Example for Configuring Proxy ARP Between VLANs
This section provides an example of how to configure proxy Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) between virtual local area networks (VLANs).
Networking Requirements
Assume that an enterprise has many departments and IP addresses of these departments are on the same network segment, to improve the service security, IP addresses of hosts used by employees in the same department are added to the same VLAN and IP addresses of hosts used by employees in different departments are added to different VLANs. IP addresses of hosts used by employees in different departments need to communicate with each other.
As shown in Figure 1, IP addresses of the R&D department and test department belong to different VLANs. It is required that IP addresses of hosts used by employees in different VLANs communicate with each other.

Interfaces 1 through 3 in this example represent GE 0/1/1, GE 0/1/2, and GE 0/1/3, respectively.
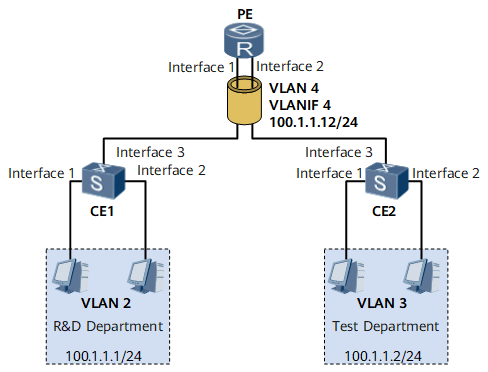
IP addresses of the R&D department and test department are on the same network segment. To save IP address resources, you can deploy VLAN aggregation on devices of the R&D department and test department. This ensures that different VLANs can communicate with each other.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Create VLAN on CE1 and CE2 to determine mappings between users and VLANs.
Configure VLAN aggregation on the PE.
Configure the Layer 2 forwarding function.
Create a super-VLAN and add sub-VLANs to the super-VLAN.
Create a VLANIF interface for the super-VLAN and assign an IP address to the VLANIF interface as the gateway address.
Enable proxy ARP on the VLANIF interface of the super-VLAN and between sub-VLANs so that sub-VLANs can communicate with each other on the Layer 3 network.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
- User IP addresses
- Number of each interface connecting a switch to a host
- Sub-VLAN ID and super-VLAN ID
- Number and IP address of the VLANIF interface of the super-VLAN
Procedure
- Create a VLAN on CEs and add Layer 2 interfaces to the VLAN.
# Configure CE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~CE1] vlan batch 2 [*CE1] commit [~CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [~CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] portswitch [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port link-type access [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port default vlan 2 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [~CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [~CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] portswitch [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port link-type access [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port default vlan 2 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] commit [~CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [~CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/3 [~CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] portswitch [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] undo shutdown [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] port link-type trunk [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] commit [~CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] quit
# Configure CE2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE2 [*HUAWEI] commit [~CE2] vlan batch 3 [*CE2] commit [~CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [~CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] portswitch [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port link-type access [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port default vlan 3 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [~CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [~CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] portswitch [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port link-type access [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port default vlan 3 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] commit [~CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [~CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/3 [~CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] portswitch [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] undo shutdown [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] port link-type trunk [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] port trunk allow-pass vlan 3 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] commit [~CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] quit
- Configure VLAN aggregation on the PE.
Configure the Layer 2 forwarding function.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE] vlan batch 2 to 4 [*PE] commit [~PE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [~PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] portswitch [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port link-type trunk [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [~PE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [~PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] portswitch [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port link-type trunk [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port trunk allow-pass vlan 3 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] commit [~PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit
Create a super-VLAN and add sub-VLANs to the super-VLAN.
[~PE] vlan 4 [*PE-vlan4] aggregate-vlan [*PE-vlan4] access-vlan 2 to 3 [*PE-vlan4] commit [~PE-vlan4] quit
Create a VLANIF interface for the super-VLAN and assign an IP address to the VLANIF interface.
[~PE] interface vlanif 4 [*PE-vlanif4] ip address 10.1.1.12 24 [*PE-vlanif4] commit
After the preceding configurations, you can configure IP addresses as shown in Figure 1 for hosts. IP address of hosts and the VLANIF interface are on the same network segment.
If the configuration succeeds, IP addresses of hosts used by employees in different VLANs and the switch can ping each other; IP addresses of hosts used by employees in VLAN 2 and VLAN 3 cannot ping each other.
- Enable proxy ARP on the VLANIF interface of the super-VLAN and between sub-VLANs.
[~PE-vlanif4] arp-proxy inter-sub-vlan-proxy enable [*PE-vlanif4] commit [~PE-vlanif4] quit
- Verify the configuration.
After the configuration, IP addresses of hosts used by employees in VLAN 2 and VLAN 3 can ping each other.
Configuration Files
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # vlan batch 2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type access port default vlan 2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type access port default vlan 2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 # return
CE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # vlan batch 3 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type access port default vlan 3 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type access port default vlan 3 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 3 # return
PE configuration file
# sysname PE # vlan batch 2 to 4 # vlan 4 aggregate-vlan access-vlan 2 to 3 # interface Vlanif4 ip address 10.1.1.12 255.255.255.0 arp-proxy inter-sub-vlan-proxy enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 3 # return