Example for Configuring IPv4 User-Side Multicast for a VPN
This section describes how to configure IPv4 user-side multicast for a VPN.
Networking Requirements
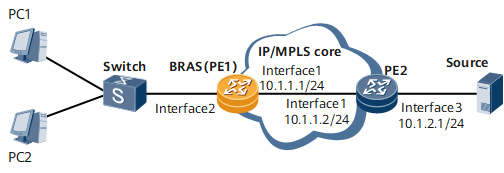
On the network shown in Figure 1, users access the network in IPoE mode through sub-interface interface 2 on a broadband remote access server (BRAS). The users and multicast source belong to the same VPN instance named red. Configure user-side multicast, allowing the users to order programs from the multicast source and allowing for refined user management.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure multicast VPN functions. An NG MVPN over an mLDP P2MP tunnel is used as an example.
Configure a BGP MPLS/IP VPN and ensure that the unicast VPN is working properly.
Enable mLDP globally on PE1 and PE2.
Establish a BGP MVPN peer relationship between PE1 and PE2.
Configure an mLDP I-PMSI tunnel on PE1.
Bind an interface on PE2 to the VPN instance.
Configure IGMP on the interface that connects the multicast-capable device to the user network segment.
Configure an IPv4 address pool.
Configure AAA schemes.
Configure a domain.
Configure the IPoE access mode.
Configure an authentication mode.
Bind a sub-interface to a VLAN.
Configure a BAS interface and specify a user access type for the interface.
Configure a multicast replication mode. Multicast replication by multicast VLAN is used as an example.
Configure basic multicast functions.
Bind an interface to the VPN instance.
Data Preparation
IP addresses of loopback 0 on the BRAS and PE2: 1.1.1.1 and 2.2.2.2, respectively
Public network OSPF process ID: 1; area ID: 0
MPLS LSR IDs of the BRAS and PE2: 1.1.1.1 and 2.2.2.2, respectively
MVPN IDs of the BRAS and PE2: 1.1.1.1 and 2.2.2.2, respectively
Names, RDs, and VPN targets of the VPN instances on the BRAS and PE2: red, 1:1, and 1:1, respectively
IPv4 address pool parameters
Authentication and accounting scheme parameters
User domain parameters
BAS interface parameters
Procedure
- Configure an NG MVPN over an mLDP P2MP tunnel. For details, see Example for Configuring an Intra-AS NG MVPN to Carry Multicast Traffic over an mLDP P2MP LSP.
- Configure an IPv4 address pool.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname BRAS [*HUAWEI] commit [~BRAS] ip pool vpn bas local [*BRAS-ip-pool-vpn] vpn-instance red [*BRAS-ip-pool-vpn] gateway 10.0.0.1 255.255.0.0 [*BRAS-ip-pool-vpn] section 255 10.0.0.1 10.0.0.255 [*BRAS-ip-pool-vpn] quit [*BRAS] commit
- Configure AAA schemes.
# Configure an authentication scheme.
[~BRAS] aaa [*BRAS-aaa] authentication-scheme none [*BRAS-aaa-authen-none] authentication-mode none [*BRAS-aaa-authen-none] quit [*BRAS-aaa] commit
# Configure an accounting scheme.
[~BRAS-aaa] accounting-scheme none [*BRAS-aaa-accounting-none] accounting-mode none [*BRAS-aaa-accounting-none] quit [*BRAS-aaa] quit [*BRAS] commit
- Configure a domain.
[~BRAS] aaa [*BRAS-aaa] domain vpn [*BRAS-aaa-domain-vpn] authentication-scheme none [*BRAS-aaa-domain-vpn] accounting-scheme none [*BRAS-aaa-domain-vpn] ip-pool vpn [*BRAS-aaa-domain-vpn] vpn-instance red [*BRAS-aaa-domain-vpn] quit [*BRAS-aaa] quit [*BRAS] commit
- Bind a sub-interface to a VLAN.
[~BRAS] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1.1 [*BRAS-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] user-vlan 1 [*BRAS-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1-vlan-1-1] quit [*BRAS-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] commit
- Configure a BAS interface and specify a user access type for the interface.
[~BRAS-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] bas [*BRAS-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1-bas] access-type layer2-subscriber default-domain authentication vpn [*BRAS-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1-bas] authentication-method bind [*BRAS-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1-bas] quit [*BRAS-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] quit [*BRAS] commit
- Configure multicast replication by multicast VLAN.
[~BRAS] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1.1 [~BRAS-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] multicast user-aggregation qinq pe-vid 2 ce-vid 9 [*BRAS-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] quit [*BRAS] commit
- Configure basic multicast functions.
[~BRAS] multicast routing-enable [*BRAS] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*BRAS-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] pim sm [*BRAS-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] igmp enable [*BRAS-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*BRAS] commit [~PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [~PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] pim sm [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*PE2] commit
- Bind the interface to a VPN instance.
[~BRAS] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [~BRAS-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] multicast binding vpn-instance red [*BRAS-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*BRAS] commit
- Verify the configuration.# Run the display multicast group-ip command to view information about users that join a specified multicast group in the VPN instance red. The command output shows that the users with IDs 96 and 97 in the VPN instance named red join the multicast program of which the group address is 225.0.0.1.
[~BRAS] display multicast group-ip 225.0.0.1 out-interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/1.1 vpn-instance red User ID User IP User type Interface 96 10.0.0.250 Local GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 97 10.0.0.249 Local GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 Local user number :2 Remote user number:0 Total user number :2
# Run the display multicast user-id command to display information about the multicast programs that a specified user joined in the VPN instance red on a BAS interface. The following uses the user whose IP address is 10.0.0.250 as an example:[~BRAS] display multicast user-ip 10.0.0.250 vpn-instance red User information: User ID :96 User IPv4 address :10.0.0.250 Gateway IPv4 address:10.0.0.1 BRAS interface :GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 User MAC-address :00-e0-fc-12-34-56 MAX program list :4 User order program: Group IP Source IP 225.0.0.1 0.0.0.0 Total:1
# Run the display pim vpn-instance vpn-instance-name routing-table command to view PIM entries of a VPN instance.[~BRAS] display pim vpn-instance red routing-table VPN-Instance: red Total 1 (S, G) entry (10.1.2.100, 225.0.0.1) Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag: SG_RCVR UpTime: 00:00:38 Upstream interface: through-BGP, Refresh time: 00:00:38 Upstream neighbor: 2.2.2.2 RPF prime neighbor: 2.2.2.2 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/1(bas) Protocol: igmp, UpTime: 00:00:38, Expires: - [~PE2] display pim vpn-instance red routing-table VPN-Instance: red Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (10.1.2.100, 225.0.0.1) RP: NULL Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT LOC ACT SG_RCVR UpTime: 16:29:06 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/2, Refresh time: 16:29:06 Upstream neighbor: NULL RPF prime neighbor: NULL Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: pseudo Protocol: BGP, UpTime: 00:13:57, Expires: -
# Run the display multicast vpn-instance vpn-instance-name routing-table command to view multicast routing entries of a VPN instance.[~BRAS] display multicast vpn-instance red routing-table Multicast routing table of VPN-Instance: red Total 1 entry 00001. (10.1.2.100, 225.0.0.1) Uptime: 00:12:28 Upstream Interface: pseudo List of 1 downstream interface 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/1(bas) [~PE2] display multicast vpn-instance red routing-table Multicast routing table of VPN-Instance: red Total 1 entry 00001. (10.1.2.100, 225.0.0.1) Uptime: 16:29:28 Upstream Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/2 List of 1 downstream interface 1: pseudo
Configuration Files
BRAS configuration file
# sysname BRAS # multicast routing-enable # multicast mvpn 1.1.1.1 # ip vpn-instance red ipv4-family route-distinguisher 1:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity multicast routing-enable mvpn sender-enable c-multicast signaling bgp ipmsi-tunnel mldp # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls # mpls ldp mldp p2mp # ip pool vpn bas local vpn-instance red gateway 10.0.0.1 255.255.0.0 section 255 10.0.0.1 10.0.0.255 # aaa # authentication-scheme none authentication-mode none # accounting-scheme none accounting-mode none # domain vpn authentication-scheme none accounting-scheme none ip-pool vpn vpn-instance red # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown multicast binding vpn-instance red pim sm igmp enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 user-vlan 1 multicast user-aggregation qinq pe-vid 2 ce-vid 9 bas # access-type layer2-subscriber default-domain authentication vpn authentication-method bind # # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv4-family mvpn policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance red import-route direct # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 # returnPE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # multicast mvpn 2.2.2.2 # ip vpn-instance red ipv4-family route-distinguisher 1:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity multicast routing-enable mvpn sender-enable c-multicast signaling bgp ipmsi-tunnel mldp # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls # mpls ldp mldp p2mp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance red ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface LoopBack0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.1 enable # ipv4-family mvpn policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.1 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.1 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance red import-route direct # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 # return