Example for Configuring BGP Default Route Advertisement
By controlling the advertising of default routes, you can specify traffic from a specific path to enter ASs.
Networking Requirements
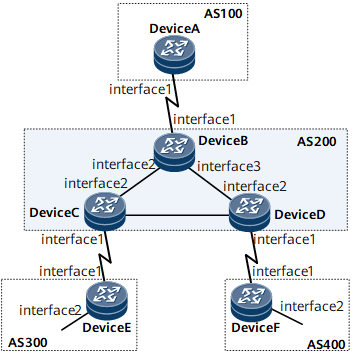
In Figure 1, all routers run BGP. To ensure that the traffic that leaves AS 200 is forwarded by Device E and Device F, EBGP connections are established between Device A and Device B, between Device C and Device E, and between Device D and Device F; IBGP connections are established between Device B and Device C, and between Device B and Device D.

Interfaces 1 through 3 in this example are GE 0/1/0, GE 0/1/8, GE 0/1/16, respectively.
Device Name |
Interface |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|
Device A |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.20.1.1/24 |
Loopback 0 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
|
Device B |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.20.1.2/24 |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.0.1.1/24 |
|
GE 0/1/16 |
10.0.3.2/24 |
|
Loopback 0 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
|
Device C |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.20.2.2/24 |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.0.1.2/24 |
|
GE 0/1/16 |
10.0.2.1/24 |
|
Loopback 0 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
|
Device D |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.20.3.2/24 |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.0.3.1/24 |
|
GE 0/1/16 |
10.0.2.2/24 |
|
Loopback 0 |
4.4.4.4/32 |
|
Device E |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.20.2.1/24 |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.21.7.1.1/24 |
|
Loopback 0 |
5.5.5.5/32 |
|
Device F |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.20.3.1/24 |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.22.8.1.1/24 |
|
Loopback 0 |
6.6.6.6/32 |
Precautions
When configuring BGP to advertise default routes, note the following rules:
Default routes have two functions. They can represent all network routes. For example, in a stub AS, instead of advertising all network routes, you can use only a default route to forward traffic destined outside the stub AS. In addition, they can represent all routes except specific routes; for example, they can be used in the multi-home load balancing scenario.
When establishing a peer relationship, if the specified IP address of the peer is a loopback interface address or a sub-interface address, run the peer connect-interface command on both ends to ensure that the two ends are correctly connected.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure OSPF on Device B, Device C, and Device D.
Establish EBGP connections between Device A and Device B, between Device C and Device E, and between Device D and Device F.
Establish IBGP connections between Device B and Device C, and between Device B and Device D.
Configure an import routing policy on Device C to accept only default routes.
Configure an import routing policy on Device D to accept default routes and all specific routes, and then set Local_Pref values for the accepted default routes.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Router IDs and AS numbers of Device A, Device B, Device C, Device D, Device E, and Device F
Names of the import routing policies to be configured on Device C and Device D
Local_Pref values to be set for the accepted default routes on Device D
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each interface. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure OSPF.
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] ospf 1 [*DeviceB-ospf-1] area 0 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.0.3.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] commit [~DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [~DeviceB-ospf-1] quit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] ospf 1 [*DeviceC-ospf-1] area 0 [*DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 [*DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] commit [~DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [~DeviceC-ospf-1] quit
# Configure Device D.
[~DeviceD] ospf 1 [*DeviceD-ospf-1] area 0 [*DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.0.3.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 [*DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] commit [~DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [~DeviceD-ospf-1] quit
- Configure BGP connections.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] bgp 100 [*DeviceA-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1 [*DeviceA-bgp] peer 10.20.1.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceA-bgp] commit [~DeviceA-bgp] quit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] bgp 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] router-id 2.2.2.2 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 10.20.1.1 as-number 100 [*DeviceB-bgp] network 10.20.1.0 24 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack0 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface LoopBack0 [*DeviceB-bgp] commit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] bgp 200 [*DeviceC-bgp] router-id 3.3.3.3 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 10.20.2.1 as-number 300 [*DeviceC-bgp] network 10.20.2.0 24 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 [*DeviceC-bgp] commit [~DeviceC-bgp] quit
# Configure Device D.
[~DeviceD] bgp 200 [*DeviceD-bgp] router-id 4.4.4.4 [*DeviceD-bgp] peer 10.20.3.1 as-number 400 [*DeviceD-bgp] network 10.20.3.0 24 [*DeviceD-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceD-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 [*DeviceD-bgp] commit [~DeviceD-bgp] quit
# Configure Device E.
[~DeviceE] bgp 300 [*DeviceE-bgp] router-id 5.5.5.5 [*DeviceE-bgp] peer 10.20.2.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceE-bgp] network 10.1.1.0 24 [*DeviceE-bgp] commit [~DeviceE-bgp] quit
# Configure Device F.
[~DeviceF] bgp 400 [*DeviceF-bgp] router-id 6.6.6.6 [*DeviceF-bgp] peer 10.20.3.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceF-bgp] network 10.2.1.0 24 [*DeviceF-bgp] commit [~DeviceF-bgp] quit
- Configure Device E and Device F to advertise default routes.
# Configure Device E to advertise default routes.
[~DeviceE-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*DeviceE-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 10.20.2.2 default-route-advertise [*DeviceE-bgp-af-ipv4] commit
# Configure Device F to advertise default routes.
[~DeviceF-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*DeviceF-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 10.20.3.2 default-route-advertise [*DeviceF-bgp-af-ipv4] commit
# Check the routing table of Device B.
[~DeviceB] display bgp routing-table BGP Local router ID is 2.2.2.2 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, N - not-found Total Number of Routes: 7 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *>i 0.0.0.0 10.20.2.1 0 100 0 300i * i 10.20.3.1 0 100 0 400i *>i 10.1.1.0/24 10.20.2.1 0 100 0 300i *>i 10.2.1.0/24 10.20.3.1 0 100 0 400i *> 10.20.1.0 0.0.0.0 0 0 i *>i 10.20.2.0 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i *>i 10.20.3.0 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 i
The command output shows that Device B has received the default routes and all specific routes of AS 300 and AS 400.
- Configure import routing policies.
# Configure an IP prefix list named default on Device C to accept only default routes.
[~DeviceC] ip ip-prefix default permit 0.0.0.0 0 [*DeviceC] commit [*DeviceC] bgp 200 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 10.20.2.1 ip-prefix default import [*DeviceC-bgp] commit
# Configure a route-policy named set-default-low on Device D to accept default routes and all specific routes, and set Local_Pref values for the accepted default routes.
[~DeviceD] ip as-path-filter 10 permit ^(400_)+$ [*DeviceD] ip as-path-filter 10 permit ^(400_)+_[0-9]+$ [*DeviceD] ip ip-prefix default permit 0.0.0.0 0 [*DeviceD] route-policy set-default-low permit node 10 [*DeviceD-route-policy] if-match ip-prefix default [*DeviceD-route-policy] apply local-preference 80 [*DeviceD-route-policy] quit [*DeviceD] route-policy set-default-low permit node 20 [*DeviceD-route-policy] quit [*DeviceD] commit [~DeviceD] bgp 200 [*DeviceD-bgp] peer 10.20.3.1 as-path-filter 10 import [*DeviceD-bgp] peer 10.20.3.1 route-policy set-default-low import [*DeviceD-bgp] commit
# Check the routing table of Device B.
[~DeviceB] display bgp routing-table BGP Local router ID is 2.2.2.2 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, N - not-found Total Number of Routes: 6 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *>i 0.0.0.0 10.20.2.1 0 100 0 300i * i 10.20.3.1 0 80 0 400i *>i 10.2.1.0/24 10.20.3.1 0 100 0 400i *> 10.20.1.0 0.0.0.0 0 0 i *>i 10.20.2.0 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i *>i 10.20.3.0 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 i
The command output shows that Device B has received only the default routes of AS 300 and the default routes and all specific routes of AS 400 and that the Local_Pref of the accepted default routes destined of AS 400 has been set to 80.
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.20.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 10.20.1.2 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast peer 10.20.1.2 enable # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.20.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.3.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # bgp 200 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 200 peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 200 peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 10.20.1.1 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast network 10.20.1.0 255.255.255.0 peer 3.3.3.3 enable peer 4.4.4.4 enable peer 10.20.1.1 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.0.3.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.20.2.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.2.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # bgp 200 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 200 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 10.20.2.1 as-number 300 # ipv4-family unicast network 10.20.2.0 255.255.255.0 peer 2.2.2.2 enable peer 10.20.2.1 enable peer 10.20.2.1 ip-prefix default import # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 network 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 # ip ip-prefix default index 10 permit 0.0.0.0 0 # return
Device D configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.20.3.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.3.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.2.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 # bgp 200 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 200 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 10.20.3.1 as-number 400 # ipv4-family unicast network 10.20.3.0 255.255.255.0 peer 2.2.2.2 enable peer 10.20.3.1 enable peer 10.20.3.1 as-path-filter 10 import peer 10.20.3.1 route-policy set-default-low import # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 network 10.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.0.3.0 0.0.0.255 # route-policy set-default-low permit node 10 if-match ip-prefix default apply local-preference 80 # route-policy set-default-low permit node 20 # ip ip-prefix default index 10 permit 0.0.0.0 0 # ip as-path-filter 10 permit ^(400_)+$ ip as-path-filter 10 permit ^(400_)+_[0-9]+$ # return
Device E configuration file
# sysname DeviceE # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.20.2.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.21.7.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255 # bgp 300 peer 10.20.2.2 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast network 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 peer 10.20.2.2 enable peer 10.20.2.2 default-route-advertise # return
Device F configuration file
# sysname DeviceF # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.20.3.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.22.8.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.255 # bgp 400 peer 10.20.3.2 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast network 10.2.1.0 255.255.255.0 peer 10.20.3.2 enable peer 10.20.3.2 default-route-advertise # return