Example for Using Telnet to Log In to Other Devices
This example shows how to log in to another device by using Telnet. You can configure the user authentication mode and password to log in to another device by using Telnet.
Networking Requirements
Large numbers of devices need to be managed and maintained on a network. You cannot connect each device to a terminal. When no reachable route exists between remote devices and a terminal, you can use Telnet to log in to the remote devices from the device that you have logged in to.
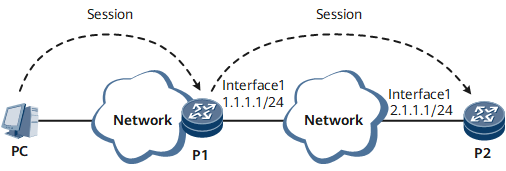
As shown in Figure 1, you can use Telnet on the PC to log in to P1 but cannot directly use Telnet to log in to P2. P1 and P2 are routable. To remotely manage and configure P2, use Telnet on P1 to log in to P2.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Configure the Telnet authentication mode and password on P2.
- Use Telnet on P1 to log in to P2.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Host address of P2: 2.1.1.1
Authentication mode: password; password: Hello-hello
Procedure
- Configure the Telnet authentication mode and password.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname P2 [*HUAWEI] commit [~P2] user-interface vty 0 4 [~P2-ui-vty0-4] authentication-mode password [~P2-ui-vty0-4] set authentication-mode password Please configure the login password (8-16) Enter Password: Confirm Password:

The password must meet the following requirements:
The password is entered in man-machine interaction mode. The system does not display the entered password.
A password is a string of 8 to 16 case-sensitive characters and must contain at least two types of the following characters: uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and special characters.
- Special characters exclude question marks (?) and spaces. However, spaces are allowed in the password if the password is enclosed in quotation marks.
- Double quotation marks cannot contain double quotation marks if spaces are used in a password.
- Double quotation marks can contain double quotation marks if no space is used in a password.
For example, the password "Aa123"45"" is valid, but the password "Aa 123"45"" is invalid.
The configured password is displayed in ciphertext in the configuration file.
[*P2-ui-vty0-4] commit [~P2-ui-vty0-4] quit
If an ACL is configured to access other devices by using Telnet, perform the following configurations on P2:
[~P2] acl 2000 [*P2-acl4-basic-2000] rule permit source 1.1.1.1 0 [*P2-acl4-basic-2000] quit [*P2] user-interface vty 0 4 [*P2-ui-vty0-4] acl 2000 inbound [*P2-ui-vty0-4] commit [~P2-ui-vty0-4] quit

The ACL configurations are optional.
- Verify the configuration.
After the configurations are complete, use Telnet on P1 to log in to P2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname P1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~P1] quit <P1> telnet 2.1.1.1 Trying 2.1.1.1 Press CTRL+K to abort Connected to 2.1.1.1 Username: root Password: <P2>
Configuration Files
P1 configuration file
# sysname P1 # interface gigabitethernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # admin returnP2 configuration file
# sysname P2 # acl number 2000 rule 5 permit source 1.1.1.1 0 # interface gigabitethernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 2.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # user-interface vty 0 4 authentication-mode password set authentication password cipher @%@%(t7h+Qu=a#pz`3Kylk1/,JXR%iy(DA!x8&+!|#b&.dEW65~.lEqGm~Np$O#2M]xJM@%@% acl 2000 inbound # return