Configuring BGP4+ RRs
BGP4+ RRs avoid fully meshed connections between multiple IBGP peers, which reduces network costs.
Usage Scenario
Fully meshed connections need to be established between IBGP peers to ensure the connectivity between IBGP peers. If there are n routers in an AS, n x (n-1)/2 IBGP connections need to be established. When there are a lot of IBGP peers, network resources and CPU resources are greatly consumed. Route reflection can solve the problem.
Using RRs reduces the total number of IBGP connections. On a large network, however, multiple RRs need to be configured to reduce the number of clients of each RR. Therefore, there are still a large number of IBGP connections on the network because fully meshed connections need to be established between the RRs. In this situation, configure hierarchical RR to further reduce the number of IBGP connections.
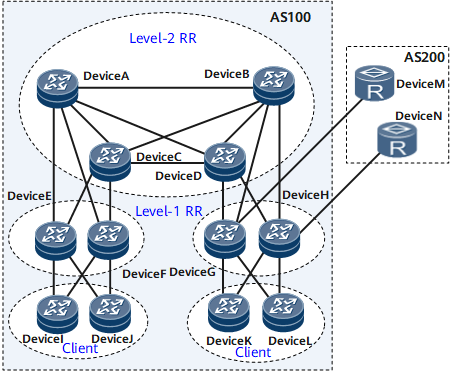
Figure 1 shows a typical hierarchical RR networking. Device A, Device B, Device C, and Device D function as level-2 RRs; Device E, Device F, Device G, and Device H function as level-1 RRs and the clients of level-2 RRs. Level-2 RRs are not the clients of any RR and must be fully meshed. Level-1 RRs function as the clients of level-2 RRs and do not need to be fully meshed.
- Configuring an RR and Specifying Its Clients
- RRs reflect routes between clients, and therefore IBGP connections do not need to be established between the clients.
- (Optional) Disabling Route Reflection Between Clients Through the RR
- If the clients of an RR are fully meshed, you can disable route reflection among them through the RR to reduce bandwidth consumption.
- (Optional) Configuring a Cluster ID for RRs
- If a cluster has multiple RRs, you can configure the same cluster ID for these RRs to prevent routing loops.
- (Optional) Preventing BGP4+ from Adding Routes to the IP Routing Table
- Disabling BGP4+ route delivery to the IP routing table on an RR can prevent traffic from being forwarded by the RR, improving route advertisement efficiency.
- (Optional) Enabling an RR to Modify Route Attributes Using an Export Policy
- You can enable an RR to modify route attributes based on the export policy to change route selection results of the BGP4+.
- Verifying the Configuration of BGP4+ RRs
- After configuring BGP4+ RRs, check information about BGP4+ routes and peer groups.