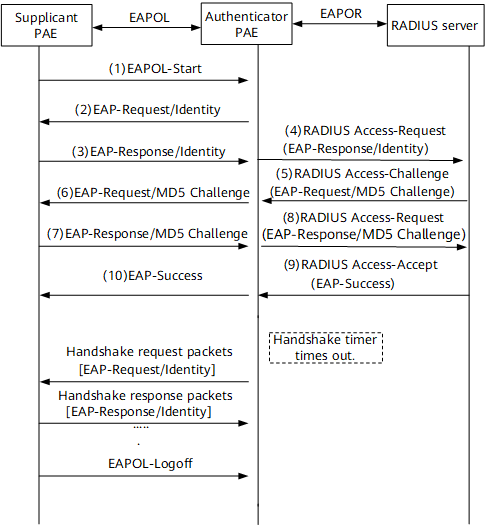
Figure 2 illustrates EAP relay authentication process. The authentication process can be initiated by the supplicant PAE or the authenticator PAE. In this example, the supplicant PAE initiates the authentication and uses the MD5-Challenge EAP authentication.
- When a user needs to access the network, the user starts the 802.1X supplicant software, enters the user name and password, and sends an EAPOL-Start frame to the authenticator.
- Upon receipt of the EAPOL-Start frame, the authenticator returns an EAP-Request/Identity packet, requesting the supplicant to send the entered user name.
- The supplicant responds with an EAP-Response/Identity frame carrying the user name to the authenticator.
- The authenticator encapsulates the EAP-Response/Identity frame into a RADIUS Access-Request packet and sends it to the RADIUS server.
- After receiving the user name from the authenticator, the RADIUS server searches the user name table in the database for the password corresponding to the user name, encrypts the password with a randomly generated MD5-Challenge value, and sends the MD5-Challenge value in a RADIUS Access-Challenge packet to the authenticator.
- The authenticator forwards the RADIUS Access-Challenge packet carrying the MD5-Challenge value to the supplicant.
- After receiving the MD5-Challenge value from the authenticator, the supplicant encrypts the password with the MD5-Challenge value, generates an EAP-Response/MD5 Challenge packet, and sends the packet to the authenticator.
- The authenticator encapsulates the EAP-Response/MD5 Challenge packet into a RADIUS Access-Request packet and sends it to the RADIUS server.
- The RADIUS server compares the encrypted password in the received RADIUS Access-Request packet with the local password encrypted using the MD5 algorithm. If the two passwords are the same, the RADIUS server considers the user as an authorized user and responds with a RADIUS Access-Accept packet.
- Upon receipt of the RADIUS Access-Accept packet, the authenticator sends an EAP-Success frame to the supplicant, and the port connected to the supplicant enters the authorized state, allowing the user to access the network.
The authenticator then periodically sends handshake packets to the supplicant to monitor the online user. The supplicant can send an EAPOL-Logoff frame to the authenticator for logout.
EAP Termination
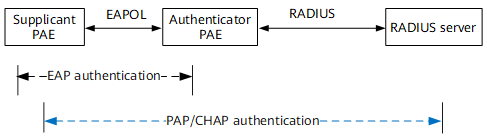
On the network as shown in Figure 3, the authenticator PAE terminates the EAP authentication process:
- Encapsulates the supplicant's authentication information in received EAP packets into standard RADIUS packets.
- Communicates with the RADIUS server using the Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) or Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) for access authentication.
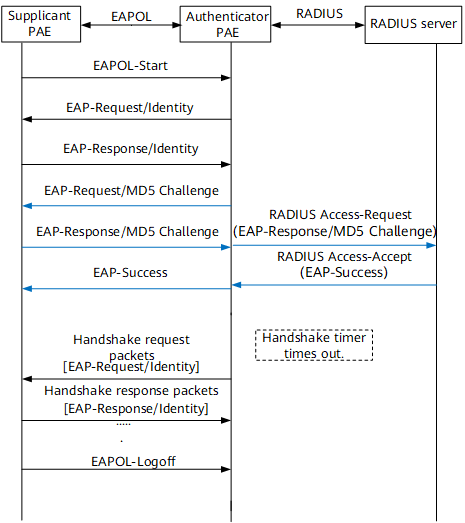
Figure 4 shows EAP termination authentication. In this example, the supplicant initiates the authentication and uses CHAP authentication.
The difference between the 802.1X authentication process in EAP termination mode and that in EAP relay mode is as follows: In EAP termination mode, the authenticator randomly generates an MD5-Challenge value for user password encryption, and then sends the user name, random MD5-Challenge value, and password encrypted on the supplicant to the RADIUS server for authentication.