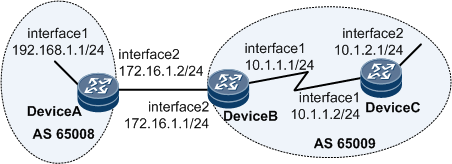
Example for Configuring BGP to Interact with an IGP
Configuring BGP to interact with an IGP can enrich routing tables.
Networking Requirements
As the Internet grows, devices in different networks need to access each other, data needs to be reliably transmitted, and the traffic interruption time needs to be minimized. This requires that routing information be transmitted widely and network convergence be accelerated. BGP can transmit routing information efficiently and widely. BGP, however, does not calculate routes by itself. An IGP can implement rapid route convergence, but it transmits routing information with a low efficiency in a limited scope. After BGP is configured to interact with an IGP, IGP routes can be imported into BGP routing tables and transmitted efficiently. BGP routes can also be imported into IGP routing tables to allow access to other ASs.
The network shown in Figure 1 is divided into AS 65008 and AS 65009. In AS 65009, an IGP is used to calculate routes. In this example, OSPF is used as an IGP. BGP can be configured to enable the two ASs to access each other. Interaction between BGP and the IGP can be configured on edge routers of the two ASs so that the two ASs can exchange routes efficiently. In addition, AS external routes can be imported into the IGP routing table to allow access to the outside of the local AS.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure OSPF on Device B and Device C.
Establish an EBGP connection between Device A and Device B.
Configure BGP and OSPF to import routes from each other on Device B and then check the routes.
Configure BGP route summarization on Device B to simplify the BGP routing table.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Router ID and AS number of Device A
Router IDs and AS numbers of Device B and Device C
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each interface. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure OSPF.
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] ospf 1 [*DeviceB-ospf-1] area 0 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] commit [~DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [~DeviceB-ospf-1] quit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] ospf 1 [*DeviceC-ospf-1] area 0 [*DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] commit [~DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [~DeviceC-ospf-1] quit
- Configure an EBGP connection.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] bgp 65008 [*DeviceA-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1 [*DeviceA-bgp] peer 172.16.1.1 as-number 65009 [*DeviceA-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*DeviceA-bgp-af-ipv4] network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 [*DeviceA-bgp-af-ipv4] commit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] bgp 65009 [*DeviceB-bgp] router-id 2.2.2.2 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 172.16.1.2 as-number 65008 [*DeviceB-bgp] commit
- Configure BGP to interact with an IGP.
# Configure BGP to import OSPF routes on Device B.
[~DeviceB-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv4] import-route ospf 1 [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv4] commit [~DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
# Check the routing table of Device A.
[~DeviceA] display bgp routing-table BGP Local router ID is 1.1.1.1 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, N - not-found Total Number of Routes: 3 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *> 192.168.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 i *> 10.1.1.0/24 172.16.1.1 1 0 65009? *> 10.1.2.0/24 172.16.1.1 2 0 65009?
# Configure OSPF to import BGP routes on Device B.
[~DeviceB] ospf [*DeviceB-ospf-1] import-route bgp [*DeviceB-ospf-1] commit [~DeviceB-ospf-1] quit
# Check the routing table of Device C.
[~DeviceC] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : _public_ Destinations : 12 Routes : 12 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 192.168.1.0/24 O_ASE 150 1 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.2.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.2.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.2.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.2.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
- Configure automatic route summarization.
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] bgp 65009 [*DeviceB-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv4] summary automatic [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv4] commit
# Check the BGP routing table of Device A.
[~DeviceA] display bgp routing-table BGP Local router ID is 1.1.1.1 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, N - not-found Total Number of Routes: 2 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *> 192.168.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 i *> 10.0.0.0 172.16.1.1 0 65009?
# Verify the configuration by using the ping command.
[~DeviceA] ping -a 192.168.1.1 10.1.2.1 PING 10.1.2.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 10.1.2.1: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=254 time=15 ms Reply from 10.1.2.1: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=254 time=31 ms Reply from 10.1.2.1: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=254 time=47 ms Reply from 10.1.2.1: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=254 time=46 ms Reply from 10.1.2.1: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=254 time=47 ms --- 10.1.2.1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 15/37/47 ms
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65008 router-id 1.1.1.1 peer 172.16.1.1 as-number 65009 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 peer 172.16.1.1 enable # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65009 router-id 2.2.2.2 peer 172.16.1.2 as-number 65008 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization summary automatic import-route ospf 1 peer 172.16.1.2 enable # ospf 1 import-route bgp area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 # return