Overview of Multicast NAT
Definition
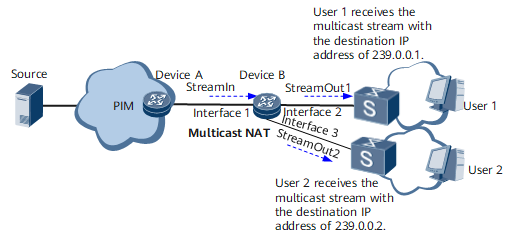
Multicast network address translation (NAT) translates the source IP address, destination IP address, and destination port number (subsequently referred to as characteristics) in multicast streams. Multicast NAT allows you to configure traffic policies on inbound interfaces to match input multicast streams. It also allows you to configure translation rules on outbound interfaces, so that a multicast stream can be replicated to multiple outbound interfaces and multicast stream characteristics can be modified according to the rules. On the network shown in Figure 1, after multicast NAT is deployed on DeviceB, DeviceB performs the following operations: uses a traffic policy to match the input multicast stream StreamIn, translates StreamIn's characteristics, and outputs the post-translation multicast streams StreamOut1 and StreamOut2.
Purpose
On the network shown in Figure 1, users 1 and 2 receive the input multicast stream StreamIn from different multicast groups. However, traditional multicast technologies cannot meet the requirement for sending the same multicast stream to different multicast groups. To resolve this issue, deploy multicast NAT on DeviceB so that DeviceB can translate StreamIn's characteristics and output the stream to users 1 and 2.
Benefits
- Multicast stream characteristics can be translated so that different downstream users can receive multicast streams.
- The matrixes of multicast streams can be conveniently switched to replace traditional serial digital interface (SDI) switching matrixes.