Bit-Error-Triggered Section Switching
Background
If bit errors occur on an interface, deploy bit-error-triggered section switching to trigger an upper-layer application associated with the interface for a service switchover.
Implementation Principles
Trigger-section bit error detection must be enabled on an interface. After detecting bit errors on an inbound interface, a device notifies the interface management module of the bit errors. The link layer protocol status of the interface then changes to bit-error-detection Down, triggering an upper-layer application associated with the interface for a service switchover. After the bit errors are cleared, the link layer protocol status of the interface changes to Up, triggering an upper-layer application associated with the interface for a service switchback. The device also notifies the BFD module of the bit error status, and then uses BFD packets to advertise the bit error status to the peer device.
If bit-error-triggered section switching also has been deployed on the peer device, the bit error status is advertised to the interface management module of the peer device. The link layer protocol status of the interface then changes to bit-error-detection Down or Up, triggering an upper-layer application associated with the interface for a service switchover or switchback.
If bit-error-triggered section switching is not deployed on the peer device, the peer device cannot detect the bit error status of the interface's link. In this case, the peer device can only depend on an upper-layer application (for example, IGP) for link fault detection.
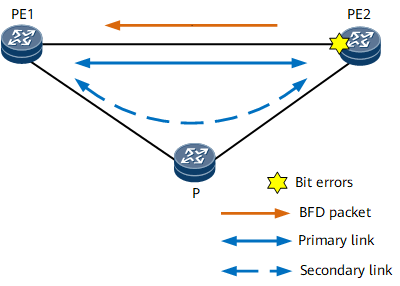
For example, on the network shown in Figure 1, trigger-section bit error detection is enabled on each interface, and nodes communicate through IS-IS routes. In normal cases, IS-IS routes on PE1 and PE2 are preferentially transmitted over the primary link. Therefore, traffic in both directions is forwarded over the primary link. If PE2 detects bit errors on the interface to PE1:
The link layer protocol status of the interface changes to bit-error-detection Down, triggering IS-IS routes to be switched to the secondary link. Traffic from PE2 to PE1 is then forwarded over the secondary link. PE2 uses a BFD packet to notify PE1 of the bit errors.
After receiving the BFD packet, PE1 sets the link layer protocol status of the corresponding interface to bit-error-detection Down, triggering IS-IS routes to be switched to the secondary link. Traffic from PE1 to PE2 is then forwarded over the secondary link.
If trigger-section bit error detection is not supported or enabled on PE1's interface to PE2, PE1 can only use IS-IS to detect that the primary link is unavailable, and then performs an IS-IS route switchover.
Usage Scenario
If LDP LSPs are used, deploy bit-error-triggered section switching to cope with link bit errors on the LDP LSPs.

After bit-error-triggered section switching is deployed, if bit errors occur on both the primary and secondary links on an LDP LSP, the interface status changes to bit-error-detection Down on both the primary and secondary links. As a result, services are interrupted. Therefore, it is recommended that you deploy bit-error-triggered IGP route switching.