Example for Configuring BGP Add-Path
With BGP Add-Path, a route reflector (RR) can send two or more routes with the same prefix to a specified IBGP peer. After reaching the IBGP peer, these routes can back up each other or load-balance traffic, which ensures high reliability in data transmission.
Networking Requirements
In a scenario with an RR and clients, if the RR has multiple BGP routes to the same destination (with the same prefix), the RR selects an optimal route from these routes and then sends only the optimal route to its clients. Therefore, the clients have only one route to the destination. If a link along this route fails, route convergence takes a long time, which cannot meet the requirements for high reliability.
To address this issue, deploy the BGP Add-Path feature on the RR. With BGP Add-Path, the RR can send two or more routes with the same prefix to a specified peer. These routes can back up each other or load-balance traffic, which ensures high reliability in data transmission.
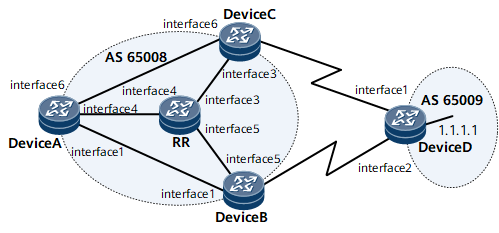
On the network shown in Figure 1, DeviceA, DeviceB, and DeviceC are clients of the RR, and DeviceB and DeviceC establish EBGP peer relationships with DeviceD.
To ensure high reliability in data transmission, configure BGP Add-Path on the RR and enable Device A to receive Add-Path routes from the RR so that DeviceA can have multiple routes with the same prefix.
Precautions
Enable BGP Add-Path on the RR, enable the RR to send Add-Path routes to a specified IBGP peer, configure the number of routes that the RR can send to the IBGP peer, and enable the IBGP peer to receive BGP Add-Path routes from the RR so that such routes are available to the IBGP peer.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IP address for each interface on each router.
Configure basic BGP functions on each router.
Enable BGP Add-Path on the RR, enable the RR to send Add-Path routes to Device A, and configure the number of routes that the RR can send to Device A.
Enable Device A to receive BGP Add-Path routes from the RR.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Router IDs of DeviceA, DeviceB, DeviceC, DeviceD, and the RR, and their AS numbers, as listed in Table 1
Device |
Router ID |
Interface Number |
IP Address |
AS Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Device A |
1.1.1.1 |
GigabitEthernet 0/1/16 |
172.16.3.1/24 |
AS 65008 |
GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 |
172.16.2.1/24 |
|||
GigabitEthernet 0/1/3 |
172.16.1.1/24 |
|||
Device B |
2.2.2.2 |
GigabitEthernet 0/1/16 |
172.16.3.2/24 |
AS 65008 |
GigabitEthernet 0/1/18 |
172.16.7.1/24 |
|||
GigabitEthernet 0/1/2 |
172.16.5.2/24 |
|||
Device C |
3.3.3.3 |
GigabitEthernet 0/1/16 |
172.16.6.1/24 |
AS 65008 |
GigabitEthernet 0/1/19 |
172.16.4.2/24 |
|||
GigabitEthernet 0/1/3 |
172.16.1.2/24 |
|||
Device D |
4.4.4.4 |
GigabitEthernet 0/1/16 |
172.16.6.2/24 |
AS 65009 |
GigabitEthernet 0/1/18 |
172.16.7.2/24 |
|||
LoopBack0 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
|||
RR |
5.5.5.5 |
GigabitEthernet 0/1/19 |
172.16.4.1/24 |
AS 65008 |
GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 |
172.16.2.2/24 |
|||
GigabitEthernet 0/1/2 |
172.16.5.1/24 |
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each interface on each router. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure basic BGP functions. Establish an IBGP peer relationship between each of DeviceA, DeviceB, and DeviceC and the RR. Configure DeviceA, DeviceB, and DeviceC as RR clients. Establish an EBGP peer relationship between DeviceB and DeviceD, and between DeviceC and DeviceD.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] bgp 65008 [*DeviceA-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1 [*DeviceA-bgp] peer 172.16.2.2 as-number 65008 [*DeviceA-bgp] import-route direct [*DeviceA-bgp] commit [~DeviceA-bgp] quit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] bgp 65008 [*DeviceB-bgp] router-id 2.2.2.2 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 172.16.5.1 as-number 65008 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 172.16.7.2 as-number 65009 [*DeviceB-bgp] import-route direct [*DeviceB-bgp] commit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] bgp 65008 [*DeviceC-bgp] router-id 3.3.3.3 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 172.16.4.1 as-number 65008 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 172.16.6.2 as-number 65009 [*DeviceC-bgp] import-route direct [*DeviceC-bgp] commit [~DeviceC-bgp] quit
# Configure Device D.
[~DeviceD] bgp 65009 [*DeviceD-bgp] router-id 4.4.4.4 [*DeviceD-bgp] peer 172.16.6.1 as-number 65008 [*DeviceD-bgp] peer 172.16.7.1 as-number 65008 [*DeviceD-bgp] import-route direct [*DeviceD-bgp] commit [~DeviceD-bgp] quit
# Configure the RR.
[~RR] bgp 65008 [*RR-bgp] router-id 5.5.5.5 [*RR-bgp] peer 172.16.2.1 as-number 65008 [*RR-bgp] peer 172.16.4.2 as-number 65008 [*RR-bgp] peer 172.16.5.2 as-number 65008 [*RR-bgp] peer 172.16.2.1 reflect-client [*RR-bgp] peer 172.16.4.2 reflect-client [*RR-bgp] peer 172.16.5.2 reflect-client [*RR-bgp] import-route direct [*RR-bgp] commit [~RR-bgp] quit
# Display information about the routes to 1.1.1.1 on Device A.
[~DeviceA] display bgp routing-table 1.1.1.1 BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 65008 Paths: 1 available, 1 best, 1 select, 0 best-external, 0 add-path BGP routing table entry information of 1.1.1.1/32: From: 172.16.2.2 (5.5.5.5) Route Duration: 0d00h00m25s Relay IP Nexthop: 172.16.2.2 Relay IP Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/1 Original nexthop: 172.16.7.2 Qos information : 0x0 AS-path 65009, origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, inte rnal, best, select, pre 255 Originator: 2.2.2.2 Cluster list: 5.5.5.5 Not advertised to any peer yet
The command output before BGP Add-Path is configured shows that Device A received only one BGP route to 1.1.1.1 from the RR.
- Enable BGP Add-Path on the RR, enable the RR to send Add-Path routes to Device A, configure the number of routes that the RR can send to Device A, and enable Device A to receive BGP Add-Path routes from the RR.
# Configure the RR.
[~RR] bgp 65008 [~RR-bgp] bestroute add-path path-number 2 [*RR-bgp] peer 172.16.2.1 capability-advertise add-path send [*RR-bgp] peer 172.16.2.1 advertise add-path path-number 2 [*RR-bgp] commit [~RR-bgp] quit
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] bgp 65008 [~DeviceA-bgp] peer 172.16.2.2 capability-advertise add-path receive [*DeviceA-bgp] commit [~DeviceA-bgp] quit
# Display information about the routes to 1.1.1.1 on Device A.
[~DeviceA] display bgp routing-table 1.1.1.1 BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 65008 Paths: 2 available, 1 best, 1 select, 0 best-external, 0 add-path BGP routing table entry information of 1.1.1.1/32: From: 172.16.2.2 (5.5.5.5) Route Duration: 0d00h00m48s Relay IP Nexthop: 172.16.2.2 Relay IP Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/1 Original nexthop: 172.16.7.2 Qos information : 0x0 AS-path 65009, origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, inte rnal, best, select, pre 255 Received path-id: 0 Originator: 2.2.2.2 Cluster list: 5.5.5.5 Not advertised to any peer yet BGP routing table entry information of 1.1.1.1/32: From: 172.16.2.2 (5.5.5.5) Route Duration: 0d00h00m48s Relay IP Nexthop: 172.16.2.2 Relay IP Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/1 Original nexthop: 172.16.6.2 Qos information : 0x0 AS-path 65009, origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, inte rnal, pre 255, not preferred for router ID Received path-id: 1 Originator: 3.3.3.3 Cluster list: 5.5.5.5 Not advertised to any peer yet
The command output shows that Device A received two routes from the RR. The route with the original nexthop 172.16.7.2 is the optimal route selected by the RR, and the other one with the original nexthop 172.16.6.2 is an Add-Path route.
# Display information about the routes to 1.1.1.1 on the RR.
[~RR] display bgp routing-table 1.1.1.1 BGP local router ID : 5.5.5.5 Local AS number : 65008 Paths: 2 available, 1 best, 1 select, 0 best-external, 1 add-path BGP routing table entry information of 1.1.1.1/32: RR-client route. From: 172.16.5.2 (2.2.2.2) Route Duration: 0d00h19m39s Relay IP Nexthop: 172.16.5.2 Relay IP Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/2 Original nexthop: 172.16.7.2 Qos information : 0x0 AS-path 65009, origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, inte rnal, best, select, pre 255 Advertised to such 3 peers: 172.16.5.2 172.16.4.2 172.16.2.1 BGP routing table entry information of 1.1.1.1/32: RR-client route. From: 172.16.4.2 (3.3.3.3) Route Duration: 0d00h19m41s Relay IP Nexthop: 172.16.4.2 Relay IP Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/19 Original nexthop: 172.16.6.2 Qos information : 0x0 AS-path 65009, origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, inte rnal, add-path, pre 255, not preferred for router ID Advertised to such 1 peers: 172.16.2.1
The command output shows that the RR sent the optimal route to all its clients but sent the Add-Path route only to Device A.
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65008 router-id 1.1.1.1 peer 172.16.2.2 as-number 65008 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 172.16.2.2 enable peer 172.16.2.2 capability-advertise add-path receive # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.3.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/18 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.7.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.5.2 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65008 router-id 2.2.2.2 peer 172.16.5.1 as-number 65008 peer 172.16.7.2 as-number 65009 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 172.16.5.1 enable peer 172.16.7.2 enable # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.6.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/19 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.4.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65008 router-id 3.3.3.3 peer 172.16.4.1 as-number 65008 peer 172.16.6.2 as-number 65009 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 172.16.4.1 enable peer 172.16.6.2 enable # return
Device D configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.6.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/18 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.7.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65009 router-id 4.4.4.4 peer 172.16.6.1 as-number 65008 peer 172.16.7.1 as-number 65008 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 172.16.6.1 enable peer 172.16.7.1 enable # return
RR configuration file
# sysname RR # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/19 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.4.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.2.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.5.1 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65008 router-id 5.5.5.5 peer 172.16.2.1 as-number 65008 peer 172.16.4.2 as-number 65008 peer 172.16.5.2 as-number 65008 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct bestroute add-path path-number 2 peer 172.16.2.1 enable peer 172.16.2.1 reflect-client peer 172.16.2.1 capability-advertise add-path send peer 172.16.2.1 advertise add-path path-number 2 peer 172.16.4.2 enable peer 172.16.4.2 reflect-client peer 172.16.5.2 enable peer 172.16.5.2 reflect-client # return