Configuring Bit-Error-Triggered L3VPN Route Switching
This section describes how to configure bit-error-triggered Layer 3 virtual private network (L3VPN) route switching.
Context
In an H-VPN scenario in which an RSVP-TE tunnel with TE hot standby protection carries services and VPN FRR is configured, you can configure bit-error-triggered L3VPN route switching in addition to bit-error-triggered RSVP-TE tunnel switching. If the primary and backup constraint-based routed label switched paths (CR-LSPs) of the RSVP-TE tunnel are both in the excessive bit error rate (BER) state or the TE hot standby tunnel fails and bit-error-triggered RSVP-TE tunnel switching cannot protect services against bit errors, bit-error-triggered L3VPN route switching can do so.
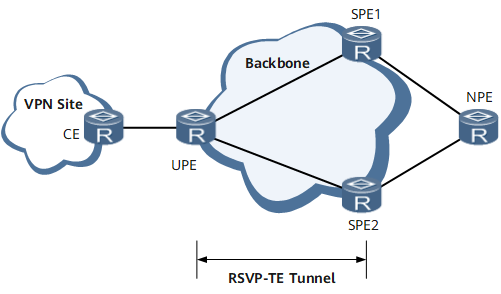
Figure 1 shows an H-VPN scenario where an RSVP-TE tunnel with TE hot standby protection configured carries L3VPN services. VPN FRR is configured on the user-end provider edge (UPE). If the primary and backup CR-LSPs of the RSVP-TE tunnel are both in the excessive BER state or the TE hot-standby tunnel fails, bit-error-triggered RSVP-TE tunnel switching cannot protect traffic against bit errors. To resolve this problem, configure bit-error-triggered L3VPN route switching on the UPE and SPE1. Bit-error-triggered L3VPN route switching triggers VPN route convergence in the case of a bit error event, diverting traffic from the link that has encountered the bit error event.