Example for Configuring the MED Attribute to Control Route Selection
By setting the MED attribute, you can flexibly control BGP route selection.
Networking Requirements
The MED attribute equals a metric used in an IGP, and is used to determine the optimal route for traffic that enters an AS. When a BGP device obtains multiple routes to the same destination address but with different next hops from EBGP peers, the route with the smallest MED value is selected as the optimal route.
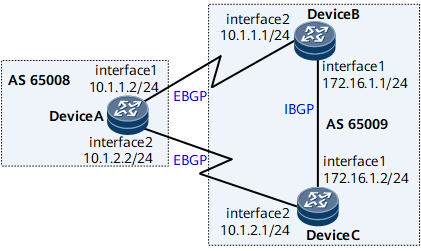
On the network shown in Figure 1, BGP is configured on all routers. Device A is in AS 65008. Device B and Device C are in AS 65009. Device A establishes EBGP connections with Device B and Device C. Device B establishes an IBGP connection with Device C. Traffic sent by Device A to 172.16.1.0 can enter AS 65009 through Device B or Device C. If the attributes excluding the MED values of the routes advertised by Devices B and C to Device A are the same, you can change the MED value of the route to be advertised by Device B or Device C to Device A to determine the device through which traffic will enter AS 65009.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Establish EBGP connections between Device A and Device B, and between Device A and Device C, and establish an IBGP connection between Device B and Device C.
- Apply a routing policy to increase the MED value of the route sent by Device B to Device A so that Device A will send traffic to AS 65009 through Device C.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
- Router ID 1.1.1.1 and AS number 65008 of Device A
- Router IDs 2.2.2.2 and 3.3.3.3, and AS number 65009 of Devices B and C
- New MED value 100 of the route on Device B
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each interface. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure BGP connections.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] bgp 65008 [*DeviceA-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1 [*DeviceA-bgp] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65009 [*DeviceA-bgp] peer 10.1.2.1 as-number 65009 [*DeviceA-bgp] commit [~DeviceA-bgp] quit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] bgp 65009 [*DeviceB-bgp] router-id 2.2.2.2 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 65008 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 172.16.1.2 as-number 65009 [*DeviceB-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv4] network 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv4] commit [~DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] bgp 65009 [*DeviceC-bgp] router-id 3.3.3.3 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 10.1.2.2 as-number 65008 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 172.16.1.1 as-number 65009 [*DeviceC-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*DeviceC-bgp-af-ipv4] network 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 [*DeviceC-bgp-af-ipv4] commit [~DeviceC-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [~DeviceC-bgp] quit
# Check the routing table of Device A.
[~DeviceA] display bgp routing-table 172.16.1.0 24 BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 65008 Paths: 2 available, 1 best, 1 select BGP routing table entry information of 172.16.1.0/24: From: 10.1.1.1 (2.2.2.2) Route Duration: 0d00h00m56s Direct Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Original nexthop: 10.1.1.1 Qos information : 0x0 AS-path 65009, origin igp, MED 0, pref-val 0, valid, external, best, select, pre 255 Advertised to such 2 peers: 10.1.1.1 10.1.2.1 BGP routing table entry information of 172.16.1.0/24: From: 10.1.2.1 (3.3.3.3) Route Duration: 0d00h00m06s Direct Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Original nexthop: 10.1.2.1 Qos information : 0x0 AS-path 65009, origin igp, MED 0, pref-val 0, valid, external, pre 255, not preferred for router ID Not advertised to any peers yet
The command output shows that there are two valid routes to 172.16.1.0/24. The route with 10.1.1.1 as the next hop is the optimal route because the router ID of Device B is smaller.
- Configure the MED attribute.
# Set the MED value for the route sent by Device B to Device A based on a routing policy.
[~DeviceB] route-policy 10 permit node 10 [*DeviceB-route-policy] apply cost 100 [*DeviceB-route-policy] commit [~DeviceB-route-policy] quit [~DeviceB] bgp 65009 [*DeviceB-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 10.1.1.2 route-policy 10 export [~DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv4] commit
# Check the routing table of Device A.
[~DeviceA] display bgp routing-table 172.16.1.0 24 BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 65008 Paths: 2 available, 1 best, 1 select BGP routing table entry information of 172.16.1.0/24: From: 10.1.2.1 (3.3.3.3) Route Duration: 0d00h07m45s Direct Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Original nexthop: 10.1.2.1 Qos information : 0x0 AS-path 65009, origin igp, MED 0, pref-val 0, valid, external, best, select, pre 255 Advertised to such 2 peers: 10.1.1.1 10.1.2.1 BGP routing table entry information of 172.16.1.0/24: From: 10.1.1.1 (2.2.2.2) Route Duration: 0d00h00m08s Direct Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Original nexthop: 10.1.1.1 Qos information : 0x0 AS-path 65009, origin igp, MED 100, pref-val 0, valid, external, pre 255, not preferred for MED Not advertised to any peers yet
The command output shows that the MED value of the next hop 10.1.1.1 (Device B) is 100 and that the MED value of the next hop 10.1.2.1 is 0. Therefore, the route with the smaller MED value is selected.
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65008 router-id 1.1.1.1 peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65009 peer 10.1.2.1 as-number 65009 # ipv4-family unicast peer 10.1.1.1 enable peer 10.1.2.1 enable # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65009 router-id 2.2.2.2 peer 172.16.1.2 as-number 65009 peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 65008 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 peer 172.16.1.2 enable peer 10.1.1.2 enable peer 10.1.1.2 route-policy 10 export # route-policy 10 permit node 10 apply cost 100 # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65009 router-id 3.3.3.3 peer 172.16.1.1 as-number 65009 peer 10.1.2.2 as-number 65008 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 peer 172.16.1.1 enable peer 10.1.2.2 enable # return