Application of Bit-Error-Triggered Protection Switching in a Scenario in Which LDP LSPs Carry an IP RAN
Networking Description
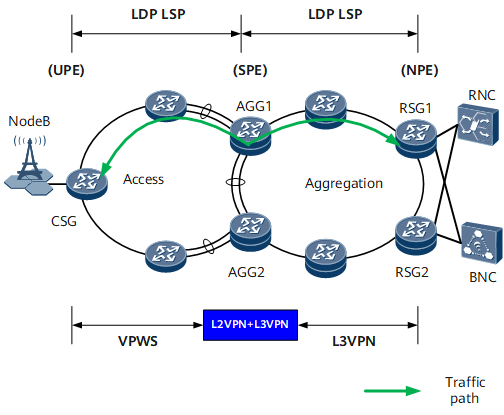
Figure 1 shows typical L2VPN+L3VPN networking in an IP RAN application. A VPWS based on an LDP LSP is deployed at the access layer, an L3VPN based on an LDP LSP is deployed at the aggregation layer, and L2VPN access to L3VPN is configured on the AGGs. To ensure reliability, deploy LDP and IGP synchronization for the LDP LSPs, and configure Eth-Trunk interfaces on key links.
Feature Deployment
To prevent the impact of bit errors on services, deploy bit-error-triggered IGP route switching in the scenario shown in Figure 1. Deploy trunk-bit-error-triggered IGP route switching on the Eth-Trunk interfaces. The deployment process is as follows:
Enable link-quality bit error detection on each physical interface and Eth-Trunk member interface.
Enable bit-error-triggered IGP route switching on each physical interface and Eth-Trunk interface.
Bit-Error-Triggered Protection Switching Scenarios
Scenario 1
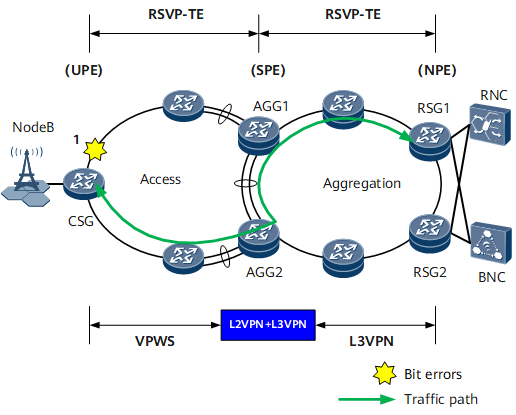
On the network shown in Figure 2, if bit errors occur on location 1 (physical interface), the CSG detects the bit errors and adjusts the quality level of the interface's link to Low, triggering an IGP to increase the cost of the link. In this case, IGP routes do not preferentially select the link. The CSG also uses a BFD packet to advertise the bit errors to the peer device, so that the peer device also performs the same processing. Both upstream and downstream traffic are then switched to the paths without bit errors.
Scenario 2
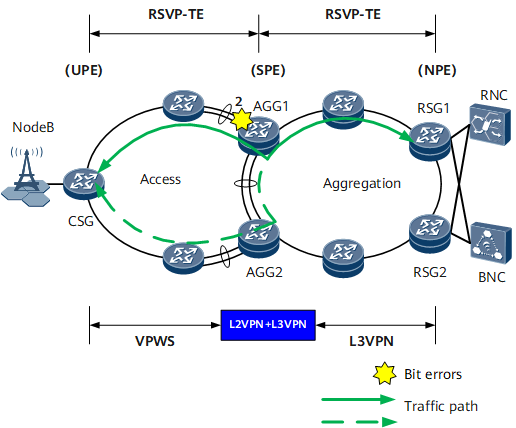
On the network shown in Figure 3, if bit errors occur on location 2 (Eth-Trunk member interface), AGG1 detects the bit errors.
If the number of member interfaces without bit errors is still higher than the lower threshold for the Eth-Trunk interface's Up links, the Eth-Trunk interface deletes the Eth-Trunk member interface from the forwarding plane. In this case, service traffic is still forwarded over the normal path.
If the number of member interfaces without bit errors is lower than the lower threshold for the Eth-Trunk interface's Up links, the Eth-Trunk interface ignores the bit errors on the Eth-Trunk member interface and remains Up. However, the link quality level of the Eth-Trunk interface becomes Low, triggering an IGP (OSPF or IS-IS) to increase the cost of the Eth-Trunk interface's link. IGP routes then do not preferentially select the link. AGG1 also uses a BFD packet to advertise the bit errors to the peer device, so that the peer device also performs the same processing. Both upstream and downstream traffic are then switched to the paths without bit errors.