Example for Configuring BGP Route Dampening
Configuring BGP route dampening can improve network stability.
Networking Requirements
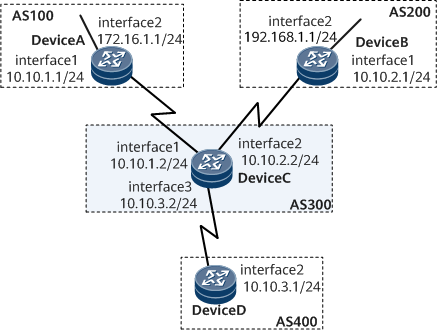
In Figure 1, all routers are configured with BGP; Device A resides in AS 100; Device B resides in AS 200; Device C resides in AS 300; Device D resides in AS 400. EBGP runs between Device C and Device A, between Device C and Device B, and between Device C and Device D. For routes from different EBGP neighbors, Device C applies different route dampening policies. It is required that BGP route dampening be configured to suppress unstable routes and improve network stability.
Precautions
When configuring BGP route dampening, note the following rules:
BGP route dampening takes effect only on EBGP routes.
Set a small MaxSuppressTime for routes with the small masks.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Establish EBGP connections between Device A and Device C, between Device B and Device C, and between Device D and Device C.
Configure route dampening policies on Device C and then check routes.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Router IDs and AS numbers of Device A, Device B, Device C, and Device D
Name of the route flap dampening policy to be applied to Device C
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each interface. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure BGP connections.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] bgp 100 [*DeviceA-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1 [*DeviceA-bgp] peer 10.10.1.2 as-number 300 [*DeviceA-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*DeviceA-bgp-af-ipv4] network 172.16.1.0 24 [*DeviceA-bgp-af-ipv4] commit [~DeviceA-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [~DeviceA-bgp] quit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] bgp 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] router-id 2.2.2.2 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 10.10.2.2 as-number 300 [*DeviceB-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv4] network 192.168.1.0 24 [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv4] commit [~DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] bgp 300 [*DeviceC-bgp] router-id 3.3.3.3 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 10.10.1.1 as-number 100 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 10.10.2.1 as-number 200 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 10.10.3.1 as-number 400 [*DeviceC-bgp] commit [~DeviceC-bgp] quit
# Configure Device D.
[~DeviceD] bgp 400 [*DeviceD-bgp] router-id 4.4.4.4 [*DeviceD-bgp] peer 10.10.3.2 as-number 300 [*DeviceD-bgp] commit [~DeviceD-bgp] quit
# Check the BGP peers of Device C.
[*DeviceC] display bgp peer BGP local router ID : 3.3.3.3 Local AS number : 300 Total number of peers : 3 Peers in established state : 3 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 10.10.1.1 4 100 3 3 0 00:00:01 Established 0 10.10.2.1 4 200 3 3 0 00:00:00 Established 0 10.10.3.1 4 400 3 3 0 00:00:01 Established 0
The command output shows that the BGP connection status of with each peer is Established.
- Configure BGP route dampening policies.
# Configure an IP prefix list named prefix-a on Device C to accept only the routes with prefix 172.16.1.0/24.
[~DeviceC] ip ip-prefix prefix-a index 10 permit 172.16.1.0 24 [*DeviceC] commit
# Configure an IP prefix list named prefix-b on Device C to accept only the routes with prefix 192.168.1.0/24.
[~DeviceC] ip ip-prefix prefix-b index 20 permit 192.168.1.0 24 [*DeviceC] commit
# Configure a route-policy named dampen-policy on Device C and then apply different route dampening policies to the routes with different prefix lengths.
[~DeviceC] route-policy dampen-policy permit node 10 [*DeviceC-route-policy] if-match ip-prefix prefix-a [*DeviceC-route-policy] apply dampening 10 1000 2000 5000 [*DeviceC-route-policy] commit [~DeviceC-route-policy] quit [*DeviceC] route-policy dampen-policy permit node 20 [*DeviceC-route-policy] if-match ip-prefix prefix-b [*DeviceC-route-policy] apply dampening 10 800 3000 10000 [*DeviceC-route-policy] commit [~DeviceC-route-policy] quit
# Apply route dampening policies to the routes that flap.
[*DeviceC] bgp 300 [*DeviceC-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*DeviceC-bgp-af-ipv4] dampening route-policy dampen-policy [*DeviceC-bgp-af-ipv4] commit [~DeviceC-bgp] quit
# Check the configured route dampening parameters on Device C.
[~DeviceC] display bgp routing-table dampening parameter Maximum Suppress Time(in second) : 3973 Ceiling Value : 16000 Reuse Value : 750 HalfLife Time(in second) : 900 Suppress-Limit : 2000 Route-policy : dampen-policy
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.10.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.1 255.0.0.0 # bgp 100 router-id 1.1.1.1 peer 10.10.1.2 as-number 300 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 peer 10.10.1.2 enable # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.10.2.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 # bgp 200 router-id 2.2.2.2 peer 10.10.2.2 as-number 300 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 peer 10.10.2.2 enable # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.10.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.10.2.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.10.3.2 255.255.255.0 # bgp 300 router-id 3.3.3.3 peer 10.10.1.1 as-number 100 peer 10.10.2.1 as-number 200 peer 10.10.3.1 as-number 400 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization dampening route-policy dampen-policy peer 10.10.1.1 enable peer 10.10.2.1 enable peer 10.10.3.1 enable # route-policy dampen-policy permit node 10 if-match ip-prefix prefix-a apply dampening 10 1000 2000 5000 # route-policy dampen-policy permit node 20 if-match ip-prefix prefix-b apply dampening 10 800 3000 10000 # ip ip-prefix prefix-a index 10 permit 8.0.0.0 8 # ip ip-prefix prefix-b index 20 permit 9.1.1.0 24 # return
Device D configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.10.3.1 255.255.255.0 # bgp 400 router-id 4.4.4.4 peer 10.10.3.2 as-number 300 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 10.10.3.2 enable # return