In an MVPNv6 over BIERv6 scenario, if a node or link fails, multicast services can be restored only after BGP peer convergence is complete. However, such convergence takes a long time and therefore cannot meet the high reliability requirements of multicast services. To speed up BGP convergence, which in turn accelerates multicast service convergence, you can configure BFD for BGP. You can also deploy the dual-root 1+1 protection solution, which further improves the performance of multicast service convergence.
Context
In Figure 1, the MVPNv6 over BIERv6 dual-root 1+1 protection solution is deployed as follows:
- Two sender PEs (Root1 and Root2) are deployed. Root1 and Root2 each set up a PMSI tunnel with themselves as the BFIRs. PE1 is a leaf node on the two tunnels.
- VPN fast reroute (FRR) is configured on PE1 so that PE1 has two routes to the same multicast source. In this example, PE1 selects the route advertised by Root1 as the primary route, and the one advertised by Root2 as the backup route.
Traffic detection-based C-multicast FRR is configured on PE1.
Figure 1 MVPNv6 over BIERv6 dual-root 1+1 protection networking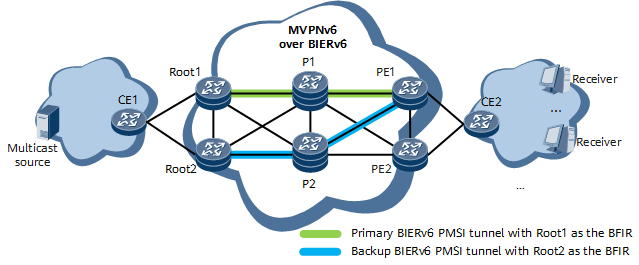
Procedure
- Deploy two sender PEs (Root1 and Root2) and configure them each to set up a PMSI tunnel with themselves as the BFIRs.
For details, see Configuring BGP MVPN Peer Relationships, (Optional) Configuring Multicast Traffic Forwarding over a BIERv6 I-PMSI Tunnel, and (Optional) Enabling the BIERv6 S-PMSI Tunnel Function and Configuring Switching Criteria.
- Configure VPN FRR on PE1.
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run ip vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
The VPN instance view is displayed.
- Run ipv6-family
The VPN instance IPv6 address family view is displayed.
- Run route-distinguisher route-distinguisher
An RD is configured for the VPN instance IPv6 address family.
- Run vpn frr
VPN FRR is enabled.
- Run quit
Exit the VPN instance IPv6 address family view.
- Run quit
Exit the VPN instance view.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
- Configure traffic detection-based C-multicast FRR on PE1.
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run acl ipv6 [ number ] basic-acl6-number
A basic ACL6 to be associated with C-multicast FRR is created, and the basic ACL6 view is displayed.
- Run rule [ rule-id ] [ name rule-name ] { permit | deny } [ source { source-ip-address { source-wildcard | 0 | src-netmask } | any } | time-range time-name | [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name | vpn-instance-any ] | logging ] *
A rule is configured for the ACL6.
- Run quit
Exit the basic ACL6 view.
- Run ip vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
The VPN instance view is displayed.
- Run ipv6-family
The VPN instance IPv6 address family view is displayed.
- Run route-distinguisher route-distinguisher
An RD is configured for the VPN instance IPv6 address family.
- Run mvpn
The VPN instance IPv6 address family MVPN view is displayed.
- Run c-multicast frr [ frrPlyNum | acl6-name frrPlyName ]
C-multicast FRR is enabled.
- Run c-multicast frr flow-detection-based { frrPlyNum | acl6-name acl-name }
The traffic detection mode is configured for C-multicast FRR.
- Run quit
Exit the VPN instance IPv6 address family MVPN view.
- Run quit
Exit the VPN instance IPv6 address family view.
- Run quit
Exit the VPN instance view.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
